Abstract
Rationale
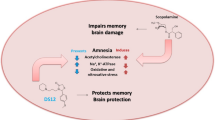
Dimethylaminoethanol pyroglutamate (DMAE p-Glu) is a compound resulting from the reaction between dimethylaminoethanol (an indirect precursor of acetylcholine) and pyroglutamic acid (a cyclic derivative of glutamic acid having procholinergic properties and promnesic effects in both animals and man).
Objectives
The present study undertook preclinical and clinical evaluations to test a potential therapeutic utility for DMAE p-Glu in cognitive impairments related to central cholinergic deficit.
Materials and methods
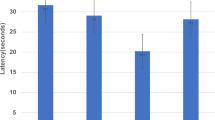
In preclinical study, DMAE p-Glu was studied in rats by intracerebral microdialysis in conscious freely moving animals, on performance of rats in the Morris water maze test of spatial memory, and on the deficit in passive avoidance behavior induced by scopolamine. The clinical study examined the effect of DMAE p-Glu on cognitive deficits induced by an intravenous injection of scopolamine in healthy young male subjects.
Results
In rat experiments, DMAE p-Glu increased the extracellular levels of choline and acetylcholine in the medial prefrontal cortex, as assessed by intracerebral microdialysis, improved performance in a test of spatial memory, and reduced scopolamine-induced memory deficit in passive avoidance behavior. Clinical study results show that scopolamine induced a memory deficit and that DMAE p-Glu produced a significant positive effect on scores in the Buschke test, as well as a slight but significant difference on choice reaction time.
Conclusion
These results indicate that DMAE p-Glu reduces the deleterious effect of scopolamine on long-term memory in healthy volunteers and suggest that DMAE p-Glu might be effective in reducing memory deficits in patients with cognitive impairment.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonelli T, Carlà V, Lambertini L, Moroni F, Bianchi C (1984) Pyroglutamic acid administration modifies the electrocorticogram and increases the release of acetylcholine and GABA from the guinea-pig cerebral cortex. Pharmacol Res Commun 16:189–197
Bond A, Lader M (1974) The use of analogue scales in rating subjective feelings. Br J Med Psychol 47:211–218
Bozzali M, MacPherson SE, Dolan RJ, Shallice T (2006) Left prefrontal control of novel occurrence during recollection: a psychopharmacological study using scopolamine and event-related fMRI. NeuroImage 33:286–295
Breese CR, Lee MJ, Adams CE, Sullivan B, Logel J, Gillen KM, Marks MJ, Collins AC, Leonard S (2000) Abnormal regulations of high affinity nicotinic receptors in subjects with schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:351–364
Buschke H (1973) Selective reminding for analysis of memory and learning. J Verbal Learn Verbal Behav
Caine ED, Weingartner H, Ludlow DL, Cudahy EA, Wehry S (1981) Qualitative analysis of scopolamine-induced amnesia. Psychopharmacology 74:74–80
Chopin P, Briley M (1992) Effects of four non-cholinergic cognitive enhancers in comparison with tacrine and galanthamine on scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Psychopharmacology 106:26–30
Chopin P, Colpaert FC, Marien M (2002) Effects of acute and subchronic administration of dexefaroxan, an alpha(2)-adrenoceptor antagonist, on memory performance in young adult and aged rodents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:187–196
Coyle JT, Price DL, DeLong MR (1983) Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science 219:1184–1190
Damsma G, Lammerts van Bueren D, Westerink BHC, Horn AS (1987) Determination of acetylcholine and choline in the femtomole range by means of HPLC, a postcolumn enzyme reactor, and electrochemical detection. Chromatographia 24:827–831
Drachman DA (1977) Memory and cognitive function in man: does the cholinergic system have a specific role? Neurology 27:783–790
Drachman DA, Leavitt J (1974) Human memory and the cholinergic system: a relationship to aging? Arch Neurol 30:113–121
Drago F, Continella G, Valerio C, D’Agata V, Astuto C, Spadaro F, Scapagnini U (1987) Effects of pyroglutamic acid on learning and memory processes of the rat. Acta Therapeutica 13:587–594
Ebert U, Oertel R, Kirch W (2000) Influence of grapefruit juice on scopolamine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy male and female subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 38:532–531
Ebert U, Grossmann M, Oertel R, Grammaté T, Kirch W (2001) Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic modeling of the electroencephalogram effects of scopolamine in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 41:51–60
Edginton T, Rusted J (2003) Separate and combined effects of scopolamine and nicotine on retrieval-induced forgetting. Psychopharmacology 170:351–357
Ellis JR, Ellis KA, Bartholomeusz CF, Harrison BJ, Wesnes KA, Erskine FF, Vitetta L, Nathan PJ (2006) Muscarinic and nicotinic receptors synergistically modulate working memory and attention in humans. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 9:175–189
Erskine FF, Ellis JR, Ellis KA, Stuber E, Hogan K, Miller V, Moore E, Bartholomeusz C, Harrison BJ, Lee B, Phan KL, Liley D, Nathan PJ (2004) Evidence for synergistic modulation of early information processing by nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in humans. Hum Psychopharmacol 19:503–509
Flood JF, Smith GE, Cherkin A (1983) Memory retention: potentiation of cholinergic drug combinations in mice. Neurobiol Aging 4:37–43
