Abstract
Rationale
F13640 (befiradol) is a novel 5-HT1A receptor agonist with exceptional selectivity vs. other receptors and binding sites. It shows analgesic activity in animal models and is currently developed for human use.
Objectives
Given the potential dual role of the serotonergic system in pain, through the modulation of ascending signals in spinal cord and their emotional processing by corticolimbic areas, we examined the in vivo activity of F13640 at somatodendritic autoreceptors and postsynaptic 5-HT1A heteroreceptors in medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC).
Methods
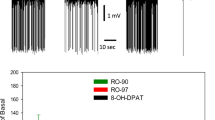
In vivo single unit recordings and intracerebral microdialysis in the rat.
Results
F13640 reduced the activity of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons at 0.2–18.2 μg kg−1, i.v. (cumulative doses; ED50 = 0.69 μg kg−1, i.v.) and increased the discharge rate of 80% of mPFC pyramidal neurons in the same dose range (ED50 = 0.62 μg kg−1, i.v.). Both effects were reversed by the subsequent administration of the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist (±)WAY100635. In microdialysis studies, F13640 (0.04–0.63 mg kg−1, i.p.) dose-dependently decreased extracellular 5-HT in the hippocampus and mPFC. Likewise, F13640 (0.01–2.5 mg kg−1, i.p.) dose-dependently increased extracellular DA in mPFC, an effect dependent on the activation of postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in mPFC. Local perfusion of F13640 in mPFC (1–1,000 μM) also increased extracellular DA in a concentration-dependent manner. Both the systemic and local effects of F13640 were prevented by prior (±)WAY100635 administration.
Conclusions
These results indicate that, upon systemic administration, F13640 activates both 5-HT1A autoreceptors and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in prefrontal cortex with a similar potency. Both activities are likely involved in the analgesic properties of the compound.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- DR:
-
Dorsal raphe nucleus
- F13640:
-
[(3-Chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-[4-fluoro-4-{[(5-methyl-pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-amino]-methyl}piperidin-1-yl]methanone Fumaric acid salt
- mPFC:
-
Medial prefrontal cortex
References
Adell A, Carceller A, Artigas F (1993) In vivo brain dialysis study of the somatodendritic release of serotonin in the Raphe nuclei of the rat: effects of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin. J Neurochem 60:1673–1681
Akimova E, Lanzenberger R, Kasper S (2009) The serotonin-1A receptor in anxiety disorders. Biol Psychiatry 66:627–635
Albert PS (1999) Longitudinal data analysis (repeated measures) in clinical trials. Stat Med 18:1707–1732
Amargos-Bosch M, Bortolozzi A, Puig MV, Serrats J, Adell A, Celada P, Toth M, Mengod G, Artigas F (2004) Co-expression and in vivo interaction of serotonin1A and serotonin2A receptors in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 14:281–299
Andrade R, Nicoll RA (1987) Pharmacologically distinct actions of serotonin on single pyramidal neurones of the rat hippocampus recorded in vitro. J Physiol 394:99–124
Araneda R, Andrade R (1991) 5-Hydroxytryptamine2 and 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors mediate opposing responses on membrane excitability in rat association cortex. Neuroscience 40:399–412
Ashby CR Jr, Edwards E, Wang RY (1994) Electrophysiological evidence for a functional interaction between 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors in the rat medial prefrontal cortex: an iontophoretic study. Synapse 17:173–181
Assie MB, Lomenech H, Ravailhe V, Faucillon V, Newman-Tancredi A (2006) Rapid desensitization of somatodendritic 5-HT1A receptors by chronic administration of the high-efficacy 5-HT1A agonist, F13714: a microdialysis study in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 149:170–178
Assie MB, Ravailhe V, Faucillon V, Newman-Tancredi A (2005) Contrasting contribution of 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor activation to neurochemical profile of novel antipsychotics: frontocortical dopamine and hippocampal serotonin release in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:265–272
