Abstract
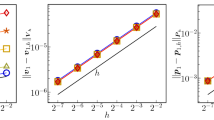
We present the formulation and the numerical analysis of the Brinkman problem derived in Allaire (Arch Rational Mech Anal 113(3): 209–259,1990. doi:10.1007/BF00375065, Arch Rational Mech Anal 113(3): 261–298, 1990. doi:10.1007/BF00375066) with a lognormal random permeability. Specifically, the permeability is assumed to be a lognormal random field taking values in the symmetric matrices of size \(d\times d\), where \(d\) denotes the spatial dimension of the physical domain \(D\). We prove that the solutions admit bounded moments of any finite order with respect to the random input’s Gaussian measure. We present a Mixed Finite Element discretization in the physical domain \(D\), which is uniformly stable with respect to the realization of the lognormal permeability field. Based on the error analysis of this mixed finite element method (MFEM), we develop a multi-level Monte Carlo (MLMC) discretization of the stochastic Brinkman problem and prove that the MLMC-MFEM allows the estimation of the statistical mean field with the same asymptotical accuracy versus work as the MFEM for a single instance of the stochastic Brinkman problem. The robustness of the MFEM implies in particular that the present analysis also covers the Darcy diffusion limit. Numerical experiments confirm the theoretical results.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
CSC - IT Center for Science, www.csc.fi.
Matlab R2010a, compiler version 4.11, gcc version 4.4.3.
OpenMPI version 1.4.3.
References
Adams, R.A., Fournier, J.J.F.: Sobolev spaces, Pure and Applied Mathematics (Amsterdam), vol. 140, 2nd edn. Elsevier/Academic Press, Amsterdam (2003)
Allaire, G.: Homogenization of the Navier-Stokes equations in open sets perforated with tiny holes. I. Abstract framework, a volume distribution of holes. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 113(3), 209–259 (1990). doi:10.1007/BF00375065
Allaire, G.: Homogenization of the Navier-Stokes equations in open sets perforated with tiny holes. II. Noncritical sizes of the holes for a volume distribution and a surface distribution of holes. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 113(3), 261–298 (1990). doi:10.1007/BF00375066
Barth, A., Schwab, C., Zollinger, N.: Multi-level Monte Carlo finite element method for elliptic PDEs with stochastic coefficients. Numerische Mathematik 119, 132–161 (2011)
Bogachev, V.I.: Gaussian measures, Mathematical Surveys and Monographs, vol. 62. American Mathematical Society, RI (1998)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and hybrid Finite Element Methods, Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 15. Springer, New York (1991)
Charrier, J.: Strong and weak error estimates for elliptic partial differential equations with random coefficients. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(1), 216–246 (2012)
Charrier, J., Scheichl, R., Teckentrup, A.: Finite element error analysis of elliptic PDEs with random coefficients and its application to multilevel Monte Carlo methods. Tech. Rep. 2, Bath Institute for, Complex Systems (2011)
Dauge, M.: Stationary Stokes and Navier-Stokes systems on two- or three-dimensional domains with corners. I. Linearized equations. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 20(1), 74–97 (1989). doi:10.1137/0520006
Dunavant, D.A.: High degree efficient symmetrical gaussian quadrature rules for the triangle. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 21(6), 1129–1148 (1985). doi:10.1002/nme.1620210612
Fernique, X.: Intégrabilité des vecteurs gaussiens. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris Sér. A-B 270, A1698–A1699 (1970)
Franca, L.P., Stenberg, R.: Error analysis of Galerkin least squares methods for the elasticity equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 28(6), 1680–1697 (1991). doi:10.1137/0728084
Galvis, J., Sarkis, M.: Approximating infinity-dimensional stochastic Darcy’s equations without uniform ellipticity. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(5), 3624–3651 (2009). doi:10.1137/080717924
Gittelson, C.J.: Stochastic Galerkin discretization of the log-normal isotropic diffusion problem. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 20(2), 237–263 (2010). doi:10.1142/S0218202510004210
Juntunen, M., Stenberg, R.: Analysis of finite element methods for the Brinkman problem. Calcolo 47, 129–147 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10092-009-0017-6
Kellogg, R.B., Osborn, J.E.: A regularity result for the Stokes problem in a convex polygon. J. Funct. Anal. 21(4), 397–431 (1976)
Könnö, J., Stenberg, R.: Analysis of $H ({\rm div})$-elements for the Brinkman problem. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 21, 2227–2248 (2011)
Könnö, J., Stenberg, R.: Numerical computations with $H ({\rm div})$-elements for the Brinkman problem. Comput. Geosci. 2011, 1–20 (2011). doi:10.1007/s10596-011-9259-x
Lovadina, C., Stenberg, R.: Energy norm a posteriori error estimates for mixed finite element methods. Math. Comp. 75(256), 1659–1674 (2006). doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-06-01872-2
Matsumoto, M., Nishimura, T.: Mersenne twister: a 623-dimensionally equidistributed uniform pseudo-random number generator. ACM Trans. Model. Comput. Simul. 8(1), 3–30 (1998). doi:10.1145/272991.272995
Rajagopal, K.R.: On a hierarchy of approximate models for flows of incompressible fluids through porous solids. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 17(2), 215–252 (2007). doi:10.1142/S0218202507001899
Schwab, C., Gittelson, C.J.: Sparse tensor discretization of high-dimensional parametric and stochastic PDEs. In: Acta Numerica, Acta Numer., vol. 20, pp. 291–467. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge (2011)
Schwab, C., Todor, R.A.: Karhunen-Loève approximation of random fields by generalized fast multipole methods. J. Comput. Phys. 217(1), 100–122 (2006)
Teckentrup, A.L., Scheichl, R., Giles, M.B., Ullmann, E.: Further analysis of multilevel monte carlo methods for elliptic pdes with random coefficients (2012). ArXiv:1204.3476v1
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the Swiss National Science Foundation grant No. SNF 200021-120290/1 and by the European Research Council under grant ERC AdG 247277 to CS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gittelson, C.J., Könnö, J., Schwab, C. et al. The multi-level Monte Carlo finite element method for a stochastic Brinkman Problem. Numer. Math. 125, 347–386 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-013-0537-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-013-0537-5