Friedman P (1991) GB-STAT: Computer-aided statistics & graphics, ver 3.0. Silver Spring: Dynamic Microsystems, Inc
Gage FH, Kelly PAT, Björklund A (1984) Regional changes in brain glucose metabolism reflect cognitive impairments in aged rats. J Neurosci 4:2856–2865
Gilles C, Luthringer R (2007) Pharmacological models in healthy volunteers: their use in the clinical development of psychotropic drugs. Journal of Psycopharmacology 21:272–282
Glick SD, Zimmerberg B (1972) Amnesic effects of scopolamine. Behav Biol 7:245–254
Hall ST, Puech A, Schaffler K, Wesnes K, Gamzu ER (1990) Early clinical testing of cognition enhancers: prediction of efficacy. Pharmacopsychiatry 23:57–58
Huang F, Buchwald P, Browne CE, Farag HH, Wu WM, Ji F, Hochhaus G, Bodor N (2001) Receptor binding studies of soft anticholinergic agents. AAPS pharmSci 3:E30
Jope RS, Jenden DJ (1979) Dimethylaminoethanol (deanol) metabolism in rat brain and its effect on acetylcholine synthesis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 211:472–429
Kolb B, Tees RC (1990) The cerebral cortex of the rat. MIT Press, Cambridge
McCann UD, Eligulashvili V, Mertl M, Murphy DL, Ricaurte GA (1999) Altered neuroendocrine and behavioral responses to m-chlorophenylpiperazine in 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) users. Psychopharmacology 147:56–65
Martinez R, Molchan SE, Lawlor BA, Thompson K, Martinson H, Latham G, Weingartner H, Sunderland T (1997) Minimal effects of dextroamphetamine on scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments in humans. Biol Psychiatry 41:50–57
Mauri M, Sinforiani E, Reverberi F, Merlo P, Bono G (1994) Pramiracetam effects on scopolamine-induced amnesia in healthy volunteers. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2:133–139
Mintzer MZ, Griffiths RR (2003) Lorazepam and scopolamine: a single-dose comparison of effects on human memory and attentional processes. Exp clin psychopharmacol 11:56–72
Molchan SE, Mellow AM, Lawlor BA, Weingartner HJ, Cohen RM, Cohen MR, Sunderland T (1990) TRH attenuates scopolamine-induced memory impairment in humans. Psychopharmacology 100:84–89
Morris RGM (1981) Spatial localization does not require the presence of local cues. Learn Motiv 12:239–260
Patat A, Klein MJ, Surjus A, Hucher M, Granier J (1991) RU 41 656 does not reverse the scopolamine-induced cognitive deficit in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41:225–231
Pepeu G, Freedman GX, Giarman NJ (1960) Biochemical and pharmacological studies of dimethylaminoethanol (deanol). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 129:291–295
Perry EK, Tomlinson BE, Blessed G, Bergmann K, Gibson PH, Perry RH (1978) Correlation of cholinergic abnormalities with senile plaques and mental tests scores in senile dementia. Br Med J 2:1457–1459
Potter DD, Pickles CD, Roberts RC, Rugg MD (2000) The effect of cholinergic receptor blockade by scopolamine on memory performance and the auditory P3. Psychophysiology 14:11–23
Riedel W, Hogervorst E, Leboux R, Verhey F, Van Praag H, Jolles J (1995) Caffeine attenuates scopolamine-induced memory impairment in humans. Psychopharmacology 122:158–168
Rusted JM, Warburton DM (1988) The effects of scopolamine on working memory in healthy young volunteers. Psychopharmacology 96:145–152
Sarter M, Bruno JP (1997) Cognitive functions of cortical acetylcholine: toward a unifying hypothesis. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 23:28–46
Sarter M, Bruno JP (2000) Cortical cholinergic inputs mediating arousal, attentional processing and dreaming: differential afferent regulation of the basal forebrain by telencephalic and brainstem afferents. Neuroscience 95:933–952
Tellez S, Colpaert F, Marien M (1999) α2-Adrenoceptor modulation of cortical acetylcholine release in vivo. Neuroscience 89:1041–1050
Terry AV Jr, Buccafusco JJ (2003) The cholinergic hypothesis of age and Alzheimer's disease-related cognitive deficits: recent challenges and their implications for novel drug development. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:821–827
Vernikos-Danellis J, Winget CM, Leach CS, Rosenblatt LS, Lyman J, Beljan JR (1977) Space motion sickness medications: interference with biomedical parameters. Acta Astronautica 4:1159–1169
Wesnes KA (2001) The use of cognitive tests to facilitate drug and dose selection in phase I and to optimize dosing in phase IV. Int Congr Ser 1220:35–50
Wesnes KA, Simpson PM, Kidd AG (1988) An investigation of the range of cognitive impairments induced by scopolamine 0.6 mg sc. Hum Psychopharmacol 3:27–41
Wesnes KA, Simpson PM, White L, Pinker S, Jertz G, Murphy M, Siegfried K (1991) Cholinesterase inhibition in the scopolamine model of dementia. Ann N Y Acad Sci 640:268–271
Winkler J, Suhr ST, Gage FH, Thal LJ, Fischer LJ (1995) Essential role of neocortical acetylcholine in spatial memory. Nature 375:484–487
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Martine Mas (CRPF) in performing the rat microdialysis experiments and HPLC analyses and Pascale Petiot (CRPF) in performing the rat behavioral experiments. Experiments comply with the current laws of the country as they were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blin, O., Audebert, C., Pitel, S. et al. Effects of dimethylaminoethanol pyroglutamate (DMAE p-Glu) against memory deficits induced by scopolamine: evidence from preclinical and clinical studies. Psychopharmacology 207, 201–212 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1648-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1648-7