Abstract
Rationale
Cotreatment with clorgyline shifts the development of sensitization to the D2/D3 dopamine receptor agonist quinpirole from locomotion to mouthing, an effect apparently unrelated to the monoamine oxidase inhibition property of clorgyline. This phenomenon was demonstrated in rats examined in small activity chambers. However, like with other psychostimulant drugs, sensitization to quinpirole is modulated by environmental context. It is not known whether the clorgyline cotreatment effect is likewise influenced by the environment.
Objective
To determine the generality of the clorgyline effect on behavioral sensitization by evaluating the effects of clorgyline cotreatment on sensitization to quinpirole in two different environments: a small activity chamber and a large open field.
Methods
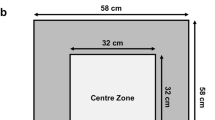
Male rats received eight injections of quinpirole (0.5 mg/kg, twice weekly) in an open field or activity chamber; one group in each environment received a constant infusion of clorgyline (1 mg/kg/day via osmotic minipumps) while the other group served as the sham surgery control. For quinpirole injection 7 or 8, rats were tested in the alternate environment.
Results
In activity chambers, clorgyline cotreatment switched sensitization to quinpirole from locomotion to mouthing. In the open field, clorgyline cotreatment increased mouthing and expanded the explored space without a change in path stereotypy or the amount of locomotion compared to treatment with quinpirole alone.
Conclusions
Structure of the environment can modulate the clorgyline cotreatment effect on behavioral sensitization to quinpirole. The behavioral profiles produced by clorgyline cotreatment in the two environments resembled the behavioral effects observed with quinpirole and D1 agonist cotreatment. It is suggested that clorgyline cotreatment produces a behavioral profile characteristic of enhanced dopamine D1 and D2 receptor costimulation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnt J, Hyttel J, Perregaard J (1987) Dopamine D-1 receptor agonists combined with the selective D-2 agonist quinpirole facilitate the expression of oral stereotyped behaviour in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 133:137–145
Aulakh CS, Hill JL, Murphy DL (1993) Attenuation of hypercortisolemia in fawn-hooded rats by antidepressant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 240:85–88
Badiani A, Robinson TE (2004) Drug-induced neurobehavioral plasticity: the role of environmental context. Behav Pharmacol 15:327–339
Campbell IC, Robinson DS, Lovenberg W, Murphy DL (1979) The effects of chronic regimens of clorgyline and pargyline on monoamine metabolism in the rat brain. J Neurochem 32:49–55
Campbell IC, Durcan MJ, Cohen RM, Pickar D, Chugani D, Murphy DL (1985) Chronic clorgyline and pargyline increase apomorphine-induced stereotypy in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:921–925
Canadian Council on Animal Care (1993) Guide to the care and use of experimental animals, vol 1, 2nd edn. CCAC, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Cleveland WS (1979) Robust locally weighted regression and smoothing scatterplots. J Am Stat Assoc 74:829–836
Culver KE, Szechtman H (1997) Monoamine oxidase inhibitor sensitive site implicated in sensitization to quinpirole. Eur J Pharmacol 339:109–111
Culver KE, Szechtman H (2003) Clorgyline-induced switch from locomotion to mouthing in sensitization to the dopamine D2/D3 agonist quinpirole in rats: role of sigma and imidazoline I2 receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 167:211–218
Culver KE, Szechtman H (2004) Hypophysectomy does not block sensitization to the dopamine agonist quinpirole or its modulation by the MAOI clorgyline. Horm Behav 45:23–30
Culver KE, Rosenfeld JM, Szechtman H (2000) A switch mechanism between locomotion and mouthing implicated in sensitization to quinpirole in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 151:202–210
Culver KE, Rosenfeld JM, Szechtman H (2002) Monoamine oxidase inhibitor-induced blockade of locomotor sensitization to quinpirole: role of striatal dopamine uptake inhibition. Neuropharmacology 43:385–393
Drai D, Golani I (2001) SEE: a tool for the visualization and analysis of rodent exploratory behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:409–426
Drai D, Benjamini Y, Golani I (2000) Statistical discrimination of natural modes of motion in rat exploratory behavior. J Neurosci Methods 96:119–131
Drai D, Kafkafi N, Benjamini Y, Elmer G, Golani I (2001) Rats and mice share common ethologically relevant parameters of exploratory behavior. Behav Brain Res 125:133–140
Eilam D, Szechtman H (1989) Biphasic effect of D-2 agonist quinpirole on locomotion and movements. Eur J Pharmacol 161:151–157
