Abstract
Rationale
Selective cognitive impairments, including those of executive function as assessed using the Wisconsin Card Sort Test or intradimensional–extradimensional (ID–ED) tests, are a key feature of schizophrenia but remain inadequately treated by existing therapies. Recently, however, modafinil has been shown to improve attentional set-shifting performance in patients with schizophrenia.
Objective
The present study evaluated the recently described analogous rat ID–ED attentional set-shifting task by investigating the effects of various pharmacological challenges to a phencyclidine (PCP)-induced ED shift impairment, namely, haloperidol, risperidone, sertindole, and modafinil.
Materials and methods
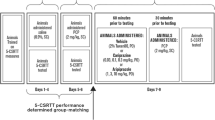
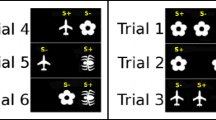
Rats were subjected to a subchronic systemic administration of either saline vehicle or PCP (5 mg/kg i.p. b.i.d. for 7 days) followed by a 7-day washout period. During this period, rats were trained to dig in baited bowls for a food reward and to discriminate based on odor or digging media. In a single test session conducted the day after the washout period (day 8), rats performed a series of discriminations following acute administration of either vehicle, or haloperidol (0.1 mg/kg s.c.), or risperidone (0.2 mg/kg i.p.), or sertindole (1.25 mg/kg p.o.) or modafinil (64 mg/kg p.o.).
Results
The subchronic PCP-induced ED deficit was ameliorated by sertindole and modafinil but not by haloperidol or risperidone.
Conclusions
Overall, these findings further support that the rat ID–ED test in subchronic PCP-treated rats has utility and validity as a preclinical model of the cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia and demonstrates back-translational potential.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amitai N, Semenova S, Markou A (2007) Cognitive–disruptive effects of the psychotomimetic phencyclidine and attenuation by atypical antipsychotic medications in rats. Psychopharmacology 193:521–537
Badcock JC, Michie PT, Johnson L, Combrinck J (2002) Acts of control in schizophrenia: dissociating the components of inhibition. Psychol Med 32:287–297
Barense MD, Fox MT, Baxter MG (2002) Aged rats are impaired on an attentional set-shifting task sensitive to medial frontal cortex damage in young rats. Learn Mem 9:191–201
Baviera M, Invernizzi RW, Carli M (2008) Haloperidol and clozapine have dissociable effects in a model of attentional performance deficits induced by blockade of NMDA receptors in the mPFC. Psychopharmacology 196:269–280
Birrell JM, Brown VJ (2000) Medial frontal cortex mediates perceptual attentional set shifting in the rat. J Neurosci 20:4320–4324
Block AE, Dhanji H, Thompson-Tardif SF, Floresco SB (2007) Thalamic–prefrontal cortical–ventral striatal circuitry mediates dissociable components of strategy set shifting. Cereb Cortex 17:1625–1636
Borkowska A, Araszkiewicz A, Rajewski A, Rybabowski JK (2002) Risperidone treatment of schizophrenia: improvement in psychopathology and neuropsychological tests. Neuropsychobiology 46:85–89
Cornblatt BA, Erlenmeyer-Kimling L (1985) Global attentional deviance as a marker of risk for schizophrenia: specificity and predictive validity. J Abnorm Psychol 94:470–486
Dias R, Robbins TW, Roberts AC (1996) Primate analogue of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test: effects of excitotoxic lesions of the prefrontal cortex in the marmoset. Behav Neurosci 110:872–886
Didriksen M, Skarsfeldt T, Arnt J (2007) Reversal of PCP-induced learning and memory deficits in the Morris’ water maze by sertindole and other antipsychotics. Psychopharmacology 193:225–233
Dunn MJ, Killcross S (2007) Clozapine, SCH 23390 and alpha-flupenthixol but not haloperidol attenuate acute phencyclidine-induced disruption of conditional discrimination performance. Psychopharmacology 190:403–414
Egerton A, Reid L, McKerchar CE, Morris BJ, Pratt JA (2005) Impairment in perceptual attentional set-shifting following PCP administration: a rodent model of set-shifting deficits in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 179:77–84
Elliott R, McKenna PJ, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (1995) Neuropsychological evidence for frontostriatal dysfunction in schizophrenia. Psychol Med 25:619–630
Featherstone RE, Rizos Z, Nobrega JN, Kapur S, Fletcher PJ (2007) Gestational methylazoxymethanol acetate treatment impairs select cognitive functions: parallels to schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:483–492