Bardin L, Assie MB, Pelissou M, Royer-Urios I, Newman-Tancredi A, Ribet JP, Sautel F, Koek W, Colpaert FC (2005) Dual, hyperalgesic, and analgesic effects of the high-efficacy 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A (5-HT1A) agonist F 13640 [(3-chloro-4-fluoro-phenyl)-[4-fluoro-4-{[(5-methyl-pyridin-2-ylmethyl)-am ino]-methyl}piperidin-1-yl]methanone, fumaric acid salt]: relationship with 5-HT1A receptor occupancy and kinetic parameters. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:1034–1042
Bardin L, Colpaert FC (2004) Role of spinal 5-HT(1A) receptors in morphine analgesia and tolerance in rats. Eur J Pain 8:253–261
Bardin L, Tarayre JP, Koek W, Colpaert FC (2001) In the formalin model of tonic nociceptive pain, 8-OH-DPAT produces 5-HT1A receptor-mediated, behaviorally specific analgesia. Eur J Pharmacol 421:109–114
Bardin L, Tarayre JP, Malfetes N, Koek W, Colpaert FC (2003) Profound, non-opioid analgesia produced by the high-efficacy 5-HT(1A) agonist F 13640 in the formalin model of tonic nociceptive pain. Pharmacology 67:182–194
Blier P, de Montigny C (1987) Modification of 5-HT neuron properties by sustained administration of the 5-HT1A agonist gepirone: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Synapse 1:470–480
Blier P, Ward NM (2003) Is there a role for 5-HT1A agonists in the treatment of depression? Biol Psychiatry 53:193–203
Borsini F, Ceci A, Bietti G, Donetti A (1995) BIMT 17, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist/5-HT2A receptor antagonist, directly activates postsynaptic 5-HT inhibitory responses in the rat cerebral cortex. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 352:283–290
Bortolozzi A, Diaz-Mataix L, Toth M, Celada P, Artigas F (2007) In vivo actions of aripiprazole on serotonergic and dopaminergic systems in rodent brain. Psychopharmacology 191:745–758
Briley M (2004) Clinical experience with dual action antidepressants in different chronic pain syndromes. Hum Psychopharmacol 19(Suppl 1):S21–S25
Bruins Slot LA, Koek W, Tarayre JP, Colpaert FC (2003) Tolerance and inverse tolerance to the hyperalgesic and analgesic actions, respectively, of the novel analgesic, F 13640. Eur J Pharmacol 466:271–279
Buritova J, Berrichon G, Cathala C, Colpaert F, Cussac D (2009) Region-specific changes in 5-HT1A agonist-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 phosphorylation in rat brain: a quantitative ELISA study. Neuropharmacology 56:350–361
Casanovas JM, Berton O, Celada P, Artigas F (2000) In vivo actions of the selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist BAY x 3702 on serotonergic cell firing and release. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 362:248–254
Celada P, Puig MV, Casanovas JM, Guillazo G, Artigas F (2001) Control of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons by the medial prefrontal cortex: involvement of serotonin-1A, GABA(A), and glutamate receptors. J Neurosci 21:9917–9929
Colpaert FC (2006) 5-HT(1A) receptor activation: new molecular and neuroadaptive mechanisms of pain relief. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 7:40–47
Colpaert FC, Tarayre JP, Koek W, Pauwels PJ, Bardin L, Xu XJ, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Cosi C, Carilla-Durand E, Assie MB, Vacher B (2002) Large-amplitude 5-HT1A receptor activation: a new mechanism of profound, central analgesia. Neuropharmacology 43:945–958
Cox RF, Meller E, Waszczak BL (1993) Electrophysiological evidence for a large receptor reserve for inhibition of dorsal raphe neuronal firing by 5-HT1A agonists. Synapse 14:297–304
Cruz DA, Eggan SM, Azmitia EC, Lewis DA (2004) Serotonin1A receptors at the axon initial segment of prefrontal pyramidal neurons in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 161:739–742
Diaz-Mataix L, Artigas F, Celada P (2006) Activation of pyramidal cells in rat medial prefrontal cortex projecting to ventral tegmental area by a 5-HT1A receptor agonist. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16:288–296
Diaz-Mataix L, Scorza MC, Bortolozzi A, Toth M, Celada P, Artigas F (2005) Involvement of 5-HT1A receptors in prefrontal cortex in the modulation of dopaminergic activity: role in atypical antipsychotic action. J Neurosci 25:10831–10843
Dong J, de Montigny C, Blier P (1997) Effect of acute and repeated versus sustained administration of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist ipsapirone: electrophysiological studies in the rat hippocampus and dorsal raphe. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 356:303–311
Dong J, de Montigny C, Blier P (1998) Full agonistic properties of BAY x 3702 on presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors electrophysiological studies in the rat hippocampus and dorsal raphe. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:1239–1247
