Abstract
Rationale
Auditory gating deficits observed in patients with schizophrenia have been modeled in animals administered the indirect-acting monoaminergic agonist, d-amphetamine (AMPH). The atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine (CLOZ) reverses the disruption of auditory gating in schizophrenic patients. However, its effects on psychostimulant-induced deficits in animals have yet to be assessed.
Objectives
In the present series of experiments, an auditory evoked potential paradigm was used to: (a) confirm the ability of AMPH to alter auditory gating in the anesthetized rat, (b) specify the nature of the accompanying change(s) in evoked potential waveforms and (c) determine the effects of CLOZ administration on AMPH-induced alterations in auditory gating.
Methods
We compared the effects of acute (5 mg/kg, i.p.) and chronic (28 days, 0.5 mg/ml in drinking water) CLOZ on AMPH-induced (1.8 mg/kg, i.p.) alterations in evoked potentials recorded in the hippocampus of anesthetized rats during presentation of a pair of identical tones. Gating was assessed by comparing the amplitude of conditioning and test responses in CLOZ and AMPH-treated rats.
Results
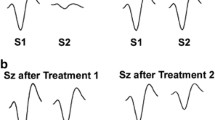
The ratio of test to conditioning response amplitude (T/C ratio) was not altered by vehicle or CLOZ alone. However, T/C ratio was significantly increased following AMPH due to suppression of the conditioning response. Acute but not chronic CLOZ attenuated but did not prevent the increase in T/C ratio.
Conclusions
Qualitative differences between the idiopathic gating deficits observed in schizophrenic patients and AMPH-induced increases in T/C ratio in animals limit this models utility as a means of evaluating the ability of atypical antipsychotic drugs to restore normal sensory gating.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler LE, Pachtman E, Franks RD, Pecevich M, Waldo MC, Freedman R (1982) Neurophysiological evidence for a defect in neuronal mechanisms involved in sensory gating in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 17:639–654
Adler LE, Rose G, Freedman R (1986) Neurophysiological studies of sensory gating in rats: effects of amphetamine, phencyclidine, and haloperidol. Biol Psychiatry 21:787–798
Adler LE, Pang K, Gerhardt G, Rose GM (1988) Modulation of the gating of auditory evoked potentials by norepinephrine: pharmacological evidence obtained using a selective neurotoxin. Biol Psychiatry 24:179–190
Adler LE, Gerhardt GA, Franks R, Baker N, Nagamoto H, Drebing C, Freedman R (1990) Sensory physiology and catecholamines in schizophrenia and mania. Psychiatry Res 31:297–309
Adler LE, Olincy A, Waldo M, Harris JG, Griffith J, Stevens K, Flach K, Nagamoto H, Bickford P, Leonard S, Freedman R (1998) Schizophrenia, sensory gating and nicotinic receptors. Schizophr Bull 24:189–202
Bakshi VP, Swerdlow NR, Geyer MA (1994) Clozapine antagonizes phencyclidine-induced deficits in sensorimotor gating of the startle response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:787–794
Bickford PC, Luntz-Leybman V, Freedman R (1993) Auditory sensory gating in the rat hippocampus: modulation by brainstem activity. Brain Res 607:33–38
Bickford-Wimer PC, Nagamoto H, Johnson R, Adler LE, Egan M, Rose GM, Freedman R (1990) Auditory sensory gating in hippocampal neurons: a model system in the rat. Biol Psychiatry 27:183–192
Boutros NN, Zouridakis G, Overall J (1991) Replication and extension of P50 findings in schizophrenia. Clin Electroencephalogr 22:40–45
Boutros NN, Bonnet KA, Millana R, Liu J (1997) A parametric study of the N40 auditory evoked response in rats. Biol Psychiatry 42:1051–1059
Braff DL (1993) Information processing and attention dysfunctions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 19:233–259
Braff DL, Geyer MA (1990) Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:181–188
Broadbent DE (1958) Perception and communication. Pergamon Press, London
Clementz BA, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1998a) Multiple site evaluation of P50 suppression among schizophrenia and normal comparison subjects. Schizophr Res 30:71–80
Clementz BA, Geyer MA, Braff DL (1998b) Poor P50 suppression among schizophrenia patients and their first-degree biological relatives. Am J Psychiatry 155:1691–1694
