Abstract
Rationale
A few recent studies suggest that brain histamine levels and signaling via H3 receptors play an important role in modulation of alcohol stimulation and reward in rodents.
Objective
The present study characterized the effects of a novel, selective, and brain penetrant H3 receptor antagonist (JNJ-39220675) on the reinforcing effects of alcohol in rats.
Methods
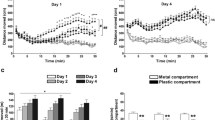
The effect of JNJ-39220675 on alcohol intake and alcohol relapse-like behavior was evaluated in selectively bred alcohol-preferring (P) rats using the standard two-bottle choice method. The compound was also tested on operant alcohol self administration in non-dependent rats and on alcohol-induced ataxia using the rotarod apparatus. In addition, alcohol-induced dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens was tested in freely moving rats.
Results
Subcutaneous administration of the selective H3 receptor antagonist dose-dependently reduced both alcohol intake and preference in alcohol-preferring rats. JNJ-39220675 also reduced alcohol preference in the same strain of rats following a 3-day alcohol deprivation. The compound significantly and dose-dependently reduced alcohol self-administration without changing saccharin self-administration in alcohol non-dependent rats. Furthermore, the compound did not change the ataxic effects of alcohol, alcohol elimination rate, nor alcohol-induced dopamine release in nucleus accumbens.
Conclusions
These results indicate that blockade of H3 receptor should be considered as a new attractive mechanism for the treatment of alcoholism.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anichtchik OV, Peitsaro N, Rinne JO, Kalimo H, Panula P (2001) Distribution and modulation of histamine H3 receptors in basal ganglia and frontal cortex of healthy controls and patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 8:707–716
Barbier AJ, Aluisio L, Lord B, Qu Y, Wilson SJ, Boggs JD, Bonaventure P, Miller K, Fraser I, Dvorak L, Pudiak C, Dugovic C, Shelton J, Mazur C, Letavic MA, Carruthers NI, Lovenberg TW (2007) Pharmacological characterization of JNJ-28583867, a histamine H3 receptor antagonist and serotonin reuptake inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 576:43–54
Bonaventure P, Kelly L, Aluisio L, Shelton J, Lord B, Galici R, Miller K, Atack J, Lovenberg TW, Dugovic C (2007) Selective blockade of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)7 receptors enhances 5-HT transmission, antidepressant-like behavior, and rapid eye movement sleep suppression induced by citalopram in rodents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:690–698
Doreulee N, Yanovsky Y, Flagmeyer I, Stevens DR, Haas HL, Brown RE (2000) Histamine H3 receptors depress synaptic transmission in the corticostriatal pathway. Neuropharmacology 40:106–113
Dugovic C, Shelton JE, Aluisio LE, Fraser IC, Jiang X, Sutton SW, Bonaventure P, Yun S, Li X, Lord B, Dvorak CA, Carruthers NI, Lovenberg TW (2009) Blockade of orexin-1 receptors attenuates orexin-2 receptor antagonism-induced sleep promotion in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330:142–151
Esbenshade TA, Browman KE, Bitner RS, Strakhova M, Cowart MD, Brioni JD (2009) The histamine H3 receptor: an attractive target for the treatment of cognitive disorders. Br J Pharmacol 154:1166–1181
Ferrada C, Ferré S, Casadó V, Cortés A, Justinova Z, Barnes C, Canela EI, Goldberg SR, Leurs R, Lluis C, Franco R (2008) Interactions between histamine H3 and dopamine D2 receptors and the implications for striatal function. Neuropharmacology 55:190–197
Galici R, Boggs JD, Aluisio L, Fraser IC, Bonaventure P, Lord B, Lovenberg TW (2009) JNJ-10181457, a selective non-imidazole histamine H3 receptor antagonist, normalizes acetylcholine neurotransmission and has efficacy in translational rat models of cognition. Neuropharmacology 56:1131–1137
Garbutt JC (2009) The state of pharmacotherapy for the treatment of alcohol dependence. J Subst Abuse Treat 36:S15–S23, quiz S24-5
Garcia M, Floran B, Arias-Montano JA, Young JM, Aceves J (1997) Histamine H3 receptor activation selectively inhibits dopamine D1 receptor-dependent [3H] GABA release from depolarization-stimulated slices of rat substantia nigra pars reticulata. Neurosci Oxf 80:241–249
George FK, Amanda JR, Gery S, Loren HP, Charles JH, Petri H, Emilio M-P, Friedbert W (1998) Neurocircuitry targets in ethanol reward and dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:3–9
Haas H, Panula P (2003) The role of histamine and the tuberomamillary nucleus in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:121–130
Heilig M, Egli M (2006) Pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence: target symptoms and target mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 111:855–876
Huston JP, Wagner U, Hasenohrl RU (1997) The tuberomammillary nucleus projections in the control of learning, memory and reinforcement processes: evidence for an inhibitory role. Behav Brain Res 83:97–105
Imperato A, Di Chiara G (1986) Preferential stimulation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats by ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 239:219–228
Johnson BA (2008) Update on neuropharmacological treatments for alcoholism: scientific basis and clinical findings. Biochem Pharmacol 75:34–56
