Abstract
Rationale
Serotonin (5-HT) plays a key role in the pathophysiology of psychotic disorders, presumably through a modulation of dopamine (DA) transmission. Reduction of 5-HT signaling has been suggested to enhance dopaminergic responses in animal models of psychosis. An intriguing naturalistic strategy to reduce 5-HT brain content is afforded by the dietary restriction to its precursor, l-tryptophan (TRP).
Objective
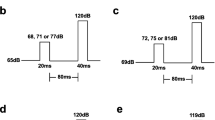
We investigated the impact of a TRP-deficient diet in rats on the prepulse inhibition of the startle (PPI), a measure of sensorimotor gating which is typically impaired by psychotomimetic substances.
Materials and methods
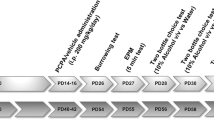
After either short-term (6 h) or long-term (14 days) TRP deprivation, rats were tested for startle reflex and PPI. Moreover, we assessed the impact of both TRP deprivation regimens on PPI reduction induced by the psychotomimetic substance d-amphetamine (AMPH).
Results
Both TRP-deficient regimens failed to significantly affect PPI responses. However, chronic, but not short-term, TRP-deficient diet induced a significant sensitization to the effects of AMPH (1.25–2.5 mg/kg, subcutaneous). The enhanced predisposition to PPI disruption elicited by prolonged TRP deprivation was completely reversed 24 h after reinstatement of TRP in the diet, as well as pretreatment with antipsychotic drugs haloperidol (0.1 mg/kg, intraperitoneal) and clozapine (5 mg/kg, intraperitoneal), which exert their therapeutic action mostly through blockade of DA D2 receptors.
Conclusions
The present results confirm and extend previous findings on the impact of serotonergic signaling in the modulation of DA transmission in schizophrenia and point to chronic TRP deprivation as a potential model of environmental manipulation that may produce a sensitization to psychotic-like symptoms induced by dopaminergic activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi-Dargham A, Laruelle M, Aghajanian GK, Charney D, Krystal J (1997) The role of serotonin in the pathophysiology and treatment of schizophrenia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9:1–17
Adell A, Myers RD (1995) Synthesis of dopamine and 5-HT in anatomical regions of the rat’s brain is unaffected by sustained infusion of amperozide. Pharmacol Toxicol 77:341–345
Akil M, Pierri JN, Whitehead RE, Edgar CL, Mohila C, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (1999) Lamina-specific alterations in the dopamine innervation of the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenic subjects. Am J Psychiatry 156:1580–1589
Asin KE, Fibiger HC (1983) An analysis of neuronal elements within the median nucleus of the raphe that mediate lesion-induced increases in locomotor activity. Brain Res 268:211–223
Auclair A, Drouin C, Cotecchia S, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (2004a) 5-HT2A and alpha1b-adrenergic receptors entirely mediate dopamine release, locomotor response and behavioural sensitization to opiates and psychostimulants. Eur J Neurosci 20:3073–3084
Auclair A, Blanc G, Glowinski J, Tassin JP (2004b) Role of serotonin 2A receptors in the d-amphetamine-induced release of dopamine:comparison with previous data on alpha1b-adrenergic receptors. J Neurochem 91:318–26
Biggio G, Fadda F, Fanni P, Tagliamonte A, Gessa GL (1974) Rapid depletion of serum tryptophan, brain tryptophan, serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid by a tryptophan-free diet. Life Sci 14:1321–1329
Braff D, Stone C, Callaway E, Geyer M, Glick I, Bali L (1978) Prestimulus effects on human startle reflex in normals and schizophrenics. Psychophysiology 15:339–343
Braff DL, Geyer MA, Light GA, Sprock J, Perry W, Cadenhead KS, Swerdlow NR (2001) Impact of prepulse characteristics on the detection of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 49:171–178
Branchey L, Branchey M, Worner TM, Zucker D, Shaw S, Lieber CS (1985) Association between amino acid alterations and hallucinations in alcoholic patients. Biol Psychiatry 20(11):1167–1173
Brezun JM, Daszuta A (1999) Depletion is serotonin decreases neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone of adult rats. Neuroscience 89:899–1002
Cahir M, Ardis T, Reynolds GP, Cooper SJ (2007) Acute and chronic tryptophan depletion differentially regulate central 5-HT1A and 5-HT 2A receptor binding in the rat. Psychopharmacology 190:497–506
Caine SB, Humby T, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2001) Behavioral effects of psychomotor stimulants in rats with dorsal or ventral subiculum lesions: locomotion, cocaine self-administration, and prepulse inhibition of startle. Behav Neurosci 155:880–894
Carta M, Fadda F, Stancampiano R (2006) Tryptophan-deficient diet increases the neurochemical and behavioral response to amphetamine. Brain Res 1094:86–91
