Abstract
Rationale
Voluntary aerobic exercise has shown promise as a treatment for substance abuse, reducing relapse in cocaine-dependent people. Wheel running also attenuates drug-primed and cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats, an animal model of relapse. However, in most of these studies, wheel access was provided throughout cocaine self-administration and/or extinction and had effects on several parameters of drug seeking. Moreover, the effects of exercise on footshock stress-induced reinstatement have not been investigated.
Objectives
The purposes of this study were to isolate and specifically examine the protective effect of exercise on relapse-like behavior elicited by a drug prime or stress.
Methods
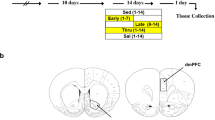
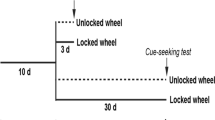
Rats were trained to self-administer cocaine at a stable level, followed by extinction training. Once extinction criteria were met, rats were split into exercise (24 h, continuous access to running wheel) and sedentary groups for 3 weeks, after which, drug-seeking behavior was assessed following a cocaine prime or footshock. We also measured galanin messenger RNA (mRNA) in the locus coeruleus and A2 noradrenergic nucleus.
Results
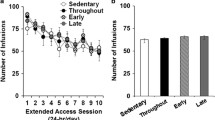
Exercising rats ran ∼4–6 km/day, comparable to levels previously reported for rats without a history of cocaine self-administration. Post-extinction exercise significantly attenuated cocaine-primed, but not footshock stress-induced, reinstatement of cocaine seeking, and increased galanin mRNA expression in the LC but not A2.
Conclusion
These results indicate that chronic wheel running can attenuate some forms of reinstatement, even when initiated after the cessation of cocaine self-administration, supporting the idea that voluntary exercise programs may help maintain abstinence in clinical populations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blumenthal JA, Sherwood A, Babyak MA, Watkins LL, Smith PJ, Hoffman BM, O’Hayer CV, Mabe S, Johnson J, Doraiswamy PM, Jiang W, Schocken DD, Hinderliter AL (2012) Exercise and pharmacological treatment of depressive symptoms in patients with coronary heart disease: results from the UPBEAT (Understanding the Prognostic Benefits of Exercise and Antidepressant Therapy) study. J Am Coll Cardiol 60:1053–1063
Brown ZJ, Tribe E, D’Souza NA, Erb S (2009) Interaction between noradrenaline and corticotrophin-releasing factor in the reinstatement of cocaine seeking in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 203:121–130
Brown RA, Abrantes AM, Read JP, Marcus BH, Jakicic J, Strong DR, Oakley JR, Ramsey SE, Kahler CW, Stuart GG, Dubreuil ME, Gordon AA (2010) A pilot study of aerobic exercise as an adjunctive treatment for drug dependence. Mental Health Phys Act 3:27–34
Cooney GM, Dwan K, Greig CA, Lawlor DA, Rimer J, Waugh FR, McMurdo M, Mead GE (2013) Exercise for depression. Cochrane Data Syst Rev 9:CD004366
Epps SA, Kahn AB, Holmes PV, Boss-Williams KA, Weiss JM, Weinshenker D (2013) Antidepressant and anticonvulsant effects of exercise in a rat model of epilepsy and depression comorbidity. Epilepsy Behav 29:47–52
Erb S, Hitchcott PK, Rajabi H, Mueller D, Shaham Y, Stewart J (2000) Alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonists block stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:138–150
Gaval-Cruz M, Weinshenker D (2009) mechanisms of disulfiram-induced cocaine abstinence: antabuse and cocaine relapse. Mol Interv 9:175–187
Hawes JJ, Brunzell DH, Narasimhaiah R, Langel U, Wynick D, Picciotto MR (2008) Galanin protects against behavioral and neurochemical correlates of opiate reward. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1864–1873
Holmes A, Picciotto MR (2006) Galanin: a novel therapeutic target for depression, anxiety disorders and drug addiction? CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 5:225–232
Holmes PV, Yoo HS, Dishman RK (2006) Voluntary exercise and clomipramine treatment elevate prepro-galanin mRNA levels in the locus coeruleus in rats. Neurosci Lett 408:1–4
Jones BE, Moore RY (1977) Ascending projections of the locus coeruleus in the rat. II. Autoradiographic study. Brain Res 127:25–53
Kupferschmidt DA, Brown ZJ, Erb S (2011) A procedure for studying the footshock-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in laboratory rats. J Visual Exp. doi:10.3791/2265
