Abstract
Rationale
Discrepancies in an expected outcome have been demonstrated to result in modification of behaviour in both appetitive and aversive conditioning settings.
Objectives
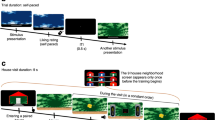
In this study, we sought to establish whether overexpectation generated from compound conditioning with two previously rewarded stimuli was able to induce memory destabilisation and subsequent reconsolidation in a Pavlovian conditioned approach setting.
Results
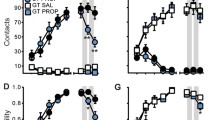
It was shown that 4 days, but not 1 day, of overexpectation training was required to induce memory reconsolidation, and this was disrupted by application of the NMDA subtype of glutamate receptor antagonist MK-801 prior to overexpectation training, but not by MK-801 application 6 h post-training.
Conclusions
These data provide evidence that the memories underlying Pavlovian conditioned approach do undergo reconsolidation and that such reconsolidation can be triggered by overexpectation. Therefore, the updating of appetitive conditioned stimulus and unconditioned stimulus associations underpinning conditioned responding in manners other than extinction training is likely achieved through memory reconsolidation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberini CM (2005) Mechanisms of memory stabilization: are consolidation and reconsolidation similar or distinct processes? Trends Neurosci 28:51–56
Blaiss CA, Janak PH (2007) Post-training, but not post-reactivation, administration of amphetamine and anisomycin modulates Pavlovian conditioned approach. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87(4):644–658
Ceretta AP, Camera K, Mello CF, Rubin MA (2008) Arcaine and MK-801 make recall state-dependent in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 201:405–411
Debiec J, Doyere V, Nader K, LeDoux JE (2006) Directly reactivated, but not indirectly reactivated, memories undergo reconsolidation in the amygdala. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:3428–3433
Duvarci S, Nader K (2004) Characterization of fear memory reconsolidation. J Neurosci 24:9269–9275
Flavell CR, Barber DJ, Lee JL (2011) Behavioural memory reconsolidation of food and fear memories. Nat Commun 2:504
Fricks-Gleason AN, Marshall JF (2008) Post-retrieval beta-adrenergic receptor blockade: effects on extinction and reconsolidation of cocaine-cue memories. Learn Mem 15:643–648
Garfield JB, McNally GP (2009) The effects of FG7142 on overexpectation of Pavlovian fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci 123:75–85
Huh KH, Guzman YF, Tronson NC, Guedea AL, Gao C, Radulovic J (2009) Hippocampal Erk mechanisms linking prediction error to fear extinction: roles of shock expectancy and contextual aversive valence. Learn Mem 16:273–278
Kelley BJ, Yeager KR, Pepper TH, Bornstein RA, Beversdorf DQ (2007) The effect of propranolol on cognitive flexibility and memory in acute cocaine withdrawal. Neurocase 13:320–327
Lattal K, Nakajima S (1998) Overexpectation in appetitive Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning. Learn Behav 26:351–360
Lee H, Kim JJ (1998) Amygdalar NMDA receptors are critical for new fear learning in previously fear-conditioned rats. J Neurosci 18:8444–8454
Lee JL (2008) Memory reconsolidation mediates the strengthening of memories by additional learning. Nat Neurosci 11:1264–1266
Lee JL (2009) Reconsolidation: maintaining memory relevance. Trends Neurosci 32:413–420
Lee JL, Everitt BJ (2008) Appetitive memory reconsolidation depends upon NMDA receptor-mediated neurotransmission. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:147–154
Lee JL, Milton AL, Everitt BJ (2006a) Cue-induced cocaine seeking and relapse are reduced by disruption of drug memory reconsolidation. J neurosci: Offl J Soc Neurosci 26:5881–5887
