Abstract
Rationale
Mood disorders can be triggered by stress and are characterized by deficits in reward processing, including disrupted reward learning (the ability to modulate behavior according to past rewards). Reward learning is regulated by the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and striatal circuits, both of which are implicated in the pathophysiology of mood disorders.
Objectives
Here, we assessed in rats the effects of a potent stressor (social defeat) on reward learning and gene expression in the ACC, ventral tegmental area (VTA), and striatum.
Methods
Adult male Wistar rats were trained on an operant probabilistic reward task (PRT) and then exposed to 3 days of social defeat before assessment of reward learning. After testing, the ACC, VTA, and striatum were dissected, and expression of genes previously implicated in stress was assessed.
Result
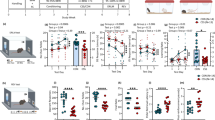
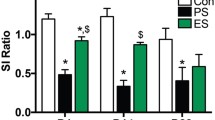
Social defeat blunted reward learning (manifested as reduced response bias toward a more frequently rewarded stimulus) and was associated with increased nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) peptide mRNA levels in the striatum and decreased Fos mRNA levels in the VTA. Moreover, N/OFQ peptide and nociceptin receptor mRNA levels in the ACC, VTA and striatum were inversely related to reward learning.
Conclusions
The behavioral findings parallel previous data in humans, suggesting that stress similarly disrupts reward learning in both species. Increased striatal N/OFQ mRNA in stressed rats characterized by impaired reward learning is consistent with accumulating evidence that antagonism of nociceptin receptors, which bind N/OFQ, has antidepressant-like effects. These results raise the possibility that nociceptin systems represent a molecular substrate through which stress produces reward learning deficits in mood disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, American Psychiatric Association
Amiez C, Joseph JP, Procyk E (2006) Reward encoding in the monkey anterior cingulate cortex. Cereb Cortex 16:1040–1055
Barch DM, Pagliaccio D, Luking K (2016) Mechanisms underlying motivational deficits in psychopathology: similarities and differences in depression and schizophrenia. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 27:411–449
Berenbaum H, Connelly J (1993) The effect of stress on hedonic capacity. J Abnorm Psychol 102:474–481
Berthele A, Platzer S, Dworzak D, Schadrack J, Mahal B, Buttner A, Assmus HP, Wurster K, Zieglgansberger W, Conrad B, Tolle TR (2003) [3H]-nociceptin ligand-binding and nociceptin opioid receptor mrna expression in the human brain. Neuroscience 121:629–640
Bogdan R, Pizzagalli DA (2006) Acute stress reduces reward responsiveness: implications for depression. Biol Psychiatry 60:1147–1154
Bogdan R, Perlis RH, Fagerness J, Pizzagalli DA (2010) The impact of mineralocorticoid receptor ISO/VAL genotype (rs5522) and stress on reward learning. Genes Brain Behav 9:658–667
Bogdan R, Santesso DL, Fagerness J, Perlis RH, Pizzagalli DA (2011) Corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1 (CRHR1) genetic variation and stress interact to influence reward learning. J Neurosci 31:13246–13254
Bush G, Vogt BA, Holmes J, Dale AM, Greve D, Jenike MA, Rosen BR (2002) Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex: a role in reward-based decision making. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:523–528
Carlezon WA Jr, Krystal AD (2016) Kappa-opioid antagonists for psychiatric disorders: from bench to clinical trials. Depress Anxiety 33:895–906
Charney DS, Manji HK (2004) Life stress, genes, and depression: multiple pathways lead to increased risk and new opportunities for intervention. Sci STKE 2004: re5
Chartoff EH, Ebner SR, Sparrow A, Potter D, Baker PM, Ragozzino ME, Roitman MF (2016) Relative timing between kappa opioid receptor activation and cocaine determines the impact on reward and dopamine release. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:989–1002
Der-Avakian A, Markou A (2012) The neurobiology of anhedonia and other reward-related deficits. Trends Neurosci 35:68–77
Der-Avakian A, D'Souza MS, Pizzagalli DA, Markou A (2013) Assessment of reward responsiveness in the response bias probabilistic reward task in rats: implications for cross-species translational research. Transl Psychiatry 3:e297
Der-Avakian A, Mazei-Robison MS, Kesby JP, Nestler EJ, Markou A (2014) Enduring deficits in brain reward function after chronic social defeat in rats: susceptibility, resilience, and antidepressant response. Biol Psychiatry 76:542–549
Devine DP, Watson SJ, Akil H (2001) Nociceptin/orphanin FQ regulates neuroendocrine function of the limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Neuroscience 102:541–553
