Heading
Abstract
Rationale. Critics have called into question findings from double-blind placebo-controlled studies because subjects are given drug administration instructions informing them of a placebo condition. The assertion that these drug administration instructions bias estimates of effectiveness has undergone surprisingly little empirical investigation.
Objectives. The primary objective of this study was to determine whether drug administration instructions informing subjects of a placebo condition affect the drug response and affect the saliva concentration of the stimulant.
Methods. We assessed caffeine responses and levels of saliva concentration of caffeine in 52 subjects who were randomly assigned to receive one of two drug administration instructions: (a) placebo-informed instructions (i.e., individuals informed of the placebo) analogous to those used in double-blind studies and (b) placebo-uninformed instructions (i.e., individuals informed they are taking an active stimulant).
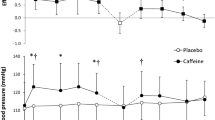
Results. On most measures (systolic blood pressure, heart rate, hand steadiness, reaction time, fatigue, and tension), drug administration instructions did not significantly influence caffeine response. Instructions also had no significant effect on saliva concentration of caffeine. However, only individuals who were uninformed of the placebo condition showed significant diastolic blood pressure and vigor increases with 125 mg caffeine, and significant hand steadiness impairment and vigor increases with 325 mg caffeine compared to placebo.
Conclusions. These overall findings suggest that a limited bias is introduced by drug administration instructions. The results do not support any suggestion that information about the existence of a placebo condition dramatically influences conclusions drawn about drug responses in placebo-controlled trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nash, J.M., Holroyd, K.A., Rokicki, L.A. et al. The influence of placebo awareness on stimulant drug response in a double-blind trial. Psychopharmacology 161, 213–221 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1050-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1050-1