Fletcher PJ, Ten CC, Rizos Z, Lovic V, Kapur S (2005) Sensitization to amphetamine, but not PCP, impairs attentional set shifting: reversal by a D1 receptor agonist injected into the medial prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 183:190–200
Floresco SB, Ghods-Sharifi S, Vexelman C, Magyar O (2006a) Dissociable roles for the nucleus accumbens core and shell in regulating set-shifting. J. Neurosci 26:2449–2457
Floresco SB, Magyar O, Ghods-Sharafi S, Vexelman C, Tse MTL (2006b) Multiple dopamine receptor subtypes in the medial prefrontal cortex of the rat regulate set-shifting. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:297–309
Fox MT, Barense MD, Baxter MG (2003) Perceptual attentional set-shifting is impaired in rats with neurotoxic lesions of posterior parietal cortex. J Neurosci 23:676–681
Gallhofer B, Jaanson P, Mittoux A, Tanghøj P, Lis S, Krieger S (2007) Course of recovery of cognitive impairment in patients with schizophrenia: a randomised double-blind study comparing sertindole and haloperidol. Pharmacopsychiatry 40:275–286
Goldberg TE, Greenberg RD, Griffin SJ, Gold JM, Kleinman JE, Pickar D, Schulz SC, Weinberger DR (1993) The effect of clozapine on cognition and psychiatric symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 162:43–48
Goldberg TE, Goldman RS, Burdick KE, Malhotra AK, Lencz T, Patel RC, Woerner MG, Schooler NR, Kane JM, Robinson DG (2007) Cognitive improvement after treatment with second-generation antipsychotic medications in first-episode schizophrenia: is it a practice effect? Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:1115–1122
Grayson B, Idris NF, Neill JC (2007) Atypical antipsychotics attenuate a sub-chronic PCP-induced cognitive deficit in the novel object recognition task in the rat. Behav Brain Res 184:31–38
Green MF (1996) What are the functional consequences of neurocognitive deficits in schizophrenia? Am J Psychiatry 153:321–330
Harvey PD, Koren D, Reichenberg A, Bowie CR (2006) Negative symptoms and cognitive deficits: what is the nature of their relationship? Schizophr Bull 32:250–258
Hatcher PD, Brown VJ, Tait DS, Bate S, Overend P, Hagan JJ, Jones DN (2005) 5-HT6 receptor antagonists improve performance in an attentional set shifting task in rats. Psychopharmacology 181:253–259
Haut MW, Cahill J, Cutlip WD, Stevenson JM, Makela EH, Bloomfield SM (1996) On the nature of Wisconsin Card Sorting Test performance in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 65:15–22
Hill MN, Froese LM, Morrish AC, Sun JC, Floresco SB (2006) Alterations in behavioral flexibility by cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonists and antagonists. Psychopharmacology 187:245–259
Hyman SE, Fenton WS (2003) Medicine. What are the right targets for psychopharmacology? Science 299:350–351
Jentsch JD, Roth RH (1999) The neuropsychopharmacology of phencyclidine: from NMDA receptor hypofunction to the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:201–225
Jentsch JD, Tran A, Le D, Youngren KD, Roth RH (1997) Sub-chronic phencyclidine administration reduces mesoprefrontal dopamine utilization and impairs prefrontal cortical-dependent cognition in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 17:92–99
Joyce E, Hutton S, Mutsatsa S, Gibbins H, Webb E, Paul S, Robbins T, Barnes T (2002) Executive dysfunction in first-episode schizophrenia and relationship to duration of untreated psychosis: the West London Study. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 43:s38–s44
Keefe RS, Silva SG, Perkins DO, Lieberman JA (1999) The effects of atypical antipsychotic drugs on neurocognitive impairment in schizophrenia: a review and meta-analysis. Schizophr Bull 25:201–222
Keefe RS, Young CA, Rock SL, Purdon SE, Gold JM, Breier A (2006) One-year double-blind study of the neurocognitive efficacy of olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 281(1):1–15
Lapiz MDS, Morilak DA (2008) Noradrenergic modulation of cognitive function in rat medial prefrontal cortex as measured by attentional set shifting capacity. Neurosci 137:1039–1049
Lapiz MDS, Bondi CO, Morilak DA (2007) Chronic treatment with desipramine improves cognitive performance of rats in an attentional set-shifting task. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1000–1010
McGurk SR, Mueser KT, Harvey PD, LaPuglia R, Marder J (2003) Cognitive and symptom predictors of work outcomes for clients with schizophrenia in supported employment. Psychiatr Serv 54:1129–1135