Donahue RJ, Muschamp JW, Russo SJ, Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA Jr (2014) Effects of striatal DeltaFosB overexpression and ketamine on social defeat stress-induced anhedonia in mice. Biol Psychiatry 76:550–558
Dunlop BW, Nemeroff CB (2007) The role of dopamine in the pathophysiology of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:327–337
Ernst M, Nelson EE, McClure EB, Monk CS, Munson S, Eshel N, Zarahn E, Leibenluft E, Zametkin A, Towbin K, Blair J, Charney D, Pine DS (2004) Choice selection and reward anticipation: an fMRI study. Neuropsychologia 42:1585–1597
Gavioli EC, Marzola G, Guerrini R, Bertorelli R, Zucchini S, De Lima TC, Rae GA, Salvadori S, Regoli D, Calo G (2003) Blockade of nociceptin/orphanin FQ-NOP receptor signalling produces antidepressant-like effects: pharmacological and genetic evidences from the mouse forced swimming test. Eur J Neurosci 17:1987–1990
Gavioli EC, Vaughan CW, Marzola G, Guerrini R, Mitchell VA, Zucchini S, De Lima TC, Rae GA, Salvadori S, Regoli D, Calo G (2004) Antidepressant-like effects of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor antagonist UFP-101: new evidence from rats and mice. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 369:547–553
Glimcher PW (2011) Understanding dopamine and reinforcement learning: the dopamine reward prediction error hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(Suppl 3):15647–15654
Gold JM, Waltz JA, Prentice KJ, Morris SE, Heerey EA (2008) Reward processing in schizophrenia: a deficit in the representation of value. Schizophr Bull 34:835–847
Green TA, Alibhai IN, Roybal CN, Winstanley CA, Theobald DE, Birnbaum SG, Graham AR, Unterberg S, Graham DL, Vialou V, Bass CE, Terwilliger EF, Bardo MT, Nestler EJ (2010) Environmental enrichment produces a behavioral phenotype mediated by low cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding (CREB) activity in the nucleus accumbens. Biol Psychiatry 67:28–35
Gu H, Hu D, Hong XR, Mao J, Cui Y, Hui N, Sha JY (2003) Changes and significance of orphanin and serotonin in patients with postpartum depression. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi 38:727–728
Hollis F, Kabbaj M (2014) Social defeat as an animal model for depression. ILAR J 55:221–232
Kendler KS, Karkowski LM, Prescott CA (1999) Causal relationship between stressful life events and the onset of major depression. Am J Psychiatry 156:837–841
Kennerley SW, Walton ME, Behrens TE, Buckley MJ, Rushworth MF (2006) Optimal decision making and the anterior cingulate cortex. Nat Neurosci 9:940–947
Koizumi M, Midorikawa N, Takeshima H, Murphy NP (2004a) Exogenous, but not endogenous nociceptin modulates mesolimbic dopamine release in mice. J Neurochem 89:257–263
Koizumi M, Sakoori K, Midorikawa N, Murphy NP (2004b) The NOP (ORL1) receptor antagonist Compound B stimulates mesolimbic dopamine release and is rewarding in mice by a non-NOP-receptor-mediated mechanism. Br J Pharmacol 143:53–62
Lambert G, Johansson M, Agren H, Friberg P (2000) Reduced brain norepinephrine and dopamine release in treatment-refractory depressive illness: evidence in support of the catecholamine hypothesis of mood disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:787–793
Lezak KR, Roman CW, Braas KM, Schutz KC, Falls WA, Schulkin J, May V, Hammack SE (2014) Regulation of bed nucleus of the stria terminalis PACAP expression by stress and corticosterone. J Mol Neurosci 54:477–484
Liu WH, Chan RC, Wang LZ, Huang J, Cheung EF, Gong QY, Gollan JK (2011) Deficits in sustaining reward responses in subsyndromal and syndromal major depression. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1045–1052
Lohith TG, Zoghbi SS, Morse CL, Araneta MF, Barth VN, Goebl NA, Tauscher JT, Pike VW, Innis RB, Fujita M (2012) Brain and whole-body imaging of nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide receptor in humans using the PET ligand 11C-NOP-1A. J Nucl Med 53:385–392
Lohith TG, Zoghbi SS, Morse CL, Araneta MD, Barth VN, Goebl NA, Tauscher JT, Pike VW, Innis RB, Fujita M (2014) Retest imaging of [11C]NOP-1A binding to nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) receptors in the brain of healthy humans. NeuroImage 87:89–95
Maia TV, Frank MJ (2011) From reinforcement learning models to psychiatric and neurological disorders. Nat Neurosci 14:154–162
Murphy NP, Maidment NT (1999) Orphanin FQ/nociceptin modulation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission determined by microdialysis. J Neurochem 73:179–186
Murphy NP, Ly HT, Maidment NT (1996) Intracerebroventricular orphanin FQ/nociceptin suppresses dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of anaesthetized rats. Neuroscience 75:1–4
Murphy NP, Tan AM, Lam HA, Maidment NT (2004) Nociceptin/orphanin FQ modulation of rat midbrain dopamine neurons in primary culture. Neuroscience 127:929–940
