Abstract
Rationale
Alcohol use disorders have become one of the most damaging psychiatric disorders in the world; however, there are no ideal treatments in clinic. Phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), an enzyme that specifically hydrolyzes intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP), has been involved in alcohol use disorders. Roflumilast is the first PDE4 inhibitor approved for treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases in clinic. It was of particular interest to researchers to determine whether roflumilast altered ethanol consumption.
Objectives
The present study tried to determine the effects of roflumilast on ethanol intake and preference.
Methods
We used the two-bottle choice paradigm to assess ethanol intake and preference in C57BL/6J mice treated with roflumilast (1, 3, or 10 mg/kg) or rolipram (0.5 mg/kg; positive control). The effect of roflumilast was verified using the ethanol drinking-in-dark (DID) test. Locomotor activity was examined using the open-field test. Intake of sucrose or quinine was also tested to determine whether natural reward preference and aversive stimuli were involved in the effect of PDE4 inhibitors.
Results
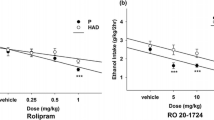
Similar to rolipram, roflumilast decreased ethanol intake and preference in two-bottle choice and DID tests in a dose-dependent manner, with significant changes at the dose of 10 mg/kg; in contrast, roflumilast did not affect sucrose or quinine drinking, although it decreased locomotor activity at the high dose within 3 h of treatment.
Conclusions
These data provide novel demonstration for the effect of roflumilast on ethanol consumption and suggest that roflumilast may be beneficial for treatment of alcoholism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell RL, Lopez MF, Cui C, Egli M, Johnson KW, Franklin KM, Becker HC (2013) Ibudilast reduces alcohol drinking in multiple animal models of alcohol dependence. Addict Biol 20(1):38–42. doi:10.1111/adb.12106
Blednov YA, Benavidez JM, Black M, Harris RA (2014) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 4 reduces ethanol intake and preference in C57BL/6J mice. Front Neurosci 8:129. doi:10.3389/fnins.2014.00129
Boswell-Smith V, Spina D (2007) PDE4inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents in the treatment of COPD-focus on roflumilast. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2(2):121–129
Bouchery EE, Harwood HJ, Sacks JJ, Simon CJ, Brewer RD (2011) Economic costs of excessive alcohol consumption in the U.S., 2006. Am J Prev Med 41(5):516–524. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2011.06.045
Bundschuh DS, Eltze M, Barsig J, Wollin L, Hatzelmann A, Beume RJ (2001) In vivo efficacy in airway disease models of roflumilast, a novel orally active PDE4 inhibitor. Pharmacol Exp Ther 297(1):280–290
Camarini R, Hodge CW (2004) Ethanol preexposure increases ethanol self-administration in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79(4):623–632. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2004.09.012
Carroll ME, Morgan AD, Anker JJ, Perry JL, Dess NK (2008) Selective breeding for differential saccharin intake as an animal model of drug abuse. Behav Pharmacol 19:435–460. doi:10.1097/FBP.0b013e32830c3632
Crabbe JC (2014) Use of animal models of alcohol-related behavior. Handb Clin Neurol 125:71–86. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-62619-6.00005-7
Chiang T, Sansuk K, van Rijn RM (2016) β-Arrestin 2 dependence of δ opioid receptor agonists is correlated with alcohol intake. Br J Pharmacol 173(2):332–343. doi:10.1111/bph.13374
Davis TG, Peterson JJ, Kou JP, Capper-Spudich EA, Ball D, Nials AT, Wiseman J, Solanke YE, Lucas FS, Williamson RA, Ferrari L, Wren P, Knowles RG, Barnette MS, Podolin PL (2009) The identification of a novel phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, 1-ethyl-5-{5-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl}-N-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-4-amine (EPPA-1), with improved therapeutic index using pica feeding in rats as a measure of emetogenicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330(3):922–931
García-Osta A, Cuadrado-Tejedor M, García-Barroso C, Oyarzábal J, and Franco R (2012) Phosphodiesterases as therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's disease. ACS Chem Neurosci 3(11):832–844. doi:10.1021/cn3000907
George S, Chaturvedi P (2008) Protective role of Ocimum canum plant extract in alcohol-induced oxidative stress in albino rats. Br J Biomed Sci 65(2):80–85
Grant BF, Saha TD, Ruan WJ, Goldstein RB, Chou SP, Jung J, Zhang H, Smith SM, Pickering RP, Huang B, Hasin DS (2016) Epidemiology of DSM-5 drug use disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions-III. JAMA Psychiatry 73(1):39–47. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2132
Griffin WC 3rd, Lopez MF, Yanke AB, Middaugh LD, Becker HC (2009) Repeated cycles of chronic intermittent ethanol exposure in mice increases voluntary ethanol drinking and ethanol concentrations in the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology 201(4):569–580. doi:10.1007/s00213-008-1324-3
Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Ogburn E, Grant BF (2007) Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64(7):830–842
Hatzelmann A, Schudt C (2001) Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential of the novel PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297(1):267–279
Hu W, Lu T, Chen A, Huang Y, Hansen R, Chandler LJ, Zhang HT (2011) Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 decreases ethanol intake in mice. Psychopharmacology 218(2):331–339. doi:10.1007/s00213-011-2290-8
Jabaris SS, Sumathy H, Girish R, Narayanan S, Sugumar M, Saravana Babu C, Thanikachalam S, Thanikachalam M (2015a) Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors ameliorates cognitive deficits in deoxycorticosterone acetate induced hypertensive rats via cAMP/CREB signaling system. Brain Res 1622:279–291. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2015.07.003
Jabaris SG, Sumathy H, Kumar RS, Narayanan S, Thanikachalam S, Babu CS (2015b) Effects of rolipram and roflumilast, phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors, on hypertension-induced defects in memory function in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 746:138–147. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar
Kamdar NK, Miller SA, Syed YM, Bhayana R, Gupta T, Rhodes JS (2007) Acute effects of naltrexone and GBR 12909 on ethanol drinking-in-the-dark in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology 192(2):207–217. doi:10.1007/s00213-007-0711-5
Kanes SJ, Tokarczyk J, Siegel SJ, Bilker W, Abel T, Kelly MP (2007) Rolipram: a specific phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor with potential antipsychotic activity. Neuroscience 144(1):239–246
Kraft P, Schwarz T, Gob E, Heydenreich N, Brede M, Meuth SG, Kleinschnitz C (2013) The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram protects from ischemic stroke in mice by reducing blood–brain-barrier damage, inflammation and thrombosis. Exp Neurol 247:80–90. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.03.026
Li LX, Cheng YF, Lin HB, Wang C, Xu JP, Zhang HT (2011) Prevention of cerebral ischemia-induced memory deficits by inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4 in rats. Metab Brain Dis 26:37–47. doi:10.1007/s11011-011-9235-0
Li YF, Huang Y, Amsdell SL, Xiao L, O’Donnell JM, Zhang HT (2009) Antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects of the phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor rolipram on behavior depend on cyclic AMP-response element binding protein (CREB)-mediated neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2404–2419. doi:10.1038/npp.2009.66
Lai M, Zhu H, Sun A, Zhuang D, Fu D, Chen W, Zhang HT (2014) Zhou W. The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor rolipram attenuates heroin-seeking behavior induced by cues or heroin priming in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 17(9):1397–1407. doi:10.1017/S1461145714000595
Liang J, Olsen RW (2014) Alcohol use disorders and current pharmacological therapies: the role of GABA (A) receptors. Acta Pharmacol Sin 35(8):981–993. doi:10.1038/aps.2014.50
Lindholm S, Werme M, Brené S, Franck J (2001) The selective k-opioid receptor agonist U50,488H attenuates voluntary ethanol intake in the rat. Behav Brain Res 120(2):137–146
Logrip ML (2015) Phosphodiesterase regulation of alcohol drinking in rodents. Alcohol 49(8):795–802. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2015.03.007
Logrip ML, Janak PH, Ron D (2009) Blockade of ethanol reward by the kappa opioid receptor agonist U50,488h. Alcohol 43(5):359–365. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.05.001
Misra K, Pandey SC (2006) The decreased cyclic-AMP dependent-protein kinase A function in the nucleus accumbens: a role in alcohol drinking but not in anxiety-like behaviors in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(7):1406–1419. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1300900
Nishi A, Kuroiwa M, Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP, Bateup HS, Shuto T, Sotogaku N, Fukuda T, Heintz N, Greengard P, Snyder GL (2008) Distinct roles of PDE4 and PDE10A in the regulation of cAMP/PKA signaling in the striatum. J Neurosci 28(42):10460–10471
O’Donnell JM, Zhang HT (2004) Antidepressant effects of inhibitors of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase (PDE4). Trends Pharmacol Sci (TIPS) 25:158–163
Pandey SC (2004) The gene transcription factor cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein: role in positive and negative affective states of alcohol addiction. Pharmacol Ther 104(1):47–58
Pandey SC, Roy A, Zhang H (2003) The decreased phosphorylation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) response element binding (CREB) protein in the central amygdala acts as a molecular substrate for anxiety related to ethanol withdrawal in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27(3):396–409. doi:10.1097/01.ALC.0000056616.81971.49