Eilam D, Szechtman H (2005) Psychostimulant-induced behavior as an animal model of obsessive-compulsive disorder: an ethological approach to the form of compulsive rituals. CNS Spectr 10:191–202
Eilam D, Clements KV, Szechtman H (1991) Differential effects of D1 and D2 dopamine agonists on stereotyped locomotion in rats. Behav Brain Res 45:117–124
Eilam D, Talangbayan H, Canaran G, Szechtman H (1992) Dopaminergic control of locomotion, mouthing, snout contact, and grooming: opposing roles of D1 and D2 receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 106:447–454
Fang J, Yu PH (1994) Effect of L-deprenyl, its structural analogues and some monoamine oxidase inhibitors on dopamine uptake. Neuropharmacology 33:763–768
Golani I, Benjamini Y, Eilam D (1993) Stopping behavior: constraints on exploration in rats (Rattus norvegicus). Behav Brain Res 53:21–33
Greenshaw AJ (1986) Osmotic mini-pumps: a convenient program for weight-adjusted filling concentrations. Brain Res Bull 16:759–761
Haefely W, Burkard WP, Cesura AM, Kettler R, Lorez HP, Martin JR, Richards JG, Scherschlicht R, Da Prada M (1992) Biochemistry and pharmacology of moclobemide, a prototype RIMA. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 106:S6–S14
Imperato A, Tanda G, Frau R, Di Chiara G (1988) Pharmacological profile of dopamine receptor agonists as studied by brain dialysis in behaving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:257–264
Itzhak Y, Mash D, Zhang SH, Stein I (1991a) Characterization of N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) binding sites in C57BL/6 mouse brain: mutual effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors and sigma ligands on MPTP and sigma binding sites. Mol Pharmacol 39:385–393
Itzhak Y, Stein I, Zhang SH, Kassim CO, Cristante D (1991b) Binding of sigma-ligands to C57BL/6 mouse brain membranes: effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors and subcellular distribution studies suggest the existence of sigma-receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:141–148
Kettler R, Da Prada M, Burkard WP (1990) Comparison of monoamine oxidase-A inhibition by moclobemide in vitro and ex vivo in rats. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 360:101–102
Koeltzow TE, Austin JD, Vezina P (2003) Behavioral sensitization to quinpirole is not associated with increased nucleus accumbens dopamine overflow. Neuropharmacology 44:102–110
Lai JC, Leung TK, Guest JF, Lim L, Davison AN (1980) The monoamine oxidase inhibitors clorgyline and L-deprenyl also affect the uptake of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin by rat brain synaptosomal preparations. Biochem Pharmacol 29:2763–2767
Lee SP, So CH, Rashid AJ, Varghese G, Cheng R, Lanca AJ, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2004) Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor co-activation generates a novel phospholipase C-mediated calcium signal. J Biol Chem 279:35671–35678
Lefever DW (1926) Measuring geographic concentration by means of the standard deviation ellipse. AJS 32:88–94
Levant B (2002) Novel drug interactions at D2 dopamine receptors: modulation of [3H]quinpirole binding by monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Life Sci 71:2691–2700
Levant B, Grigoriadis DE, DeSouza EB (1993) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors inhibit [3H]quinpirole binding in rat striatal membranes. Eur J Pharmacol 246:171–178
Levant B, Moehlenkamp JD, Morgan KA, Leonard NL, Cheng CC (1996) Modulation of [H-3]quinpirole binding in brain by monoamine oxidase inhibitors: evidence for a potential novel binding site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:145–153
Levant B, Gilliland SL, Culver KE, Szechtman H (2000) Novel drug interactions at CNS dopamine receptors: potential role in psychopathology and toxicity. In: Williams GM, Aruoma OI (eds) Molecular drug metabolism and toxicity. OICA, St. Lucia, pp 201–216
Levant B, Morgan KA, Ahlgren-Beckendorf JA, Grandy DK, Chen K, Shih JC, Seif I (2001) Modulation of [3H]quinpirole binding at striatal D2 dopamine receptors by a monoamine oxidase A-like site: evidence from radioligand binding studies and D2 receptor- and MAO(A)-deficient mice. Life Sci 70:229–241
Levine N (2004) CrimeStat III: a spatial statistics program for the analysis of crime incident locations (version 3.0). Ned Levine & Associates, Houston, TX/National Institute of Justice, Washington, DC. Available at http://www.nedlevine.com/nedlevine17.htm
Lione LA, Nutt DJ, Hudson AL (1998) Characterisation and localisation of [3H]2-(2-benzofuranyl)-2-imidazoline binding in rat brain: a selective ligand for imidazoline I2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 353:123–135
Noldus LP, Trienes RJ, Hendriksen AH, Jansen H, Jansen RG (2000) The Observer Video-Pro: new software for the collection, management, and presentation of time-structured data from videotapes and digital media files. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 32:197–206