Muschamp JW, Van't Veer A, Parsegian A, Gallo MS, Chen M, Neve RL, Meloni EG, Carlezon WA Jr (2011) Activation of CREB in the nucleus accumbens shell produces anhedonia and resistance to extinction of fear in rats. J Neurosci 31:3095–3103
Nativio P, Pascale E, Maffei A, Scaccianoce S, Passarelli F (2012) Effect of stress on hippocampal nociceptin expression in the rat. Stress 15:378–384
Neal CR Jr, Mansour A, Reinscheid R, Nothacker HP, Civelli O, Akil H, Watson SJ Jr (1999) Opioid receptor-like (ORL1) receptor distribution in the rat central nervous system: comparison of ORL1 receptor mRNA expression with (125)I-[(14)Tyr]-orphanin FQ binding. J Comp Neurol 412:563–605
Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA Jr (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine reward circuit in depression. Biol Psychiatry 59:1151–1159
Nikolova Y, Bogdan R, Pizzagalli DA (2012) Perception of a naturalistic stressor interacts with 5-HTTLPR/rs25531 genotype and gender to impact reward responsiveness. Neuropsychobiology 65:45–54
Nutt DJ (2006) The role of dopamine and norepinephrine in depression and antidepressant treatment. J Clin Psychiatry 67(Suppl 6):3–8
Onn SP, Wang XB (2005) Differential modulation of anterior cingulate cortical activity by afferents from ventral tegmental area and mediodorsal thalamus. Eur J Neurosci 21:2975–2992
Paxinos G, Watson C (2007) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press/Elsevier, Academic Press/Elsevier
Pechtel P, Dutra SJ, Goetz EL, Pizzagalli DA (2013) Blunted reward responsiveness in remitted depression. J Psychiatr Res 47:1864–1869
Pergadia ML, Der-Avakian A, D'Souza MS, Madden PA, Heath AC, Shiffman S, Markou A, Pizzagalli DA (2014) Association between nicotine withdrawal and reward responsiveness in humans and rats. JAMA Psychiatry 71:1238–1245
Pizzagalli DA, Jahn AL, O'Shea JP (2005) Toward an objective characterization of an anhedonic phenotype: a signal-detection approach. Biol Psychiatry 57:319–327
Pizzagalli DA, Bogdan R, Ratner KG, Jahn AL (2007) Increased perceived stress is associated with blunted hedonic capacity: potential implications for depression research. Behav Res Ther 45:2742–2753
Pizzagalli DA, Goetz E, Ostacher M, Iosifescu DV, Perlis RH (2008a) Euthymic patients with bipolar disorder show decreased reward learning in a probabilistic reward task. Biol Psychiatry 64:162–168
Pizzagalli DA, Iosifescu D, Hallett LA, Ratner KG, Fava M (2008b) Reduced hedonic capacity in major depressive disorder: evidence from a probabilistic reward task. J Psychiatr Res 43:76–87
Pliakas AM, Carlson RR, Neve RL, Konradi C, Nestler EJ, Carlezon WA Jr (2001) Altered responsiveness to cocaine and increased immobility in the forced swim test associated with elevated cAMP response element-binding protein expression in nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 21:7397–7403
Post A, Smart TS, Krikke-Workel J, Dawson GR, Harmer CJ, Browning M, Jackson K, Kakar R, Mohs R, Statnick M, Wafford K, McCarthy A, Barth V, Witkin JM (2016) A selective nociceptin receptor antagonist to treat depression: evidence from preclinical and clinical studies. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:2624
Redrobe JP, Calo G, Regoli D, Quirion R (2002) Nociceptin receptor antagonists display antidepressant-like properties in the mouse forced swimming test. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 365:164–167
Rizzi A, Gavioli EC, Marzola G, Spagnolo B, Zucchini S, Ciccocioppo R, Trapella C, Regoli D, Calo G (2007) Pharmacological characterization of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor antagonist SB-612111 [(−)-cis-1-methyl-7-[[4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]methyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrah ydro-5H-benzocyclohepten-5-ol]: in vivo studies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:968–974
Roman CW, Lezak KR, Hartsock MJ, Falls WA, Braas KM, Howard AB, Hammack SE, May V (2014) PAC1 receptor antagonism in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) attenuates the endocrine and behavioral consequences of chronic stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 47:151–165
Rushworth MF, Behrens TE, Rudebeck PH, Walton ME (2007) Contrasting roles for cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex in decisions and social behaviour. Trends Cogn Sci 11:168–176
Rygula R, Abumaria N, Havemann-Reinecke U, Ruther E, Hiemke C, Zernig G, Fuchs E, Flugge G (2008) Pharmacological validation of a chronic social stress model of depression in rats: effects of reboxetine, haloperidol and diazepam. Behav Pharmacol 19:183–196
