Abstract
Rationale and objectives
We and others have shown that a stressor commonly used in laboratory studies, intermittent footshock, reinstates alcohol seeking in a rat relapse model. The effects of more ethologically relevant stressors on reinstatement have not been examined. Here, we characterized the effects of social defeat (a naturalistic stressor) or a cue associated with the defeat experience on reinstatement of alcohol seeking. We also examined the effect of unconditioned and conditioned social defeat on alcohol self-administration.
Methods
Rats were trained to self-administer alcohol (12% w/v, 1 h day−1), and after stable responding, one group of animals received five exposures to social defeat paired with peppermint odor prior to daily self-administration sessions. After three more self-administration sessions, these rats were tested for the effects of the peppermint odor cue on self-administration. In another group of rats, the effects of three daily exposures to social defeat paired with peppermint odor on extinction of responding were examined. After further extinction sessions, the effect of the odor cue on reinstatement was tested in these animals. The acute effect of social defeat on reinstatement was examined in another group of animals.
Results
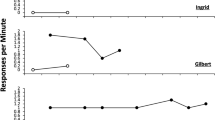
Acute exposure to social defeat decreased alcohol self-administration, reduced rates of responding during extinction, and did not reinstate alcohol seeking. Exposure to a discrete odor cue previously paired with social defeat decreased alcohol self-administration but induced modest reinstatement of alcohol seeking.
Conclusions
Results provide the first demonstration of reinstatement of alcohol seeking by a cue paired with social defeat and are also in agreement with previous findings on the suppressive effect of social defeat stress on alcohol self-administration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown SA, Vik PW, Patterson TL, Grant I, Schuckit MA (1995) Stress, vulnerability and adult alcohol relapse. J Stud Alcohol 56:538–545
Chung KK, Martinez M, Herbert J (1999) Central serotonin depletion modulates the behavioural, endocrine and physiological responses to repeated social stress and subsequent c-fos expression in the brains of male rats. Neuroscience 92:613–625
Chung KK, Martinez M, Herbert J (2000) c-fos expression, behavioural, endocrine and autonomic responses to acute social stress in male rats after chronic restraint: modulation by serotonin. Neuroscience 95:453–463
Cooper ML, Russell M, Skinner JB, Frone MR, Mudar P (1992) Stress and alcohol use: moderating effects of gender, coping and alcohol expectancies. J Abnorm Psychol 101:139–152
Covington HE 3rd, Miczek KA (2001) Repeated social-defeat stress, cocaine or morphine. Effects on behavioral sensitization and intravenous cocaine self-administration “binges”. Psychopharmacology 158:388–398
Covington HE 3rd, Kikusui T, Goodhue J, Nikulina EM, Hammer RP Jr, Miczek KA (2005) Brief social defeat stress: long lasting effects on cocaine taking during a binge and zif268 mRNA expression in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:310–321
Fuchs RA, Evans KA, Parker MP, See RE (2004) Differential involvement of orbitofrontal cortex subregions in conditioned cue-induced and cocaine-primed reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. J Neurosci 24:6600–6610
Funk D, Vohra S, Le AD (2004) Influence of stressors on the rewarding effects of alcohol in Wistar rats: studies with alcohol deprivation and place conditioning. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 176:82–87
Haller J, Leveleki C, Baranyi J, Mikics E, Bakos N (2003) Stress, social avoidance and anxiolytics: a potential model of stress-induced anxiety. Behav Pharmacol 14:439–446
Haney M, Maccari S, Le Moal M, Simon H, Piazza PV (1995) Social stress increases the acquisition of cocaine self-administration in male and female rats. Brain Res 698:46–52
Kabbaj M, Norton CS, Kollack-Walker S, Watson SJ, Robinson TE, Akil H (2001) Social defeat alters the acquisition of cocaine self-administration in rats: role of individual differences in cocaine-taking behavior. Psychopharmacology 158:382–387
Kierniesky N, Beaton R, McAbee D, Sheftic J (1980) Acquisition of an avoidance response in rats during conditioned suppression. J Gen Psychol 103:221–225
Koob GF, Britton KT (1996) Neurobiological substrates for the anti-anxiety effects of ethanol. In: Begleiter H, Kissin B (eds) The pharmacology of alcohol and alcohol dependence. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 477–506
Le A, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to alcohol in rats. Pharmacol Ther 94:137–156
Le AD, Quan B, Juzystch W, Fletcher PJ, Joharchi N, Shaham Y (1998a) Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 135:169–174
Le AD, Quan B, Juzytsch W, Fletcher PJ, Joharchi N, Shaham Y (1998b) Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 135:169
Le AD, Poulos CX, Harding S, Watchus W, Juzytsch W, Shaham Y (1999) Effects of naltrexone and fluoxetine on alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol seeking induced by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:435–444
Le AD, Harding S, Watchus W, Juzytsch W, Shalev U, Shaham Y (2000) The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in stress-induced relapse to alcohol-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 150:317–324
Le AD, Harding S, Juzytsch W, Fletcher PJ, Shaham Y (2002) The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in the median raphe nucleus in relapse to alcohol. J Neurosci 22:7844–7849
Le AD, Harding S, Juzytsch W, Funk D, Shaham Y (2005) Role of alpha-2 adrenoceptors in stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking and alcohol self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:366–373
LeDoux JE (2000) Emotion circuits in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 23:155–184