McGurk SR, Mueser KT, Walling D, Harvey PD, Meltzer HY (2004) Cognitive functioning predicts outpatient service utilization in schizophrenia. Ment Health Serv Res 6:185–188
Milner B (1963) Effects of different brain lesions on card sorting: the role of the frontal lobes. Arch Neurol 9:90–110
Minzenberg MJ, Carter CS (2007) Modafinil: a review of neurochemical actions and effects on cognition. Neuropsychopharmacology DOI 10.1038/sj.npp.1301534, Epub ahead of print
Morein-Zamir S, Turner DC, Sahakian BJ (2007) A review of the effects of modafinil on cognition in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 33:1298–1306
Nicolle MM, Baxter MG (2003) Glutamate receptor binding in the frontal cortex and dorsal striatum of aged rats with impaired attentional set-shifting. Eur J Neurosci 18:3335–3342
Owen AM, Roberts AC, Polkey CE, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (1991) Extra-dimensional versus intra-dimensional set shifting performance following frontal lobe excisions, temporal lobe excisions or amygdalo-hippocampectomy in man. Neuropsychologia 29:993–1006
Pantelis C, Barber FZ, Barnes TR, Nelson HE, Owen AM, Robbins TW (1999) Comparison of set-shifting ability in patients with chronic schizophrenia and frontal lobe damage. Schizophr Res 37:251–270
Ragozzino ME, Detrick S, Kesner RP (1999) Involvement of the prelimbic-infralimbic areas of the rodent prefrontal cortex in behavioral flexibility for place and response learning. J Neurosci 19:4585–4594
Rémillard S, Pourcher E, Cohen H (2005) The effect of neuroleptic treatments on executive function and symptomatology in schizophrenia: a 1-year follow up study. Schizophr Res 80(1):99–106
Rodefer JS, Murphy ER, Baxter MG (2005) PDE10A inhibition reverses sub-chronic PCP-induced deficits in attentional set-shifting in rats. Eur J Neurosci 21:1070–1076
Rodefer JS, Nguyen TN, Karlsson JJ, Arnt J (2007) Reversal of subchronic PCP-induced deficits in attentional set shifting in rats by sertindole and a 5-HT6 receptor antagonist: comparison among antipsychotics. Neuropsychopharmacology DOI 10.1038/sj.npp.1301654, Epub ahead of print
Stefani MR, Moghaddam B (2005) Systemic and prefrontal cortical NMDA receptor blockade differentially affect discrimination learning and set-shift ability in rats. Behav Neurosci 119:420–428
Stefani MR, Moghaddam B (2006) Rule learning and reward contingency are associated with dissociable patterns of dopamine activation in the rat prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens and dorsal striatum. J Neurosci 26:8810–8818
Stefani MR, Groth K, Moghaddam B (2003) Glutamate receptors in the rat medial prefrontal cortex regulate set-shifting ability. Behav Neurosci 117:728–737
Tait DS, Brown VJ, Farovik A, Theobald DE, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2007) Lesions of the dorsal noradrenergic bundle impair attentional set-shifting in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 25:3719–3724
Tunbridge EM, Bannerman DM, Sharp T, Harrison PJ (2004) Catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibition improves set-shifting performance and elevates stimulated dopamine release in the rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 24:5331–5335
Turner DC, Clark L, Pomarol-Clotet E, McKenna P, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2004) Modafinil improves cognition and attentional set shifting in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1363–1373
Waters KA, Burnham KE, O’Connor D, Dawson GR, Dias R (2005) Assessment of modafinil on attentional processes in a five-choice serial reaction time test in the rat. J Psychopharm 19:149–158
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to extend special thanks to Mr. Christian Spang Pedersen, Ms. Tanja Bruun, and Mr. Claus Nørgaard Johansson for their assistance in running the behavioral intradimensional–extradimensional experiment and in their contribution to the “Materials and methods” section of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goetghebeur, P., Dias, R. Comparison of haloperidol, risperidone, sertindole, and modafinil to reverse an attentional set-shifting impairment following subchronic PCP administration in the rat—a back translational study. Psychopharmacology 202, 287–293 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1132-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1132-9