Santesso DL, Dillon DG, Birk JL, Holmes AJ, Goetz E, Bogdan R, Pizzagalli DA (2008) Individual differences in reinforcement learning: behavioral, electrophysiological, and neuroimaging correlates. NeuroImage 42:807–816
Santesso DL, Evins AE, Frank MJ, Schetter EC, Bogdan R, Pizzagalli DA (2009) Single dose of a dopamine agonist impairs reinforcement learning in humans: evidence from event-related potentials and computational modeling of striatal-cortical function. Hum Brain Mapp 30:1963–1976
Seo H, Lee D (2007) Temporal filtering of reward signals in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex during a mixed-strategy game. J Neurosci 27:8366–8377
Sim LJ, Childers SR (1997) Anatomical distribution of mu, delta, and kappa opioid- and nociceptin/orphanin FQ-stimulated [35S]guanylyl-5'-O-(gamma-thio)-triphosphate binding in guinea pig brain. J Comp Neurol 386:562–572
Sim LJ, Xiao R, Childers SR (1996) Identification of opioid receptor-like (ORL1) peptide-stimulated [35S]GTP gamma S binding in rat brain. Neuroreport 7:729–733
Swanson LW (1982) The projections of the ventral tegmental area and adjacent regions: a combined fluorescent retrograde tracer and immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res Bull 9:321–353
Treadway MT, Zald DH (2011) Reconsidering anhedonia in depression: lessons from translational neuroscience. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:537–555
Tripp G, Alsop B (1999) Sensitivity to reward frequency in boys with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Child Psychol 28:366–375
Venzala E, Garcia-Garcia AL, Elizalde N, Delagrange P, Tordera RM (2012) Chronic social defeat stress model: behavioral features, antidepressant action, and interaction with biological risk factors. Psychopharmacology 224:313–325
Vitale G, Ruggieri V, Filaferro M, Frigeri C, Alboni S, Tascedda F, Brunello N, Guerrini R, Cifani C, Massi M (2009) Chronic treatment with the selective NOP receptor antagonist [Nphe 1, Arg 14, Lys 15]N/OFQ-NH 2 (UFP-101) reverses the behavioural and biochemical effects of unpredictable chronic mild stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 207:173–189
Vrieze E, Pizzagalli DA, Demyttenaere K, Hompes T, Sienaert P, de Boer P, Schmidt M, Claes S (2013) Reduced reward learning predicts outcome in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 73:639–645
Wang LN, Liu LF, Zhang JX, Zhao GF (2009) Plasma levels of nociceptin/orphanin FQ in patients with bipolar disorders and health adults. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 89:916–918
Whitton AE, Treadway MT, Pizzagalli DA (2015) Reward processing dysfunction in major depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Curr Opin Psychiatry 28:7–12
Whitton AE, Kakani P, Foti D, Veer AV, Haile A, Crowley DJ, Pizzagalli DA (2016) Blunted neural responses to reward in remitted major depression: a high-density event-related potential study. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging 1:87–95
Witkin JM, Statnick MA, Rorick-Kehn LM, Pintar JE, Ansonoff M, Chen Y, Tucker RC, Ciccocioppo R (2014) The biology of nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence. Pharmacol Ther 141:283–299
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ms. Jessica Benedict for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Over the past 3 years, Dr. Pizzagalli received consulting fees from Akili Interactive Labs, BlackThorn Therapeutics, Pfizer, and Posit Science, for activities unrelated to the current research. Dr. Markou received contract research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., and honoraria/consulting fees from Abbott GmbH and Company, AstraZeneca, and Pfizer during the past 2 years for projects unrelated to the present research. Dr. Markou also had a patent on the use of metabotropic glutamate compounds for the treatment of nicotine dependence that is unrelated to the present research. Dr. Carlezon discloses that he is an inventor on several patents that claim the use of selective kappa opioid ligands to treat psychiatric illness (Assignee: McLean Hospital) and during the past 2 years, has received compensation as a consultant for Cerecor. No other authors report any conflicts of interest.
Support
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants R21MH078979 (DAP) and R01MH063266 (WAC). Dr. Pizzagalli was further supported by R01MH0958092 and R37MH068376. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Additional information
Diego A. Pizzagalli and Athina Markou contributed equally as senior authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Der-Avakian, A., D’Souza, M.S., Potter, D.N. et al. Social defeat disrupts reward learning and potentiates striatal nociceptin/orphanin FQ mRNA in rats. Psychopharmacology 234, 1603–1614 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4584-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4584-y