Hajos M, Hajos-Korcsok E, Sharp T (1999) Role of the medial prefrontal cortex in 5-HT1A receptor-induced inhibition of 5-HT neuronal activity in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 126:1741–1750
Hestrin S, Galarreta M (2005) Electrical synapses define networks of neocortical GABAergic neurons. Trends Neurosci 28:304–309
Hoyer D, Boddeke HW (1993) Partial agonists, full agonists, antagonists: dilemmas of definition. Trends Pharmacol Sci 14:270–275
Hutson PH, Sarna GS, O’Connell MT, Curzon G (1989) Hippocampal 5-HT synthesis and release in vivo is decreased by infusion of 8-OHDPAT into the nucleus raphe dorsalis. Neurosci Lett 100:276–280
Innis RB, Aghajanian GK (1987) Pertussis toxin blocks 5-HT1A and GABAB receptor-mediated inhibition of serotonergic neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 143:195–204
Kargieman L, Santana N, Mengod G, Celada P, Artigas F (2007) Antipsychotic drugs reverse the disruption in prefrontal cortex function produced by NMDA receptor blockade with phencyclidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14843–14848
Kia HK, Miquel MC, Brisorgueil MJ, Daval G, Riad M, El Mestikawy S, Hamon M, Verge D (1996) Immunocytochemical localization of serotonin1A receptors in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 365:289–305
Kleven MS, Assié MB, Cosi C, Barret-Grévoz C, Newman-Tancredi A (2005) Anticataleptic properties of alpha2 adrenergic antagonists in the crossed leg position and bar tests: differential mediation by 5-HT1A receptor activation. Psychopharmacology 177(4):373–380
Laviolette SR, Lipski WJ, Grace AA (2005) A subpopulation of neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex encodes emotional learning with burst and frequency codes through a dopamine D4 receptor-dependent basolateral amygdala input. J Neurosci 25:6066–6075
Llado-Pelfort L, Assie MB, Newman-Tancredi A, Artigas F, Celada P (2010) Preferential in vivo action of F15599, a novel 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist, at postsynaptic 5-HT(1A) receptors. Br J Pharmacol 160:1929–1940
Lladó-Pelfort L, Santana N, Ghisi V, Artigas F, Celada P (2011) 5-HT1A receptor agonists enhance pyramidal cell firing in prefrontal cortex through a preferential action on GABA interneurons. Cereb Cortex (online publication) Sept. 5; PMID: 21893679
Martinez D, Hwang D, Mawlawi O, Slifstein M, Kent J, Simpson N, Parsey RV, Hashimoto T, Huang Y, Shinn A, Van Heertum R, Abi-Dargham A, Caltabiano S, Malizia A, Cowley H, Mann JJ, Laruelle M (2001) Differential occupancy of somatodendritic and postsynaptic 5HT(1A) receptors by pindolol: a dose-occupancy study with [11 C]WAY 100635 and positron emission tomography in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:209–229
McQuade R, Sharp T (1997) Functional mapping of dorsal and median raphe 5-hydroxytryptamine pathways in forebrain of the rat using microdialysis. J Neurochem 69:791–796
Meller E, Goldstein M, Bohmaker K (1990) Receptor reserve for 5-hydroxytryptamine1A-mediated inhibition of serotonin synthesis: possible relationship to anxiolytic properties of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A agonists. Mol Pharmacol 37:231–237
Mico JA, Berrocoso E, Ortega-Alvaro A, Gibert-Rahola J, Rojas-Corrales MO (2006) The role of 5-HT1A receptors in research strategy for extensive pain treatment. Curr Top Med Chem 6:1997–2003
Millan MJ, Colpaert FC (1990) Attenuation of opioid induced antinociception by 5-HT1A partial agonists in the rat. Neuropharmacology 29:315–318
Myers JL, Well AD (1995) Research design and statistical analysis. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ
Newman-Tancredi A (2010) The importance of 5-HT1A receptor agonism in antipsychotic drug action: rationale and perspectives. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 11:802–812
Newman-Tancredi A, Martel JC, Assie MB, Buritova J, Lauressergues E, Cosi C, Heusler P, Bruins SL, Colpaert FC, Vacher B, Cussac D (2009) Signal transduction and functional selectivity of F15599, a preferential post-synaptic 5-HT1A receptor agonist. Br J Pharmacol 156:338–353
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Sydney
Pazos A, Palacios JM (1985) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain: I. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res 346:205–230
