Abstract
Rationale
GABAA receptors containing the α5 subunit (i.e., α5GABAA receptors) appear to be critically involved in the reinforcing and subjective effects of alcohol. Their role in alcohol relapse remains unknown.
Objectives
Pharmacological approaches were used to probe the role of α5GABAA receptors in alcohol seeking induced by re-exposure to a sweetened alcohol-paired cue, as well as in alcohol + sucrose vs. sucrose self-administration.
Methods
For reinstatement studies, rats were trained to self-administer alcohol under a fixed-ratio schedule in which responding was maintained by alcohol + sucrose deliveries and an alcohol-paired stimulus. Sweetened alcohol seeking was extinguished by eliminating solution deliveries and the sweetened alcohol-paired stimulus. During reinstatement tests, animals received pretreatments of an α5GABAA inverse agonist (L-655,708) or an agonist (QH-ii-066) prior to sessions in which presentation of the sweetened alcohol-paired stimulus was restored, but no solution was delivered. For self-administration studies, rats were trained to self-administer alcohol + sucrose or sucrose under a fixed-ratio schedule. Once stable, animals received pretreatments of QH-ii-066, L-655,708, the inverse agonist RY-023, or naltrexone.
Results
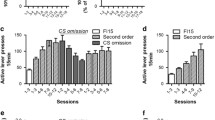
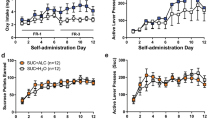
L-655,708 attenuated reinstatement of sweetened alcohol seeking by alcohol + sucrose-paired cues; whereas sweetened alcohol-seeking behavior was augmented by QH-ii-066, albeit at different doses in different rats. Both L-655,708 and RY-023 selectively reduced alcohol + sucrose vs. sucrose self-administration. In contrast, naltrexone reduced both alcohol + sucrose and sucrose self-administration; whereas QH-ii-066 enhanced sucrose self-administration only.
Conclusions
α5GABAA receptors play a key role in the modulation of sweetened alcohol cue-induced reinstatement, as well as in alcohol + sucrose but not sucrose self-administration. Inverse agonist activity at α5GABAA receptors may offer a novel strategy for both the reduction of problematic drinking and the prevention of relapse.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral DG, Witter MP (1989) The three-dimensional organization of the hippocampal formation: a review of anatomical data. Neuroscience 31:571–591
Atack JR (2010) Preclinical and clinical pharmacology of the GABAA receptor alpha5 subtype-selective inverse agonist alpha5IA. Pharmacol Ther 125:11–26
Atack JR, Bayley PJ, Seabrook GR, Wafford KA, McKernan RM, Dawson GR (2006) L-655,708 enhances cognition in rats but is not proconvulsant at a dose selective for alpha5-containing GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology 51:1023–1029
Backstrom P, Bachteler D, Koch S, Hyytia P, Spanagel R (2004) mGluR5 antagonist MPEP reduces ethanol seeking and relapse behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:921–928
Besheer J, Faccidomo S, Grondin JJ, Hodge CW (2008) Regulation of motivation to self-administer ethanol by mGluR5 in alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:209–221
Besheer J, Fisher KR, Lindsay TG, Cannady R (2013) Transient increase in alcohol self-administration following a period of chronic exposure to corticosterone. Neuropharmacology 72:139–147
Boehm SL 2nd, Ponomarev I, Jennings AW, Whiting PJ, Rosahl TW, Garrett EM, Blednov YA, Harris RA (2004) Gamma-aminobutyric acid a receptor subunit mutant mice: new perspectives on alcohol actions. Biochem Pharmacol 68:1581–1602
Cannady R, Fisher KR, Durant B, Besheer J, Hodge CW (2013) Enhanced AMPA receptor activity increases operant alcohol self-administration and cue-induced reinstatement. Addict Biol 18:54–65
Casula MA, Bromidge FA, Pillai GV, Wingrove PB, Martin K, Maubach K, Seabrook GR, Whiting PJ, Hadingham KL (2001) Identification of amino acid residues responsible for the alpha-5 subunit binding selectivity of L-655,708, a benzodiazepine binding site ligand at the GABA-A receptor. J Neurochem 77:445–451