Cullum CM, Harris JG, Waldo MC, Smernoff E, Madison A, Nagamoto HT, Griffith J, Adler LE, Freedman R (1993) Neurophysiological and neuropsychological evidence for attentional dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 10:131–141
de Bruin NM, Ellenbroek BA, Cools AR, Coenen AM, van Luijtelaar EL (1999) Differential effects of ketamine on gating of auditory evoked potentials and prepulse inhibition in rats. Psychopharmacology 142:9–17
Erwin RJ, Turetsky BI, Moberg P, Gur RC, Gur RE (1998) P50 abnormalities in schizophrenia: relationship to clinical and neuropsychological indices of attention. Schizophr Res 33:157–167
Flach KA, Adler LE, Gerhardt GA, Miller C, Bickford P, MacGregor RJ (1996) Sensory gating in a computer model of the CA3 neural network of the hippocampus. Biol Psychiatry 40:1230–1245
Freedman R, Adler LE, Waldo MC, Pachtman E, Franks RD (1983) Neurophysiological evidence for a defect in inhibitory pathways in schizophrenia: comparison of medicated and drug-free patients. Biol Psychiatry 18:537–551
Freedman R, Adler LE, Gerhardt GA (1987) Neurobiological studies of sensory gating in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:669–678
Freedman R, Waldo M, Bickford-Wimer P, Nagamoto H (1991) Elementary neuronal dysfunctions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 4:233–243
Freedman R, Adler LE, Myles-Worsley M, Nagamoto HT, Miller C, Kisley M, McRae K, Cawthra E, Waldo M (1996) Inhibitory gating of an evoked response to repeated auditory stimuli in schizophrenic and normal subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:1114–1121
Gao XM, Hashimoto T, Cooper TB, Tamminga CA (1997) The dose-response characteristics of rat oral dyskinesias with chronic haloperidol or clozapine administration. J Neural Transm 104:97–104
Geyer MA, Markou A (1995) Animal models of psychiatric disorders. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 787–798
Jin Y, Potkin SG, Patterson JV, Sandman CA, Hetrick WP, Bunney WE Jr (1997) Effects of P50 temporal variability on sensory gating in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 70:71–81
Jin Y, Bunney WE Jr, Sandman CA, Patterson JV, Fleming K, Moenter JR, Kalali AH, Hetrick WP, Potkin SG (1998) Is P50 suppression a measure of sensory gating in schizophrenia? Biol Psychiatry 43:873–878
Joy B, Shepard PD (2002) Clozapine attenuates the disruptive effects of d-amphetamine on auditory sensory gating in the rat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 28:185.11
Kapur S, Seeman P (2000) Antipsychotic agents differ in how fast they come off the dopamine D2 receptors. J Psychiatry Neurosci 25:161–166
Leonard S, Adams C, Breese CR, Adler LE, Bickford P, Byerley W, Coon H, Griffith JM, Miller C, Myles-Worsley M, Nagamoto HT, Rollins Y, Stevens KE, Waldo M, Freedman R (1996) Nicotinic receptor function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 22:431–445
Light GA, Braff DL (2000) Do self-reports of perceptual anomalies reflect gating deficits in schizophrenia patients? Biol Psychiatry 47:463–467
Light GA, Malaspina D, Geyer MA, Luber BM, Coleman EA, Sackeim HA, Braff DL (1999) Amphetamine disrupts P50 suppression in normal subjects. Biol Psychiatry 46:990–996
Light GA, Geyer MA, Clementz BA, Cadenhead KS, Braff DL (2000) Normal P50 suppression in schizophrenia patients treated with atypical antipsychotic medications. Am J Psychiatry 157:767–771
McGhie A, Chapman J (1961) Disorders of attention and perception in early schizophrenia. Proc R Soc Med 34:103–116
Miller CL, Bickford PC, Luntz-Leybman V, Adler LE, Gerhardt GA, Freedman R (1992) Phencyclidine and auditory sensory gating in the hippocampus of the rat. Neuropharmacology 31:1041–1048
Miller CL, Bickford PC, Wiser AK, Rose GM (1995) Long-term potentiation disrupts auditory gating in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 15:5820–5830
Nagamoto HT, Adler LE, Hea RA, Griffith JM, McRae KA, Freedman R (1996) Gating of auditory P50 in schizophrenics: unique effects of clozapine. Biol Psychiatry 40:181–188
Nagamoto HT, Adler LE, McRae KA, Huettl P, Cawthra E, Gerhardt G, Hea R, Griffith J (1999) Auditory P50 in schizophrenics on clozapine: improved gating parallels clinical improvement and changes in plasma 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol. Neuropsychobiology 39:10–17