LeDoux JE, Iwata J, Pearl D, Reis DJ (1986) Disruption of auditory but not visual learning by destruction of intrinsic neurons in the rat medial geniculate body. Brain Res 371:395–399
Li Z, Zhou Q, Li L, Mao R, Wang M, Peng W, Dong Z, Xu L, Cao J (2005) Effects of unconditioned and conditioned aversive stimuli in an intense fear conditioning paradigm on synaptic plasticity in the hippocampal CA1 area in vivo. Hippocampus 15:815–824
Linseman MA (1987) Alcohol consumption in free feeding rats: procedure, genetic and pharmacokinetic factors. Psychopharmacology 92:254–261
Liu X, Weiss F (2002) Additive effect of stress and drug cues on reinstatement of ethanol seeking: exacerbation by history of dependence and role of concurrent activation of corticotropin-releasing factor and opioid mechanisms. J Neurosci 22:7856–7861
Liu X, Weiss F (2003) Stimulus conditioned to foot-shock stress reinstates alcohol-seeking behavior in an animal model of relapse. Psychopharmacology 168:184–191
Martin-Fardon R, Ciccocioppo R, Massi M, Weiss F (2000) Nociceptin prevents stress-induced ethanol- but not cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuroreport 11:1939–1943
Martinez M, Calvo-Torrent A, Herbert J (2002) Mapping brain response to social stress in rodents with c-fos expression: a review. Stress 5:3–13
Mechiel Korte S, De Boer SF (2003) A robust animal model of state anxiety: fear-potentiated behaviour in the elevated plus-maze. Eur J Pharmacol 463:163–175
Meerlo P, Overkamp GJ, Daan S, Van Den Hoofdakker RH, Koolhaas JM (1996) Changes in behaviour and body weight following a single or double social defeat in rats. Stress 1:21–32
Miczek KA (1979) A new test for aggression in rats without aversive stimulation: differential effects of d-amphetamine and cocaine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 60:253–259
Miczek KA, Mutschler NH (1996) Activational effects of social stress on IV cocaine self-administration in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 128:256–264
Miczek KA, Nikulina E, Kream RM, Carter G, Espejo EF (1999) Behavioral sensitization to cocaine after a brief social defeat stress: c-fos expression in the PAG. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141:225–234
Nie H, Janak PH (2003) Comparison of reinstatement of ethanol- and sucrose-seeking by conditioned stimuli and priming injections of allopregnanolone after extinction in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:222–228
Nikulina EM, Marchand JE, Kream RM, Miczek KA (1998) Behavioral sensitization to cocaine after a brief social stress is accompanied by changes in fos expression in the murine brainstem. Brain Res 810:200–210
Otto T, Cousens G, Herzog C (2000) Behavioral and neuropsychological foundations of olfactory fear conditioning. Behav Brain Res 110:119–128
Pohorecky LA (1990) Interaction of ethanol and stress: research with experimental animals—an update. Alcohol and Alcoholism 25:263
Ripley TL, O'Shea M, Stephens DN (2003) Repeated withdrawal from ethanol impairs acquisition but not expression of conditioned fear. Eur J Neurosci 18:441–448
Rygula R, Abumaria N, Flugge G, Fuchs E, Ruther E, Havemann-Reinecke U (2005) Anhedonia and motivational deficits in rats: impact of chronic social stress. Behav Brain Res 162:127–134
Sanger DJ, Blackman DE (1976) Rate-dependent effects of drugs: a review of the literature. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4:73–83
Sgoifo A, Koolhaas J, Alleva E, Musso E, Parmigiani S (2001) Social stress. Acute and long-term effects on physiology and behavior. Physiol Behav 73:253–254
Shaham Y (1996) Effect of stress on opioid-seeking behavior: evidence from studies with rats. Ann Behav Med 18:255–263
Shaham Y, Erb S, Stewart J (2000) Stress-induced relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking in rats: a review. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33:13–33
Shaham Y, Miczek KA (2003) Reinstatement-toward a model of relapse. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:1–2
Shaham Y, Shalev U, Lu L, De Wit H, Stewart J (2002) The reinstatement model of drug relapse: history, methodology and major findings. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 168:3–20
Shalev U, Highfield D, Yap J, Shaham Y (2000) Stress and relapse to drug seeking in rats: studies on the generality of the effect. Psychopharmacology 150:337–346
Shalev U, Grimm JW, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: a review. Pharmacol Rev 54:1–42
Tidey JW, Miczek KA (1996) Social defeat stress selectively alters mesocorticolimbic dopamine release: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 721:140–149
Tidey JW, Miczek KA (1997) Acquisition of cocaine self-administration after social stress: role of accumbens dopamine. Psychopharmacology 130:203–212
Tornatzky W, Miczek KA (1993) Long-term impairment of autonomic circadian rhythms after brief intermittent social stress. Physiol Behav 53:983–993
Tornatzky W, Miczek KA (1994) Behavioral and autonomic responses to intermittent social stress: differential protection by clonidine and metoprolol. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 116:346–356
van Erp AM, Miczek KA (2001) Persistent suppression of ethanol self-administration by brief social stress in rats and increased startle response as index of withdrawal. Physiol Behav 73:301–311
van Erp AM, Tachi N, Miczek KA (2001) Short or continuous social stress: suppression of continuously available ethanol intake in subordinate rats. Behav Pharmacol 12:335–342
Acknowledgments
This work was support by grants from the NIAAA (AD Lê). The authors wish to thank Dr. Mohamed Kabbaj for his advice on the social defeat procedure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Funk, D., Harding, S., Juzytsch, W. et al. Effects of unconditioned and conditioned social defeat on alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 183, 341–349 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0194-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0194-1