Charlton ME, Sweetnam PM, Fitzgerald LW, Terwilliger RZ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (1997) Chronic ethanol administration regulates the expression of GABAA receptor alpha 1 and alpha 5 subunits in the ventral tegmental area and hippocampus. J Neurochem 68:121–127
Collinson N, Kuenzi FM, Jarolimek W, Maubach KA, Cothliff R, Sur C, Smith A, Otu FM, Howell O, Atack JR, McKernan RM, Seabrook GR, Dawson GR, Whiting PJ, Rosahl TW (2002) Enhanced learning and memory and altered GABAergic synaptic transmission in mice lacking the alpha 5 subunit of the GABAA receptor. J Neurosci 22:5572–5580
Cook JB, Foster KL, Eiler WJ 2nd, McKay PF, Woods J 2nd, Harvey SC, Garcia M, Grey C, McCane S, Mason D, Cummings R, Li X, Cook JM, June HL (2005) Selective GABAA alpha5 benzodiazepine inverse agonist antagonizes the neurobehavioral actions of alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:1390–1401
den Uyl TE, Gladwin TE, Wiers RW (2016) Electrophysiological and behavioral effects of combined transcranial direct current stimulation and alcohol approach bias retraining in hazardous drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Ther 40:2124–2133
Fritschy JM, Panzanelli P (2014) GABAA receptors and plasticity of inhibitory neurotransmission in the central nervous system. Eur J Neurosci 39:1845–1865
Gatto GJ, Grant KA (1997) Attenuation of the discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol by the benzodiazepine partial inverse agonist Ro 15-4513. Behav Pharmacol 8:139–146
Grant BF, Chou SP, Saha TD, Pickering RP, Kerridge BT, Ruan WJ, Huang B, Jung J, Zhang H, Fan A, Hasin DS (2017) Prevalence of 12-month alcohol use, high-risk drinking, and DSM-IV Alcohol Use Disorder in the United States, 2001-2002 to 2012-2013: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. JAMA Psychiatry 74:911–923
Groenewegen HJ, Vermeulen-Van der Zee E, te Kortschot A, Witter MP (1987) Organization of the projections from the subiculum to the ventral striatum in the rat. A study using anterograde transport of Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin. Neuroscience 23:103–120
Hamel L, Thangarasa T, Samadi O, Ito R (2017) Caudal nucleus accumbens core is critical in the regulation of cue-elicited approach-avoidance decisions. eNeuro 4:ENEURO.0330–ENEU16.2017. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0330-16.2017
Hay RA, Jennings JH, Zitzman DL, Hodge CW, Robinson DL (2013) Specific and nonspecific effects of naltrexone on goal-directed and habitual models of alcohol seeking and drinking. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37:1100–1110
Helms CM, Rogers LS, Grant KA (2009) Antagonism of the ethanol-like discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol, pentobarbital, and midazolam in cynomolgus monkeys reveals involvement of specific GABAA receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 331:142–152
Hodges LM, Fyer AJ, Weissman MM, Logue MW, Haghighi F, Evgrafov O, Rotondo A, Knowles JA, Hamilton SP (2014) Evidence for linkage and association of GABRB3 and GABRA5 to panic disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:2423–2431
Howell O, Atack JR, Dewar D, McKernan RM, Sur C (2000) Density and pharmacology of alpha5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors are preserved in hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease patients. Neuroscience 98:669–675
Huang Q, He X, Ma C, Liu R, Yu S, Dayer CA, Wenger GR, McKernan R, Cook JM (2000) Pharmacophore/receptor models for GABAA/BzR subtypes (alpha1beta3gamma2, alpha5beta3gamma2, and alpha6beta3gamma2) via a comprehensive ligand-mapping approach. J Med Chem 43:71–95
Huang Q, Zhang W, Liu R, McKernan RM, Cook JM (1996) Benzo-fused benzodiazepines as topological probes for the study of benzodiazepine receptor subtypes. Med Chem Res 6:384–391
Janak PH, Chaudhri N (2010) The potent effect of environmental context on relapse to alcohol-seeking after extinction. Open Addict J 3:76–87
Jin Z, Bazov I, Kononenko O, Korpi ER, Bakalkin G, Birnir B (2012) Selective changes of GABAA channel subunit mRNAs in the hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex but not in prefrontal cortex of human alcoholics. Front Cell Neurosci 5:30. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2011.00030