Pandey SC, Zhang H, Roy A, Xu T (2005) Deficits in amygdaloid cAMP-responsive element-binding protein signaling play a role in genetic predisposition to anxiety and alcoholism. J Clin Invest 115(10):2762–2773. doi:10.1172/JCI24381
Pleil KE, Rinker JA, Lowery-Gionta EG, Mazzone CM, McCall NM, Kendra AM, Olson DP, Lowell BB, Grant KA, Thiele TE, Kash TL (2015) NPY signaling inhibits extended amygdala CRF neurons to suppress binge alcohol drinking. Nat Neurosci 18(4):545–552. doi:10.1038/nn.3972
Rabe KF, Bateman ED, O’Donnell D, Witte S, Bredenbröker D, Bethke TD (2005) Roflumilast—an oral anti-inflammatory treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease:a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 366:563–571
Rashid MA, Kim HY (2016) N-Docosahexaenoylethanolamine ameliorates ethanol-induced impairment of neural stem cell neurogenic differentiation. Neuropharmacology 102:174–185. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.11.011
Sanz MJ, Cortijo J, Morcillo EJ (2005) PDE4 inhibitors as new anti-inflammatory drugs: effects on cell trafficking and cell adhesion molecules expression. Pharmacol Ther 106(3):269–297
Schneider HH (1984) Brain cAMP response to phosphodiesterase inhibitors in rats killed by microwave irradiation or decapitation. Biochem Pharmacol 33(10):1690–1693
Sierksma AS, van den Hove DL, Pfau F, Philippens M, Bruno O, Fedele E, Ricciarelli R, Steinbusch HW, Vanmierlo T, Prickaerts J (2014) Improvement of spatial memory function in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice after chronic inhibition of phosphodiesterase type 4D. Neuropharmacology 77:120–130. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.09.015
Soares LM, De Vry J, Steinbusch HW, Milani H, Prickaerts J, Weffort de Oliveira RM (2016) Rolipram improves cognition, reduces anxiety- and despair-like behaviors and impacts hippocampal neuroplasticity after transient global cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 326:69–83. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.03.062
Spanagel R (2009) Alcoholism: a systems approach from molecular physiology to addictive behavior. Physiol Rev 89(2):649–705. doi:10.1152/physrev.00013.2008
Thiele TE, Navarro M (2014) “Drinking in the dark” (DID) procedures: a model of binge-like ethanol drinking in non-dependent mice. Alcohol 48(3):235–241. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2013.08.005
Vanmierlo T, Creemers P, Akkerman S, van Duinen M, Sambeth A, De Vry J, Uz T, Blokland A, Prickaerts J (2016) The PDE4 inhibitor roflumilast improves memory in rodents at non-emetic doses. Behav Brain Res 303:26–33. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2016.01.031
Wen RT, Feng WY, Liang JH, Zhang HT (2015) Role of phosphodiesterase 4-mediated cyclic AMP signaling in pharmacotherapy for substance dependence. Curr Pharm Des 21(3):355–364
Wen RT, Zhang M, Qin WJ, Liu Q, Wang WP, Lawrence AJ, Zhang HT, Liang JH (2012) The phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor rolipram decreases ethanol seeking and consumption in alcohol-preferring fawn-hooded rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36(12):2157–2167. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01845.x
Wilmouth CE, Spear LP (2009) Hedonic sensitivity in adolescent and adult rats: taste reactivity and voluntary sucrose consumption. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92(4):566–573. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2009.02.009
Yamashita N, Hayashi A, Baba J, Sawa A (1997) Rolipram, a phosphodiesterase-4-selective inhibitor, promotes the survival of cultured rat dopaminergic neurons. Jpn J Pharmacol 75(2):155–159
Zhang C, Cheng Y, Wang H, Wang C, Wilson SP, Xu J, Zhang HT (2014) RNA interference-mediated knockdown of long-form phosphodiesterase-4D (PDE4D) enzyme reverses amyloid-β42-induced memory deficits in mice. J Alzheimers Dis 38:269–280. doi:10.3233/JAD-122236
Zhang HT (2009) Cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase-4 as a target for the development of antidepressant drugs. Curr Pharm Des 15(14):1688–1698
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81471212, 81271275, 81070947, and 30770759 to B.-L. Sun), the Natural Scientific Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2014CL011 to X. Liu, No. ZR2012HZ006 to B.-L. Sun), the High-Level Project Cultivating Grants of Taishan Medical University (No. 2013GCC08 to X. Liu), the High-School Scientific Research Development Program of Shandong Province (No. 2016J16LL57 to X. Liu), the research grants from the Foundation of Taishan Scholars of Shandong Province, China (to B.-L. Sun), and the research grants from the Foundation of Overseas Distinguished Taishan Scholars of Shandong Province, China (to H.-T. Zhang).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Hao, PD., Yang, MF. et al. The phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor roflumilast decreases ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacology 234, 2409–2419 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4631-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4631-8