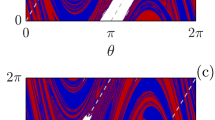
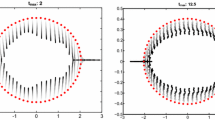
Abstract
In this paper we propose a numerical method for computing all Lyapunov coefficients of a discrete time dynamical system by spatial integration. The method extends an approach of Aston and Dellnitz (Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 170:223–237, 1999) who use a box approximation of an underlying ergodic measure and compute the first Lyapunov exponent from a spatial average of the norms of the Jacobian for the iterated map. In the hybrid method proposed here, we combine this approach with classical QR-oriented methods by integrating suitable R-factors with respect to the invariant measure. In this way we obtain approximate values for all Lyapunov exponents. Assuming somewhat stronger conditions than those of Oseledec’ multiplicative theorem, these values satisfy an error expansion that allows to accelerate convergence through extrapolation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aston P.J., Dellnitz M.: Computation of the Lyapunov exponent via spatial integration with application to blowout bifurcations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 170, 223–237 (1999)
Aston P.J., Dellnitz M.: Computation of the dominant Lyapunov exponent via spatial Integration using matrix norms. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 459, 2933–2955 (2003)
Aston, P.J., Dellnitz, M.: Computation of the dominant Lyapunov exponent via spatial integration using vector norms. In: Fiedler, B., Gröger, K., Sprekels, J. (eds.) Proceedings of the Equadiff, vol. 99, 1015–1020. World Scientific (2000)
Barreira, L., Pesin, Y.B.: Lyapunov Exponents and Smooth Ergodic Theory. University Lecture Series, vol. 23. The American Mathematical Society (2002)
Bekryaev, R.V.: Intermittent chaos and large-scale circulation regimes in the atmosphere. Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics 31(4), 1996 (English), July–August 1995 (Russian)
Beyn, W.-J., Lust, A.: Error analysis of a hybrid method for computing Lyapunov exponents. Manuscript (2009)
Bridges T.J., Reich S.: Computing Lyapunov exponents on a Stiefel manifold. Phys. D 156, 219–238 (2001)
Christiansen F., Rugh H.H.: Computing Lyapunov spectra with continous Gram-Schmidt orthonormalization. Nonlinearity 10, 1063–1072 (1997)
Dellnitz M., Froyland G., Junge O.: The algorithms behind GAIO—Set oriented numerical methods for dynamical systems. In: Fiedler, B. (eds) Ergodic Theory, Analysis and Efficient Simulation of Dynamical Systems, pp. 145–174. Springer, Heidelberg (2001)
Dellnitz M., Hohmann A.: A subdivision algorithm for the computation of unstable manifolds and global attractors. Numer. Math. 75, 293–317 (1997)
Dellnitz M., Junge O.: On the approximation of complicated dynamical behavior. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36(2), 491–515 (1999)
Dellnitz, M., Junge, O.: Set Oriented Numerical Methods for Dynamical Systems. In: Fiedler, B., Iooss, G., Kopell, N. (eds.) Handbook of Dynamical Systems II: Towards Applications, pp. 221–264. World Scientific (2002)
Dieci L., van Vleck E.S.: Computation of a few Lyapunov exponents for continuous and discrete dynamical systems. Appl. Num. Math. 17, 275–291 (1995)
Dieci L., van Vleck E.S.: Lyapunov spectral intervals: theory and computation. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 40(2), 516–542 (2002)
Dieci L., van Vleck E.S.: On the error in computing Lyapunov exponents by QR methods. Numer. Math. 101(4), 619–642 (2005)
Dieci L., van Vleck E.S.: Perturbation theory for approximation of Lyapunov exponents by QR methods. J. Dynam. Differ. Equ. 18(3), 815–840 (2006)
Eckmann J.-P., Ruelle D.: Ergodic theory of chaos and strange attractors. Rev. Mod. Phys. 57(3), 617–656 (1985)
Froyland, G., Judd, K., Mess, A.I., Murano, K.: Lyapunov exponents and triangulation. In: Proceedings of the 1993 International Symposium on Nonlinear Theory and its Applications. Hawaii, pp. 281–286 (1993)
Froyland G., Judd K., Mess A.I.: Estimation of Lyapunov exponents of dynamical systems using a spatial average. Phys. Rev. E 51(4), 2844–2855 (1995)
Geist K., Parlitz U., Lauterborn W.: Comparison of different methods for computig Lyapunov exponents. Prog. Theor. Phys. 83(5), 875–893 (1990)
Golub G.H., van Loan C.F.: Matrix Computations, 2nd edn. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore (1990)
Johnson R.A., Palmer K.J., Sell G.R.: Ergodic properties of linear dynamical systems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 18(1), 1–33 (1987)
Katok A., Hasselblatt B.: Introduction to the Modern Theory of Dynamical Systems. Cambridge University Press, London (1995)
Liapunow, A.M.: The General Problem of the Stability of Motion. Comm. Soc. Math. Kharkow 1892 (Russian); [reprinted in English, Taylor & Francis, London 1992]
Lundström, N.: Bifurcations and strange attractors in a climate related system. Differ. Equ. Control Process. (Electronic Journal) 1 (2005)
Lust, A.: Numerische Methoden zur Berechnung von Liapunow-Exponenten in dynamischen Systemen. Masters Thesis, Bielefeld University (2002)
Lust, A.: Eine hybride Methode zur Berechnung von Liapunow-Exponenten, PhD thesis, Universität Bielefeld (2006) http://www.math.uni-bielefeld.de/~beyn/AG_Numerik/html/en/preprints/misc01_06.html
Oseledets V.I.: Multiplicative ergodic theorem: Characteristic Lyapunov exponents of dynamical systems. Trudy MMO 19, 179–210 (1968) (in Russian)
Oseledec V.I.: A multiplicative ergodic theorem. Ljapunov characteristic numbers for dynamical systems. Trans. Moscow. Math. Soc. 19, 179–210 (1968)
Reitmann, V.: Reguläre und chaotische Dynamik. B.G. Teubner Verlagsgesellschaft (1996)
Tucker W.: The Lorenz attractor exists. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris Sèr. I Math. 328(12), 1197–1202 (1999)
Walters P.: An Introduction to Ergodic Theory. Springer, Heidelberg (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
W.-J. Beyn and A. Lust was supported by CRC 701 ‘Spectral Analysis and Topological Methods in Mathematics’. The paper is mainly based on the PhD thesis [27] of A. Lust.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beyn, WJ., Lust, A. A hybrid method for computing Lyapunov exponents. Numer. Math. 113, 357–375 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-009-0236-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-009-0236-4