June HL, Harvey SC, Foster KL, McKay PF, Cummings R, Garcia M, Mason D, Grey C, McCane S, Williams LS, Johnson TB, He X, Rock S, Cook JM (2001) GABAA receptors containing α5 subunits in the CA1 and CA3 hippocampal fields regulate ethanol-motivated behaviors: an extended ethanol reward circuitry. J Neurosci 21:2166–2177
Kelley AE, Domesick VB (1982) The distribution of the projection from the hippocampal formation to the nucleus accumbens in the rat: an anterograde- and retrograde-horseradish peroxidase study. Neuroscience 7:2321–2335
Knust H, Achermann G, Ballard T, Buettelmann B, Gasser R, Fischer H, Hernandez MC, Knoflach F, Koblet A, Stadler H, Thomas AW, Trube G, Waldmeier P (2009) The discovery and unique pharmacological profile of RO4938581 and RO4882224 as potent and selective GABAA alpha5 inverse agonists for the treatment of cognitive dysfunction. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:5940–5944
Langleben DD, Busch EL, O'Brien CP, Elman I (2012) Depot naltrexone decreases rewarding properties of sugar in patients with opioid dependence. Psychopharmacology 220:559–564
Li M, Szabo A, Rosenberg HC (2001) Evaluation of native GABAA receptors containing an alpha 5 subunit. Eur J Pharmacol 413:63–72
Liu R, Hu RJ, Zhang P, Skolnick P, Cook JM (1996) Synthesis and pharmacological properties of novel 8-substituted imidazobenzodiazepines: high-affinity, selective probes for alpha 5-containing GABAA receptors. J Med Chem 39:1928–1934
López-León S, Janssens ACJW, González-Zuloeta Ladd AM, Del-Favero J, Claes SJ, Oostra BA, van Duijn CM (2008) Meta-analyses of genetic studies on major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry 13:772–785
Luo AH, Tahsili-Fahadan P, Wise RA, Lupica CR, Aston-Jones G (2011) Linking context with reward: a functional circuit from hippocampal CA3 to ventral tegmental area. Science 333:353–357
McKay PF, Foster KL, Mason D, Cummings R, Garcia M, Williams LS, Grey C, McCane S, He X, Cook JM, June HL (2004) A high affinity ligand for GABAA-receptor containing alpha5 subunit antagonizes ethanol’s neurobehavioral effects in Long-Evans rats. Psychopharmacology 172:455–462
McKernan RM, Whiting PJ (1996) Which GABAA-receptor subtypes really occur in the brain? Trends Neurosci 19:139–143
Middaugh LD, Bao K, Becker HC, Daniel SS (1991) Effects of Ro 15-4513 on ethanol discrimination in C57BL/6 mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38:763–767
Möhler H, Rudolph U (2017) Disinhibition, an emerging pharmacology of learning and memory. F1000Res. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.9947.1
Navarro JF, Burón E, Martín-López M (2002) Anxiogenic-like activity of L-655,708, a selective ligand for the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors which contain the alpha-5 subunit, in the elevated plus-maze test. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 26:1389–1392
Nguyen D, Schumacher A, Erb S, Ito R (2015) Aberrant approach-avoidance conflict resolution following repeated cocaine pre-exposure. Psychopharmacology 232:3573–3583
Otani K, Ujike H, Tanaka Y, Morita Y, Katsu T, Nomura A, Uchida N, Hamamura T, Fujiwara Y, Kuroda S (2005) The GABA type a receptor α5 subunit gene is associated with bipolar I disorder. Neurosci Lett 381:10–17
Platt DM, Duggan A, Spealman RD, Cook JM, Li X, Yin W, Rowlett JK (2005) Contribution of α1GABAA and α5GABAA receptor subtypes to the discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol in squirrel monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313:658–667
Pofantis H, Papatheodoropoulos C (2014) The α5GABAA receptor modulates the induction of long-term potentiation at ventral but not dorsal CA1 hippocampal synapses. Synapse 68:394–401
Prut L, Prenosil G, Willadt S, Vogt K, Fritschy JM, Crestani F (2010) A reduction in hippocampal GABAA receptor alpha5 subunits disrupts the memory for location of objects in mice. Genes Brain Behav 9:478–488
Redrobe JP, Elster L, Frederiksen K, Bundgaard C, de Jong IE, Smith GP, Bruun AT, Larsen PH, Didriksen M (2012) Negative modulation of GABAA α5 receptors by RO4938581 attenuates discrete sub-chronic and early postnatal phencyclidine (PCP)-induced cognitive deficits in rats. Psychopharmacology 221:451–468