Crow TJ, Baker HF, Cross AJ, Joseph MH, Lofthouse R, Longden A, Owen F, Riley GJ, Glover V, Killpack WS (1979) Monoamine mechanisms in chronic schizophrenia: post-mortem neurochemical findings. Br J Psychiatry 134:249–256
De Deurwaerdere P, Spampinato U (1999) Role of serotonin(2A) and serotonin(2B/2C) receptor subtypes in the control of accumbal and striatal dopamine release elicited in vivo by dorsal raphe nucleus electrical stimulation. J Neurochem 73:1033–1042
Fadda F (2000) Tryptophan-free diets: a physiological tool to study brain serotonin function. New Physiol Sci 15:260–264
Fadda F, Concu A, Carcassi AM, Piras MB, Liguori G (1975) [Effect of the administration of corn and geletin on cerebral levels of serotonin in rats]. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper 51:951–954
Fadda F, Cocco S, Stancampiano R (2000) A physiological method to selectively decrease brain serotonin release. Brain Res Brain Res Protoc 5:219–222
Fernstrom JD, Wurtman RJ (1971) Effect of chronic corn consumption on serotonin content of rat brain. Nature New Biol 234:62–64
Fletcher PJ, Selhi ZF, Azampanah A, Sills TL (2001) Reduced brain serotonin activity disrupts prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex. Effects of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine and p-chlorophenylalanine. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:399–409
Franklin M, Cowen PJ (2001) Effect of a low tryptophan diet on the prolactin responses to the 5-HT2A agonist DOI in the rat. Pharmacopsychiatry 34:147–149
Franklin M, Craven RD, Dowling B, Campling G, Elliott JM, Cowen PJ (1999) Effect of a long-term low tryptophan diet on the prolactin responses to the 5-HT1A and 5-HT2C agonists, 8-OH-DPAT and mCPP in the male rat. J Psychopharmacol 13:58–63
Gessa GL, Biggio G, Fadda F, Corsini GU, Tagliamonte A (1975) Tryptophan-free diet: a new means for rapidly decreasing brain tryptophan content and serotonin synthesis. Acta Vitaminol Enzymol 29:72–78
Geyer MA, Markou A (1995) Animal models of psychiatric disorders. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven Press, New York. pp 787–798
Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR, Mansbach RS, Braff DL (1990) Startle response models of sensorimotor gating and habituation deficits in schizophrenia. Brain Res Bull 25:485–498
Geyer MA, Krebs-Thomson K, Braff DL, Swerdlow NR (2001) Pharmacological studies of prepulse inhibition models of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia: a decade in review. Psychopharmacology 156:117–154
Graham FK (1975) The more or less startling effects of weak prestimulation. Psychophysiology 1:238–248
Irwin MR, Marder SR, Fuentenebro F, Yuwiler A (1987) L-5-hydroxytryptophan attenuates positive psychotic symptoms induced by d-amphetamine. Psychiatry Res 22:283–289
Jospeh MH, Baker HF, Crow TJ, Riley GJ, Risby D (1979) Brain tryptophan metabolism in schizophrenia: a post mortem study of metabolites of the serotonin and kynurenine pathways in schizophrenic and control subjects. Psychopharmacology 62:279–285
Kapur S, Remington G (1996) Serotonin-dopamine interaction and its relevance to schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 153:466–476
Kapur S, Seeman P (2001) Does fast dissociation from the dopamine d(2) receptor explain the action of atypical antipsychotics? A new hypothesis. Am J Psychiatry 158:360–369
Kelly PH, Seviour P, Iversen SD (1975) Amphetamine and apomorphine responses in the rat following 6-OHDA lesions of the nucleus accumbens septi and corpus striatum. Brain Res 94:507–522
Koch M (1999) The neurobiology of startle. Prog Neurobiol 59:107–28
Koch M, Schnitzler HU (1997) The acoustic startle response in rats—circuits mediating evocation, inhibition and potentiation. Behav Brain Res 89:35–49
Kusljic S, Copolov DL, van den Buuse M (2003) Differential role of serotonergic projections arising from the dorsal and median raphe nuclei in locomotor hyperactivity and prepulse inhibition. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:2138–2147
Kusljic S, Brosda J, van den Buuse M (2006) Effects of haloperidol and clozapine on sensorimotor gating deficits induced by 5-hydroxytryptamine depletion in the brain. Br J Pharmacol 147:800–807
Mansbach RS, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1988) Dopaminergic stimulation disrupts sensorimotor gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 94:507–514
McQuade R, Sharp T (1997) Functional mapping of dorsal and median raphe 5-hydroxytryptamine pathways in forebrain of the rat using microdialysis. J Neurochem 69:791–796
Meltzer HY (1995) Role of serotonin in the action of atypical antipsychotic drugs. Clin Neurosci 3:64–75