Leri F, Flores J, Rodaros D, Stewart J (2002) Blockade of stress-induced but not cocaine-induced reinstatement by infusion of noradrenergic antagonists into the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis or the central nucleus of the amygdala. J Neurosci 22:5713–5718
Lynch WJ, Piehl KB, Acosta G, Peterson AB, Hemby SE (2010) Aerobic exercise attenuates reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior and associated neuroadaptations in the prefrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 68:774–777
Lynch WJ, Peterson AB, Sanchez V, Abel J, Smith MA (2013) Exercise as a novel treatment for drug addiction: a neurobiological and stage-dependent hypothesis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:1622–1644
Mejias-Aponte CA, Drouin C, Aston-Jones G (2009) Adrenergic and noradrenergic innervation of the midbrain ventral tegmental area and retrorubral field: prominent inputs from medullary homeostatic centers. J Neurosci 29:3613–3626
Mitrano DA, Schroeder JP, Smith Y, Cortright JJ, Bubula N, Vezina P, Weinshenker D (2012) Alpha-1 Adrenergic receptors are localized on presynaptic elements in the nucleus accumbens and regulate mesolimbic dopamine transmission. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:2161–2172
Murray PS, Groves JL, Pettett BJ, Britton SL, Koch LG, Dishman RK, Holmes PV (2010) Locus coeruleus galanin expression is enhanced after exercise in rats selectively bred for high capacity for aerobic activity. Peptides 31:2264–2268
Narasimhaiah R, Kamens HM, Picciotto MR (2009) Effects of galanin on cocaine-mediated conditioned place preference and ERK signaling in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 204:95–102
Ogbonmwan YE, Sciolino NR, Groves-Chapman JL, Freeman KG, Schroeder JP, Edwards GL, Holmes PV, Weinshenker D (2014) The galanin receptor agonist, galnon, attenuates cocaine-induced reinstatement and dopamine overflow in the frontal cortex. Addict Biol. doi:10.1111/adb.12166
O’Neal HA, Van Hoomissen JD, Holmes PV, Dishman RK (2001) Prepro-galanin messenger RNA levels are increased in rat locus coeruleus after treadmill exercise training. Neurosci Lett 299:69–72
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press Limited, London
Peterson AB, Abel JM, Lynch WJ (2014) Dose-dependent effects of wheel running on cocaine-seeking and prefrontal cortex Bdnf exon IV expression in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 231:1305–1314
Picciotto MR (2008) Galanin and addiction. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1872–1879
Reiss JI, Dishman RK, Boyd HE, Robinson JK, Holmes PV (2009) Chronic activity wheel running reduces the severity of kainic acid-induced seizures in the rat: possible role of galanin. Brain Res 1266:54–63
Schroeder JP, Cooper DA, Schank JR, Lyle MA, Gaval-Cruz M, Ogbonmwan YE, Pozdeyev N, Freeman KG, Iuvone PM, Edwards GL, Holmes PV, Weinshenker D (2010) Disulfiram attenuates drug-primed reinstatement of cocaine seeking via inhibition of dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:2440–2449
Schroeder JP, Epps SA, Grice TW, Weinshenker D (2013) The selective dopamine beta-hydroxylase inhibitor nepicastat attenuates multiple aspects of cocaine-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1032–1038
Sciolino NR, Holmes PV (2012) Exercise offers anxiolytic potential: a role for stress and brain noradrenergic-galaninergic mechanisms. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:1965–1984
Sciolino NR, Dishman RK, Holmes PV (2012) Voluntary exercise offers anxiolytic potential and amplifies galanin gene expression in the locus coeruleus of the rat. Behav Brain Res 233:191–200
Sciolino NR, Smith JM, Stranahan AM, Freeman KG, Edwards GL, Weinshenker D, Holmes PV (2014) Galanin mediates features of neural and behavioral stress resilience afforded by exercise. Neuropharmacology. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.09.029
Shaham Y, Highfield D, Delfs J, Leung S, Stewart J (2000) Clonidine blocks stress-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking in rats: an effect independent of locus coeruleus noradrenergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 12:292–302
Simon H, Le Moal M, Stinus L, Calas A (1979) Anatomical relationships between the ventral mesencephalic tegmentum—a 10 region and the locus coeruleus as demonstrated by anterograde and retrograde tracing techniques. J Neural Transm 44:77–86