Oranje B, Gispen-de Weid CC, Verbaten MN, Kahn RS (2002) Modulating sensory gating in healthy volunteers: the effects of ketamine and haloperidol. Biol Psychiatry 52:887–895
Patterson JV, Jin Y, Gierczak M, Hetrick WP, Potkin S, Bunney WE Jr, Sandman CA (2000) Effects of temporal variability on p50 and the gating ratio in schizophrenia: a frequency domain adaptive filter single-trial analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:57–64
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Perry PJ, Miller DD, Arndt SV, Cadoret RJ (1991) Clozapine and norclozapine plasma concentrations and clinical response of treatment-refractory schizophrenia patients. Am J Psychiatry 148:231–235
Potkin SG, Potkin SG, Bera R, Gulasekaram B, Costa J, Hayes S, Jin Y, Richmond G, Carreon D, Sitanggan K, Berger B, Telford J, Plon L, Plon H, Park L, Chang YJ, Oldroyd J, Cooper TB (1994) Plasma clozapine concentrations predict clinical-response in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 55[Suppl B]:133–136
Seeman P (2002) Atypical antipsychotics: mechanism of action. Can J Psychiatry 47:27–38
Seeman P, Corbett R, Van Tol HHM (1997) Atypical neuroleptics have low affinity for dopamine D-2 receptors or are selective for D-4 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 16:93–110
Shepard PD, Joy B, Clerkin L, Schwarcz R (2003) Micromolar brain levels of kynurenic acid are associated with a disruption of auditory sensory gating in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1454–1462
Simosky JK, Stevens KE, Adler LE, Freedman R (2003) Clozapine improves deficient inhibitory auditory processing in DBA/2 mice, via a nicotinic cholinergic mechanism. Psychopharmacology 165:386–396
Stevens KE, Wear KD (1997) Normalizing effects of nicotine and a novel nicotinic agonist on hippocampal auditory gating in two animal models. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 57:869–874
Stevens KE, Fuller LL, Rose GM (1991) Dopaminergic and noradrenergic modulation of amphetamine-induced changes in auditory gating. Brain Res 555:91–98
Stevens KE, Meltzer J, Rose GM (1995) Nicotinic cholinergic normalization of amphetamine-induced loss of auditory gating in freely moving rats. Psychopharmacology 119:163–170
Stevens KE, Freedman R, Collins AC, Hall M, Leonard S, Marks MJ, Rose GM (1996) Genetic correlation of inhibitory gating of hippocampal auditory evoked response and α-bungarotoxin-binding nicotinic cholinergic receptors in inbred mouse strains. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:152–162
Stevens KE, Kem WR, Mahnir VM, Freedman R (1998) Selective α7-nicotinic agonists normalize inhibition of auditory response in DBA mice. Psychopharmacology 136:320–327
Sun L, Lau CE (2000) Intravenous and oral clozapine pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and concentration-effect relations: acute tolerance. Eur J Pharmacol 398:225–238
Van Berckel BNM, Oranje B, van Ree JM, Verbaten MN, Kahn RS (1998) The effects of low-dose ketamine on sensory gating, neuroendocrine secretion and behavior in healthy human subjects. Psychopharmacology 137:271–281
Venables P (1964) Input dysfunction in schizophrenia. In: Maher BA (ed) Progress in experimental personality research, vol. 2. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 3–69
Wilson JM, Sanyal S, Van Tol HHM (1998) Dopamine D-2 and D-4 receptor ligands: relation to antipsychotic action. Eur J Pharmacol 351:273–286
Zhang J, Forkstam C, Engel JA, Svensson L (2000) Role of dopamine in prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle. Psychopharmacology 149:181–188
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their gratitude to Drs. R. Buchanan and G. Elmer, Ms. Ann Summerfelt and Lucy Clerkin for their insightful comments and editorial assistance during the preparation of this manuscript. Supported by a grant from Novartis Pharma AG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joy, B., McMahon, R.P. & Shepard, P.D. Effects of acute and chronic clozapine on d-amphetamine-induced disruption of auditory gating in the rat. Psychopharmacology 174, 274–282 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1731-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1731-4