Abstract
Rationale
Teenage drinking is a cause of growing concern in industrialized countries, where almost 35% of alcohol drinkers are under 16 years old. Increased anxiety, irritability and depression among adolescents may induce them to seek the anxiolytic and rewarding properties of alcohol. Allopregnanolone is rewarding in rodents, and therefore may contribute to the effects of alcohol.
Objective
In this paper, we studied the effects of acute alcohol intoxication on the plasma levels of allopregnanolone in male adolescents.
Methods
Blood samples were drawn from male adolescents who arrived at the Emergency Department of the Hospital. Two groups were studied: one study group was formed by adolescents who arrived with evident behavioral symptoms of acute alcohol intoxication (AAI) and the other by those arriving for mild trauma (contusions, sprains) after no consumption of alcohol (Controls).
Results
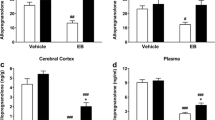
Our results demonstrate that AAI significantly increases serum allopregnanolone levels in male adolescents.
Conclusions
Because alcohol and allopregnanolone positively modulate gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors, allopregnanolone may play a major role in the anxiolytic and rewarding effects of alcohol, either directly or by influencing the sensitivity of GABAA receptors to alcohol.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson SH, Crönholm F, Sjövall J (1986) Redox effects of ethanol on steroid metabolism. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 10:55S–61S
Bailey SL, Valery RJ (1993) Dimensions of adolescent problem drinking. J Stud Alcohol 54:555–565
Colby HD, Malendowicz LK, Caffrey JL, Kitay JI (1975) Role of adrenal 5-alpha-reductase activity in determining the responsiveness of hypophysectomized rats to ACTH. Endocrinology 96:1153–1157
Finn DA, Phillip TJ, Okorn DM, Chester JA, Cunningham CL (1997) Rewarding effects of the neuroactive steroid 3α-hydroxy-5α-pregnan-20-one in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 56:261–264
Frias J, Rodriguez R, Torres JM, Ruiz E, Ortega E (2000) Effects of acute alcohol intoxication on pituitary-gonadal axis, pituitary-adrenal axis hormones, β-endorphin and prolactin in human adolescents of both sexes. Life Sci 67:1081–1806
Frias J, Torres JM, Miranda MT, Ruiz E, Ortega E (2002) Effects of acute alcohol intoxication on pituitary-gonadal axis, pituitary-adrenal axis hormones, β-endorphin and prolactin in human adults of both sexes. Alcohol Alcohol 37:169–173
Genazzani AR, Petraglia F, Bernardi F, Casarosa E, Salvestroni C, Tonetti A, Nappi E, Luisi S, Palumbo M, Purdy RH, Luisi M (1998) Circulating levels of allopregnanolone in humans: gender, age and endocrine influences. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:2099–2103
Genazzani AD, Luisi M, Malavasi B, Stucchi C, Stefano L, Casarosa E, Bernardi F, Genazzani AR, Petraglia F (2002) Pulssatile secretory characteristics of allopregnanolone, a neuroactive steroids, during the menstrual cycle and in amenorrheic subjects. Eur J Endocrinol 146:347–356
Grobin AC, Matthees DB, Devaud LL, Morrow AL (1998) The role of GABAa receptors in the acute and chronic effects of ethanol. Psychopharmacology 139:2–19
Khisti RT, Penland SN, VanDoren MJ, Grobin AC, Morrow AL (2002) GABAergic neurosteroid modulation of ethanol actions. World J Biol Psychiatry 3:87–95
Lambert JJ, Belelli D, Hill-Venning C, Peters JA (1995) Neurosteroids and GABA receptors function. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:295–303
Melcangi RC, Poletti A, Cavarretta I, Celotti F, Colciago A, Magnaghi V, Motta M, Negri-Cesi P, Martini L (1998) The 5α-reductase in the central nervous system: expression and modes of control. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 65:295–299
Morrow AL, Janis GC, VanDoren MJ, Matthews DB, Samson HH, Janak PH, Grant KA (1999) Neurosteroids mediate pharmacological effects of ethanol: a new mechanism of ethanol action? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1933–1940
Morrow AL, VanDoren MJ, Penland SN, Matthew DB (2001a) The role of GABAergic neuroactive steroids in ethanol action, tolerance and dependence. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 37:98–109
Morrow AL, VanDoren MJ, Fleming R, Penland S (2001b) Ethanol and neurosteroid interactions in the brain. Int Rev Neurobiol 46:349–377
Patchev VK, Hassan AH, Holsboer DF, Almeida OF (1996) The neurosteroid tetrahydroprogesterone attenuates the endocrine response to stress and exerts glucocorticoid-like effects on vasopressin gene transcription in the rat hypothalamus. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:533–540
Purdy RH, Morrow L, Moor PH, Paul SM (1991) Stress-induced elevation of aminobutyric acid type A receptor active steroids in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:4553–4557
Shope JT, Copeland LA, Dielman TE (1994) Measurement of alcohol use and misuse in a cohort of students followed from grade 6 through grade 12. Alcoholism 18:726–733
Torres JM, Ortega E (2003) Alcohol intoxication increases allopregnanolone levels in female adolescent human. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1207–1209
Torres JM, Ruiz E, Ortega E (2001) Effects of CRH and ACTH administration on plasma and brain neurosteroid levels. Neurochem Res 26:555–558
VanDoren MJ, Matthews DB, Janis GC, Grobin AC, Devaud LL, Morrow AL (2000) Neuroactive steroid 3alpha-hydroxy-5alpha-pregnan-20-one modulates electrophysiological and behavioral actions of ethanol. J Neurosci 20:1982–1989
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Dr. R.H. Purdy for the generous gift of allopregnanolone antibody. We thank R. Davies for revising the English text and M. Quintana and R. Arcas for their technical assistance. The authors are indebted to the Clinico University and Trauma Hospitals of Granada for their help. This work was funded in part by ISCiii FIS-PI021625 and by the Andalusian Regional Government through its “Endocrinology and Metabolism” research group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, J.M., Ortega, E. Alcohol intoxication increases allopregnanolone levels in male adolescent humans. Psychopharmacology 172, 352–355 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1662-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1662-0