Noldus LP, Spink AJ, Tegelenbosch RA (2001) EthoVision: a versatile video tracking system for automation of behavioral experiments. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 33:398–414
Olmos G, Gabilondo AM, Miralles A, Escriba PV, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1993) Chronic treatment with the monoamine oxidase inhibitors clorgyline and pargyline down-regulates non-adrenoceptor [3H]-idazoxan binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol 108:597–603
Piazza PV, Deminiere JM, Le Moal M, Simon H (1989) Factors that predict individual vulnerability to amphetamine self-administration. Science 245:1511–1513
Robinson TE, Becker JB (1986) Enduring changes in brain and behavior produced by chronic amphetamine administration: a review and evaluation of animal models of amphetamine psychosis. Brain Res 396:157–198
Segal DS, Schuckit MA (1983) Animal models of stimulant-induced psychosis. In: Creese I (ed) Stimulants: neurochemical, behavioral and clinical perspectives. Raven, NY, pp 131–167
Segal DS, Kuczenski R, Okuda C (1992) Clorgyline-induced increases in presynaptic DA: changes in the behavioral and neurochemical effects of amphetamine using in vivo microdialysis. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 42:421–429
So CH, Varghese G, Curley KJ, Kong MM, Alijaniaram M, Ji X, Nguyen T, O’Dowd BF, George SR (2005) D1 and d2 dopamine receptors form heterooligomers and cointernalize after selective activation of either receptor. Mol Pharmacol 68:568–578
Spink AJ, Tegelenbosch RA, Buma MO, Noldus LP (2001) The EthoVision video tracking system—a tool for behavioral phenotyping of transgenic mice. Physiol Behav 73:731–744
Sullivan R, Dogaru C, Szechtman H (1992) Constriction of environmental space and the behavioral response to the dopamine agonist quinpirole. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:1217–1219
Szechtman H (2004) Context gives meaning. Commentary on Badiani and Robinson drug-induced neurobehavioral plasticity: the role of environmental context. Behav Pharmacol 15:381–385
Szechtman H, Talangbayan H, Eilam D (1993) Environmental and behavioral components of sensitization induced by the dopamine agonist quinpirole. Behav Pharmacol 4:405–410
Szechtman H, Dai H, Mustafa S, Einat H, Sullivan RM (1994a) Effects of dose and interdose interval on locomotor sensitization to the dopamine agonist quinpirole. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48:921–928
Szechtman H, Talangbayan H, Canaran G, Dai H, Eilam D (1994b) Dynamics of behavioral sensitization induced by the dopamine agonist quinpirole and a proposed central energy control mechanism [published erratum appears in Psychopharmacology (Berl) 116(1):124, 1994 (Sep)]. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 115:95–104
Szechtman H, Sulis W, Eilam D (1998) Quinpirole induces compulsive checking behavior in rats: a potential animal model of obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). Behav Neurosci 112:1475–1485
Szechtman H, Culver K, Eilam D (1999) Role of dopamine systems in obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): implications from a novel psychostimulant-induced animal model. Pol J Pharmacol 51:55–61
Szumlinski KK, Allan M, Talangbayan H, Tracey A, Szechtman H (1997) Locomotor sensitization to quinpirole: environment-modulated increase in efficacy and context-dependent increase in potency. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 134:193–200
Tukey JW (1977) Exploratory data analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA
Ventura MA (1982) Effects of clorgyline and deprenil on corticosterone levels in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 81:349–355
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Antonio Páez, School of Geography and Geology, McMaster University, for suggesting the use of the standard deviational ellipse to measure spatial dispersion of trajectories; Dr. Ilan Golani, Department of Zoology, Tel-Aviv University, for making available the SEE software package used in analysis of locomotor data; Donna Waxman and Rich Hilsden for help in testing the animals; and Savio Yu, Dawn Graham, and Robyn Whitney for assistance in processing the data. This study was supported by operating grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (MOP-64424) and from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (RGPIN A0544).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dvorkin, A., Culver, K.E. & Szechtman, H. Differential effects of clorgyline on sensitization to quinpirole in rats tested in small and large environments. Psychopharmacology 186, 534–543 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0377-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0377-4