Letavic MA, Aluisio L, Atack JR, Bonaventure P, Carruthers NI, Dugovic C, Everson A, Feinstein MA, Fraser IC, Hoey K, Jiang X, Keith JM, Koudriakova T, Leung P, Lord B, Lovenberg TW, Ly KS, Morton KL, Motley ST, Nepomuceno D, Rizzolio M, Rynberg R, Sepassi K, Shelton J (2010) Pre-clinical characterization of aryloxypyridine amides as histamine H3 receptor antagonists: identification of candidates for clinical development. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:4210–4214
Lintunen M, Hyytiä P, Sallmen T, Karlstedt K, Tuomisto L, Leurs R, Kiianmaa K, Korpi ER, Panula P (2001) Increased brain histamine in an alcohol-preferring rat line, and modulation of ethanol consumption by H3 receptor mechanisms. FASEB J 15:1074–1076
Lintunen M, Raatesalmi K, Sallmen T, Anichtchik O, Karlstedt K, Kaslin J, Kiianmaa K, Korpi ER, Panula P (2002) Low brain histamine content affects ethanol-induced motor impairment. Neurobiol Dis 9:94–105
Molina-Hernandez A, Nunez A, Sierra J-J, Arias-Montano J-A (2001) Histamine H3 receptor activation inhibits glutamate release from rat striatal synaptosomes. Neuropharmacology 41:928–934
Nuutinen S, Karlstedt K, Aitta-Aho T, Korpi ER, Panula P (2009) Histamine and H3 receptor-dependent mechanisms regulate ethanol stimulation and conditioned place preference in mice. Psychopharmacology 208:75–86
Nuutinen S, Karlstedt K, Aitta-Aho T, Korpi ER, Panula P (2010) Histamine and H3 receptor-dependent mechanisms regulate ethanol stimulation and conditioned place preference in mice. Psychopharmacology 208:75–86
Overstreet DH, Rezvani AH, Parsian A (1999) Behavioral features of alcohol-preferring rats: focus on inbred strains. Alcohol Alcohol 34:378–385
Panula P, Hyytia P, Karlstedt K, Kaslin J, Kiianmaa K, Lintunen M (2008). Histamine H3 receptor confers alcohol intake in rodents. Annual Meeting Society for Neuroscience, Washington DC
Paxinos G, Watson C (1997) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd Edn. Academic Press, New York
Pillot C, Heron A, Cochois V, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Ligneau X, Schwartz JC, Arrang JM (2002) A detailed mapping of the histamine H3 receptor and its gene transcripts in rat brain. Neuroscience 114:173–193, Oxford, United Kingdom
Pollard H, Moreau J, Arrang JM, Schwartz JC (1993) A detailed autoradiographic mapping of histamine H3 receptors in rat brain areas. Neuroscience 52:169–189
Rezvani AH, Overstreet DH, Mason GA, Janowsky DS, Hamedi M, Clark E Jr, Yang Y (2000) Combination pharmacotherapy: a mixture of small doses of naltrexone, fluoxetine, and a thyrotropin-releasing hormone analogue reduces alcohol intake in three strains of alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Alcohol 35:76–83
Rezvani AH, Overstreet DH, Levin ED, Rosenthal DI, Kordik CP, Reitz AB, Vaidya AH (2007) Effects of atypical anxiolytic N-phenyl-2-[1-[3-(2-pyridinylethynyl)benzoyl]-4-piperidine]acetamide (JNJ-5234801) on alcohol intake in alcohol-preferring P rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:57–63
Rezvani AH, Overstreet DH, Vaidya AH, Zhao B, Levin ED (2009) Carisbamate, a novel antiepileptic candidate compound, attenuates alcohol intake in alcohol-preferring rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1366–1373
Rezvani AH, Slade S, Wells C, Petro A, Lumeng L, Li TK, Xiao Y, Brown ML, Paige MA, McDowell BE, Rose JE, Kellar KJ, Levin ED (2010) Effects of sazetidine-A, a selective alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor desensitizing agent on alcohol and nicotine self-administration in selectively bred alcohol-preferring (P) rats. Psychopharmacology 211:161–174
Richard LB, Zachary AR, Lawrence L, James MM, William JM (2006) The alcohol-preferring P rat and animal models of excessive alcohol drinking. Addict Biol 11:270–288
Ryu JH, Yanai K, Iwata R, Ido T, Watanabe T (1994) Heterogeneous distributions of histamine H3, dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in rat brain. NeuroReport 5:621–624
Schlicker E, Fink K, Detzner M, Goethert M (1993) Histamine inhibits dopamine release in the mouse striatum via presynaptic H3 receptors. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 93:1–10
Spanagel R (2003) Alcohol addiction research: from animal models to clinics. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 17:507–518
Vocci FJ, Acri J, Elkashef A (2005) Medication development for addictive disorders: the state of the science. Am J Psychiatry 162:1432–1440
Wagner U, Segura-Torres P, Weiler T, Huston JP (1993) The tuberomammillary nucleus region as a reinforcement inhibiting substrate: facilitation of ipsihypothalamic self-stimulation by unilateral ibotenic acid lesions. Brain Res 613:269–274
Witkin JM, Nelson DL (2004) Selective histamine H3 receptor antagonists for treatment of cognitive deficiencies and other disorders of the central nervous system. Pharmacol Ther 103:1–20
Acknowledgements
The assistance of Dr. Kevin Sharp and his staff at Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development L.L.C. (San Diego, CA) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galici, R., Rezvani, A.H., Aluisio, L. et al. JNJ-39220675, a novel selective histamine H3 receptor antagonist, reduces the abuse-related effects of alcohol in rats. Psychopharmacology 214, 829–841 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2092-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2092-4