Abstract
Rationale
Drug discrimination can be used to examine tolerance and dependence in agonist-treated animals by establishing an appropriate antagonist as a discriminative stimulus.
Objective
Establish intravenous SR 141716A as a discriminative stimulus in four rhesus monkeys pretreated with a relatively small dose of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).
Methods
Rhesus monkeys received i.v. Δ9-THC (0.32 mg/kg) and discriminated i.v. SR 141716A (1 mg/kg) from vehicle while responding under a fixed ratio (FR) 5 schedule of stimulus-shock termination.
Results
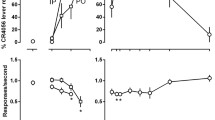
The discriminative stimulus effects of SR 141716A were dose-dependent (ED50=0.33 mg/kg) and were mimicked by the CB1 antagonist AM 251 (ED50=0.98 mg/kg), but not by a benzodiazepine (midazolam) or an N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist (ketamine). An additional dose (0.32 mg/kg in addition to 0.32 mg/kg administered before the session) of Δ9-THC shifted the SR 141716A dose–effect curve 3-fold rightward. Omitting Δ9-THC before test sessions resulted in responding on the SR 141716A lever that was attenuated by subsequent administration of Δ9-THC (ED50=0.13 mg/kg), CP 55940 (ED50=0.013 mg/kg), and WIN 55212-2 (ED50=0.35 mg/kg); midazolam and ketamine did not attenuate responding on the SR 141716A lever. SR 141716A (1 mg/kg) shifted the Δ9-THC and CP 55940 dose–effect curves 3.4-fold rightward; the WIN 55212-2 dose–effect curve was not significantly modified by a dose of 1 mg/kg of SR 141716A.
Conclusions
SR 141716A can be established as a discriminative stimulus in animals pretreated with Δ9-THC, and this assay is selective for cannabinoid activity. Differential antagonism of cannabinoids by SR 141716A might indicate that the mechanism of action of WIN 55212-2 is not identical to other cannabinoids. This study demonstrates that, under the appropriate conditions, drug discrimination has utility for examining cannabinoid dependence and withdrawal.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aceto MD, Scates SM, Lowe JA, Martin BR (1996) Dependence on Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol: studies on precipitated and abrupt withdrawal. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1290–1295
Balster RL, Prescott WR (1992) Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol discrimination in rats as a model for cannabis intoxication. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 16:55–62
Bass CE, Griffin G, Grier M, Mahadevan A, Razdan RK, Martin BR (2002) SR-141716A-induced stimulation of locomotor activity. A structure–activity relationship study. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74:31–40
Beardsley PM, Balster RL, Harris LS (1986) Dependence on tetrahydrocannabinol in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 239:311–319
Breivogel CS, Griffin G, Di Marzo V, Martin BR (2001) Evidence for a new G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor in mouse brain. Mol Pharmacol 60:155–163
Browne RG, Weissman A (1981) Discriminative stimulus properties of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol: mechanistic studies. J Clin Pharmacol 21:227S–234S
Compton DR, Aceto MD, Lowe J, Martin BR (1996) In vivo characterization of a specific cannabinoid receptor antagonist (SR141716A): inhibition of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced responses and apparent agonist activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:586–594
Deneau GA, Kaymakcalan S (1971) Physiological and psychological dependence to synthetic Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in rhesus monkeys. Pharmacologist 13:246
Emmett-Oglesby MW, Mathis DA, Moon RT, Lal H (1990) Animal models of drug withdrawal symptoms. Psychopharmacology 101:292–309
Gold LH, Balster RL, Barrett RL, Britt DT, Martin BR (1992) A comparison of the discriminative stimulus properties of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and CP 55,940 in rats and rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 262:479–486
Gong JP, Onaivi ES, Ishiguro H, Liu QR, Tagliaferro PA, Brusco A, Uhl GR (2006) Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Res 1071:10–23
Huestis MA, Gorelick DA, Heishman SJ, Preston KL, Nelson RA, Moolchan ET, Frank RA (2001) Blockade of effects of smoked marijuana by the CB1-selective cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:322–328
Järbe TUC, Lamb RJ, Lin S, Makriyannis A (2001) (R)-Methanandamide and Δ9-THC as discriminative stimuli in rats: tests with the cannabinoid antagonist SR-141716 and the endogenous ligand anandamide. Psychopharmacology 156:369–380