Mokler DJ, Lariviere D, Johnson DW, Theriault NL, Bronzino JD, Dixon M, Morgane PJ (1998) Serotonin neuronal release from dorsal hippocampus following electrical stimulation of the dorsal and median raphe nuclei in conscious rats. Hippocampus 8:262–273
Phillips MA, Oxtoby EK, Langley RW, Bradshaw CM, Szabadi E (2000) Effects of acute tryptophan depletion on prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle (eyeblink) response and the N1/P2 auditory evoked response in man. J Psychopharmacol 14:258–265
Prinssen EP, Colpaert FC, Koek W (2002a) 5-HT1A receptor activation and anti-cataleptic effects: high-efficacy agonists maximally inhibit haloperidol-induced catalepsy. Eur J Pharmacol 453:217–221
Prinssen EP, Assié MB, Koek W, Kleven MS (2002b) Depletion of 5-HT disrupts prepulse inhibition in rats: dependence on the magnitude of depletion, and reversal by a 5-HT precursor. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:340–347
Rabey JM, Vardi J, Askenazi JJ, Streifler M (1977) l-Tryptophan administration in l-dopa-induced hallucinations in elderly Parkinsonian patients. Gerontology 23(6):438–444
Randrup A, Munkvad I (1964) On the relation of tryptaminicand serotonergic mechanisms to amphetamine-induced abnormal behaviour. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 21:272–282
Richter-Liven G, Acsády L, Freund TF, Segal M (1994) Differential effects of serotonin and raphe grafts in the hippocampus and hypothalamus: a combined behavioural and anatomical study in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 6:1720–1728
Robinson TE, Becker JB (1986) Enduring changes in brain and behavior produced by chronic amphetamine administration: a review and evaluation of animal models of amphetamine psychosis. Brain Res 396:157–198
Salomon L, Lanteri C, Godeheu G, Blanc G, Gingrich J, Tassin JP (2007) Paradoxical constitutive behavioral sensitization to amphetamine in mice lacking 5-HT2A receptors. Psychopharmacology 194:11–20
Seeman P (2002) Atypical antipsychotics: mechanism of action. Can J Psychiatry 47:27–38
Seiden LS, Sabol KE, Ricaurte GA (1993) Amphetamine: effects on catecholamine systems and behavior. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 33:639–677
Stancampiano R, Melis F, Sarais L, Cocco S, Cugusi C, Fadda F (1997) Acute administration of a tryptophan-free amino acid mixture decreases 5-HT release in rat hippocampus in vivo. Am J Physiol 272:991–994
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1993) Clozapine and haloperidol in an animal model of sensorimotor gating deficits in schizophrenia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:741–744
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1998) Using an animal model of deficient sensorimotor gating to study the pathophysiology and new treatments of schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 24:285–301
Swerdlow NR, Vaccarino FJ, Amalric M, Koob GF (1986) The neural substrates for the motor-activating properties of psychostimulants: a review of recent findings. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:233–248
Swerdlow NR, Keith VA, Braff DL, Geyer MA (1991) Effects of spiperone, raclopride, SCH 23390 and clozapine on apomorphine inhibition of sensorimotor gating of the startle response in the rat. J. Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:530–536
Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA, Braff DL (2001) Neural circuit regulation of prepulse inhibition of startle in the rat: current knowledge and future challenges. Psychopharmacology 156:194–215
Ueda S, Sakakibara S, Yoshimoto K (2005) Effect of long-lasting serotonin depletion on environmental enrichment-induced neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus and spatial learning. Neuroscience 135:395–402
van der Mast RC, Fekkes D, Moleman P, Pepplinkhuizen L (1991) Is postoperative delirium related to reduced plasma tryptophan? Lancet. 338:851–852
van der Mast RC, van den Broek WW, Fekkes D, Pepplinkhuizen L, Habbema JD (2000) Is delirium after cardiac surgery related to plasma amino acids and physical condition? J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 12:57–63
Walters JK, Davis M, Sheard MH (1979) Tryptophan-free diet: effects on the acoustic startle reflex in rats. Psychopharmacology 62:103–109
Widerlöv E (1988) A critical appraisal of CSF monoamine metabolite studies in schizophrenia. Ann NY Acad Sci 537:309–323
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fabio Fadda and Roberto Stancampiano contributed equally to the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bortolato, M., Frau, R., Orrù, M. et al. Effects of tryptophan deficiency on prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle in rats. Psychopharmacology 198, 191–200 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1116-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1116-9