Lee JL, Milton AL, Everitt BJ (2006b) Reconsolidation and extinction of conditioned fear: inhibition and potentiation. J neurosci: Offl J Soc Neurosci 26:10051–10056
Mark RF, Watts ME (1971) Drug inhibition of memory formation in chickens I. Long-term memory. Proc Roy Soc Lond B Biol Sci 178:439–454
Milekic MH, Alberini CM (2002) Temporally graded requirement for protein synthesis following memory reactivation. Neuron 36:521–525
Milekic MH, Brown SD, Castellini C, Alberini CM (2006) Persistent disruption of an established morphine conditioned place preference. J Neurosci 26:3010–3020
Milton AL, Lee JL, Everitt BJ (2008) Reconsolidation of appetitive memories for both natural and drug reinforcement is dependent on {beta}-adrenergic receptors. Learn Mem 15:88–92
Milton AL, Schramm MJ, Wawrzynski JR, Gore F, Oikonomou-Mpegeti F, Wang NQ, Samuel D, Economidou D, Everitt BJ (2012) Antagonism at NMDA receptors, but not beta-adrenergic receptors, disrupts the reconsolidation of pavlovian conditioned approach and instrumental transfer for ethanol-associated conditioned stimuli. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 219:751–761
Monfils MH, Cowansage KK, Klann E, LeDoux JE (2009) Extinction-reconsolidation boundaries: key to persistent attenuation of fear memories. Science 324:951–955
Nader K, Hardt O (2009) A single standard for memory: the case for reconsolidation. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:224–234
Nader K, Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (2000) The labile nature of consolidation theory. Nat Rev Neurosci 1:216–219
Pan WX, Schmidt R, Wickens JR, Hyland BI (2008) Tripartite mechanism of extinction suggested by dopamine neuron activity and temporal difference model. J neurosci: Offl J Soc Neurosci 28:9619–9631
Przybyslawski J, Sara SJ (1997) Reconsolidation of memory after its reactivation. Behav Brain Res 84:241–246
Rescorla RA (1970) Reduction in effectiveness of reinforcement after prior excitatory conditioning. Learn Motiv 1:372–381
Rescorla RA (2006) Spontaneous recovery from overexpectation. Learn Behav 34:13–20
Rescorla RA (2007) Spontaneous recovery after reversal and partial reinforcement. Learn Behav 35:191–200
Sadler R, Herzig V, Schimdt WJ (2007) Repeated treatment with the NMDA antagonist MK-801 disrupts reconsolidation of memory for amphetamine-conditioned place preference. Behav Pharmacol 18:699–703
Santini E, Muller RU, Quirk GJ (2001) Consolidation of extinction learning involves transfer from NMDA-independent to NMDA-dependent memory. J Neurosci 21:9009–9017
Schiller D, Monfils MH, Raio CM, Johnson DC, Ledoux JE, Phelps EA (2010) Preventing the return of fear in humans using reconsolidation update mechanisms. Nature 463:49–53
Takahashi YK, Roesch MR, Stalnaker TA, Haney RZ, Calu DJ, Taylor AR, Burke KA, Schoenbaum G (2009) The orbitofrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area are necessary for learning from unexpected outcomes. Neuron 62:269–280
Witnauer JE, Miller RR (2009) Contrasting the overexpectation and extinction effects. Behav Process 81:322–327
Xue Y-X, Luo Y-X, Wu P, Shi H-S, Xue L-F, Chen C, Zhu W-L, Ding Z-B, Y-p B, Shi J, Epstein DH, Shaham Y, Lu L (2012) A memory retrieval-extinction procedure to prevent drug craving and relapse. Science 336:241–245
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by funds from the Leverhulme Trust Grant F/00 094/BK awarded to JL. We wish to thank Mr David Barber for his assistance with data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reichelt, A.C., Lee, J.L. Over-expectation generated in a complex appetitive goal-tracking task is capable of inducing memory reconsolidation. Psychopharmacology 226, 649–658 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2934-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2934-3