Järbe TUC, Harris MY, Li C, Liu Q, Makriyannis A (2004) Discriminative stimulus effects in rats of SR-141716 (rimonabant), a cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist. Psychopharmacology 177:35–45
Lichtman AH, Martin BR (1996) Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol impairs spatial memory through a cannabinoid receptor mechanism. Psychopharmacology 126:125–131
Lichtman AH, Sheikh SM, Loh HH, Martin BR (2001) Opioid and cannabinoid modulation of precipitated withdrawal in Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol and morphine-dependent mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:1007–1014
Mansbach RS, Rovetti CC, Winston EN, Lowe JA (1996) Effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A on the behavior of pigeons and rats. Psychopharmacology 124:315–322
McMahon LR, France CP (2002) Acute and chronic effects of the neuroactive steroid pregnanolone on schedule-controlled responding in rhesus monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 13:545–555
McMahon LR, France CP (2003) Discriminative stimulus effects of the cannabinoid antagonist, SR 141716A, in Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-treated rhesus monkeys. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 11:286–293
McMahon LR, Gerak LR, France CP (2001) Potency of positive gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) modulators to substitute for a midazolam discriminative stimulus in untreated monkeys does not predict potency to attenuate a flumazenil discriminative stimulus in diazepam-treated monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:1227–1235
McMahon LR, Amin MR, France CP (2005) SR 141716A differentially attenuates the behavioral effects of Δ9-THC in rhesus monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 16:363–372
National Research Council (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy, Washington, DC
Perlin E, Smith CG, Nichols AI, Almirez R, Flora KP, Cradock JC, Peck CC (1985) Disposition and bioavailability of various formulations of tetrahydrocannabinol in the rhesus monkey. J Pharm Sci 74:171–174
Pèrio A, Rinaldi-Carmona M, Maruani J, Barth F, Le Fur G, Soubrie P (1996) Central mediation of the cannabinoid cue: activity of a selective CB1 antagonist, SR 141716A. Behav Pharmacol 7:65–71
Pertwee RG (2006) The pharmacology of cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: an overview. Int J Obes (Lond) 30:S13–S18
Pugh SL, Boone MS, Emmett-Oglesby MW (1992) Tolerance, cross-tolerance and withdrawal in rats made dependent on diazepam. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 262:751–758
Rinaldi-Carmona M, Barth F, Heaulme M, Alonso R, Shire D, Congy C, Soubrie P, Breliere JC, Le Fur G (1995) Biochemical and pharmacological characterisation of SR141716A, the first potent and selective brain cannabinoid receptor antagonist. Life Sci 56:1941–1947
Sannerud CA, Young AM (1987) Environmental modification of tolerance to morphine discriminative stimulus properties in rats. Psychopharmacology 93:59–68
Smurthwaite ST, Kautz MA, Geter B, Riley AL (1992) Naloxone as a stimulus in drug discrimination learning: generalization to other opiate antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41:43–47
Tallarida RJ (2000) Drug synergism and dose–effect data analysis. Chapman and Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, FL
Tanda G, Munzar P, Goldberg SR (2000) Self-administration behavior is maintained by the psychoactive ingredient of marijuana in squirrel monkeys. Nat Neurosci 3:1073–1074
Wiley JL, Barrett RL, Balster RL, Martin BR (1993) Tolerance to the discriminative stimulus effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Behav Pharmacol 4:581–585
Wiley JL, Huffman JW, Balster RL, Martin BR (1995a) Pharmacological specificity of the of the discriminative stimulus effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rhesus monkeys. Drug Alcohol Depend 40:81–86
Wiley JL, Lowe JA, Balster RL, Martin BR (1995b) Antagonism of the discriminative stimulus effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in rats and rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:1–6
Acknowledgments
Supported by US Public Health Service Grants DA15468 and DA19222. The author thanks C. Cruz, M. Hernandez, and D. Logan for providing technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McMahon, L.R. Discriminative stimulus effects of the cannabinoid CB1 antagonist SR 141716A in rhesus monkeys pretreated with Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Psychopharmacology 188, 306–314 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0500-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0500-6