Pompeiano M, Palacios JM, Mengod G (1992) Distribution and cellular localization of mRNA coding for 5-HT1A receptor in the rat brain: correlation with receptor binding. J Neurosci 12:440–453
Puig MV, Artigas F, Celada P (2005) Modulation of the activity of pyramidal neurons in rat prefrontal cortex by raphe stimulation in vivo: involvement of serotonin and GABA. Cereb Cortex 15:1–14
Puig MV, Celada P, Diaz-Mataix L, Artigas F (2003) In vivo modulation of the activity of pyramidal neurons in the rat medial prefrontal cortex by 5-HT2A receptors: relationship to thalamocortical afferents. Cereb Cortex 13:870–882
Rea K, Folgering J, Westerink BH, Cremers TI (2010) Alpha1-adrenoceptors modulate citalopram-induced serotonin release. Neuropharmacology 58(7):962–971
Riad M, Garcia S, Watkins KC, Jodoin N, Doucet E, Langlois X, El Mestikawy S, Hamon M, Descarries L (2000) Somatodendritic localization of 5-HT1A and preterminal axonal localization of 5-HT1B serotonin receptors in adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol 417:181–194
Romero L, Celada P, Martin-Ruiz R, Diaz-Mataix L, Mourelle M, Delgadillo J, Hervas I, Artigas F (2003) Modulation of serotonergic function in rat brain by VN2222, a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and 5-HT1A receptor agonist. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:445–456
Rueter LE, Blier P (1999) Electrophysiological examination of the effects of sustained flibanserin administration on serotonin receptors in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol 126:627–638
Santana N, Bortolozzi A, Serrats J, Mengod G, Artigas F (2004) Expression of serotonin1A and serotonin2A receptors in pyramidal and GABAergic neurons of the rat prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 14:1100–1109
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1987) Electrophysiological responses of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse 1:3–9
Sprouse JS, Aghajanian GK (1988) Responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to putative serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists: a comparative study with dorsal raphe neurons. Neuropharmacology 27:707–715
Vacher B, Bonnaud B, Funes P, Jubault N, Koek W, Assie MB, Cosi C, Kleven M (1999) Novel derivatives of 2-pyridinemethylamine as selective, potent, and orally active agonists at 5-HT1A receptors. J Med Chem 42:1648–1660
Valdizan EM, Castro E, Pazos A (2010) Agonist-dependent modulation of G-protein coupling and transduction of 5-HT1A receptors in rat dorsal raphe nucleus. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13:835–843
Wang RY, Aghajanian GK (1977) Antidromically identified serotonergic neurons in the rat midbrain raphe: evidence for collateral inhibition. Brain Res 132:186–193
Westerink BHC (1995) Brain microdialysis and its application for the study of animal behaviour. Behav Brain Res 70:103–124
Xu XJ, Colpaert F, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z (2003) Opioid hyperalgesia and tolerance versus 5-HT1A receptor-mediated inverse tolerance. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:634–639
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants SAF 2007–62378, FIS PI060264, FIS PI09/1245 (PN I + D + I 2008–2011, ISCIII-Subdirección General de Investigación y Fomento de la Investigación), Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Salud Mental, CIBERSAM and Pierre Fabre Médicament. L.L.-P. was supported by a JAE fellowship from CSIC. P.C. is supported by the Researcher Stabilization Program of the Health Department of the Generalitat de Catalunya. L.L-P. and P.C. declare no conflict of interest. F.A. received lecture fees from Pierre Fabre Médicament. A.N.-T. and M.B.A. were employees of Pierre Fabre Médicament at the time of realization of the studies and were involved in the experimental design and microdialysis data interpretation. We acknowledge Véronique Ravailhe and Christelle Benas for technical assistance with microdialysis experiments and Mónica Gutiérrez and Verónica Paz for electrophysiological experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lladó-Pelfort, L., Assié, MB., Newman-Tancredi, A. et al. In vivo electrophysiological and neurochemical effects of the selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist, F13640, at pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in the rat. Psychopharmacology 221, 261–272 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2569-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2569-9