Sinyor D, Brown T, Rostant L, Seraganian P (1982) The role of a physical fitness program in the treatment of alcoholism. J Stud Alcohol 43:380–386
Smith RJ, Aston-Jones G (2011) Alpha(2) adrenergic and imidazoline receptor agonists prevent cue-induced cocaine seeking. Biol Psychiatry 70:712–719
Smith MA, Pitts EG (2011) Access to a running wheel inhibits the acquisition of cocaine self-administration. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100:237–243
Smith MA, Schmidt KT, Iordanou JC, Mustroph ML (2008) Aerobic exercise decreases the positive-reinforcing effects of cocaine. Drug Alcohol Depend 98:129–135
Smith MA, Walker KL, Cole KT, Lang KC (2011) The effects of aerobic exercise on cocaine self-administration in male and female rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 218:357–369
Smith MA, Pennock MM, Walker KL, Lang KC (2012) Access to a running wheel decreases cocaine-primed and cue-induced reinstatement in male and female rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 121:54–61
Van Hoomissen JD, Holmes PV, Zellner AS, Poudevigne A, Dishman RK (2004) Effects of beta-adrenoreceptor blockade during chronic exercise on contextual fear conditioning and mRNA for galanin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Behav Neurosci 118:1378–1390
Veale D, Le Fevre K, Pantelis C, de Souza V, Mann A, Sargeant A (1992) Aerobic exercise in the adjunctive treatment of depression: a randomized controlled trial. J R Soc Med 85:541–544
Ventura R, Morrone C, Puglisi-Allegra S (2007) Prefrontal/accumbal catecholamine system determines motivational salience attribution to both reward- and aversion-related stimuli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:5181–5186
Vila-Porcile E, Xu ZQ, Mailly P, Nagy F, Calas A, Hokfelt T, Landry M (2009) Dendritic synthesis and release of the neuropeptide galanin: morphological evidence from studies on rat locus coeruleus neurons. J Comp Neurol 516:199–212
Weinshenker D, Schroeder JP (2007) There and back again: a tale of norepinephrine and drug addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1433–1451
Weinstock J, Barry D, Petry NM (2008) Exercise-related activities are associated with positive outcome in contingency management treatment for substance use disorders. Addict Behav 33:1072–1075
Weiss JM, Boss-Williams KA, Moore JP, Demetrikopoulos MK, Ritchie JC, West CH (2005) Testing the hypothesis that locus coeruleus hyperactivity produces depression-related changes via galanin. Neuropeptides 39:281–287
Xu ZQ, Zheng K, Hokfelt T (2005) Electrophysiological studies on galanin effects in brain—progress during the last six years. Neuropeptides 39:269–275
Zachariou V, Brunzell DH, Hawes J, Stedman DR, Bartfai T, Steiner RA, Wynick D, Langel U, Picciotto MR (2003) The neuropeptide galanin modulates behavioral and neurochemical signs of opiate withdrawal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:9028–9033
Zhang XY, Kosten TA (2005) Prazosin, an alpha-1 adrenergic antagonist, reduces cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking. Biol Psychiatry 57:1202–1204
Zlebnik NE, Anker JJ, Gliddon LA, Carroll ME (2010) Reduction of extinction and reinstatement of cocaine seeking by wheel running in female rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 209:113–125
Zlebnik NE, Anker JJ, Carroll ME (2012) Exercise to reduce the escalation of cocaine self-administration in adolescent and adult rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 224:387–400
Zlebnik NE, Hedges VL, Carroll ME, Meisel RL (2014) Chronic wheel running affects cocaine-induced c-Fos expression in brain reward areas in rats. Behav Brain Res 261:71–78
Acknowledgments
We thank Cheryl Strauss for the helpful editing of the manuscript. This work was supported by the National Institute of Drug Abuse (DA027535 to DW and PVH, DA033091 and DA015040 to YEO).
Conflict of interest
DW is co-inventor on a patent concerning the use of selective dopamine β-hydroxylase inhibitors for the treatment of cocaine dependence (US-2010-0105748-A1; “Methods and Compositions for Treatment of Drug Addiction”). The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogbonmwan, Y.E., Schroeder, J.P., Holmes, P.V. et al. The effects of post-extinction exercise on cocaine-primed and stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 232, 1395–1403 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3778-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3778-9