Rees DC, Balster RL (1988) Attenuation of the discriminative stimulus properties of ethanol and oxazepam, but not of pentobarbital, by Ro 15-4513 in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:592–598
Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavomcharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y, Patra J (2009) Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 373:2223–2233
Rudolph U, Möhler H (2004) Analysis of GABAA receptor function and dissection of the pharmacology of benzodiazepines and general anesthetics through mouse genetics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44:475–498
Rüedi-Bettschen D, Rowlett JK, Rallapalli S, Clayton T, Cook JM, Platt DM (2013) Modulation of α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors alters alcohol drinking by rhesus monkeys. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 37:624–634
Samson HH (1986) Initiation of ethanol reinforcement using a sucrose-substitution procedure in food- and water-sated rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 10:436–442
Sarantis K, Sotiriou E, Papatheodoropoulos C, Matsokis N, Angelatou F (2008) Differential pharmacological properties of GABAA/benzodiazepine receptor complex in dorsal compared to ventral rat hippocampus. Neurochem Int 52:1019–1029
Schumacher A, Villaruel FR, Ussling A, Riaz S, Lee ACH, Ito R (2018) Ventral hippocampal CA1 and CA3 differentially mediate learned approach-avoidance conflict processing. Curr Biol 28:1318–1324.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.03.012
Sesack SR, Grace AA (2010) Cortico-basal ganglia reward network: microcircuitry. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:27–47
Shelton KL, Grant KA (2001) Effects of naltrexone and Ro 15-4513 on a multiple schedule of ethanol and Tang self-administration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1576–1585
Song J, Koller DL, Foroud T, Carr K, Zhao J, Rice J, Nurnberger JI Jr, Begleiter H, Porjesz B, Smith TL, Schuckit MA, Edenberg HJ (2003) Association of GABAA receptors and alcohol dependence and the effects of genetic imprinting. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 117B:39–45
Sur C, Fresu L, Howell O, McKernan RM, Atack JR (1999) Autoradiographic localization of alpha5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors in rat brain. Brain Res 822:265–270
Uusi-Oukari M, Korpi ER (2010) Regulation of GABAA receptor subunit expression by pharmacological agents. Pharmacol Rev 62:97–135
Weiss F (2010) Advances in animal models of relapse for addiction research. In: Kuhn CM, Koob GF (eds) Advances in the neuroscience of addiction, 2nd edn. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton Chapter 1
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Joyce Besheer (UNC-Chapel Hill) for invaluable advice regarding alcohol self-administration in rats; Dr. Kevin Freeman (UMMC) for use of his operant conditioning chambers, and Dr. Sally Huskinson for her Med State programming expertise. We also would like to thank the Shimadzu Analytical Laboratory of Southeastern Wisconsin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animals were maintained and experiments were conducted in accordance with the University of Mississippi Medical Center’s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and were in accordance with the National Research Council’s Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (eighth edition, 2011).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This research was supported by AA016179 (DMP), MH096463 (JMC) and NS076517 (JMC).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandler, C.M., Reeves-Darby, J., Jones, S.A. et al. α5GABAA subunit-containing receptors and sweetened alcohol cue-induced reinstatement and active sweetened alcohol self-administration in male rats. Psychopharmacology 236, 1797–1806 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5163-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5163-6