Abstract
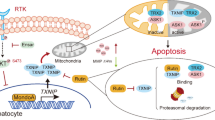
Astragaloside IV (AS-IV), one of the major compounds extract from Astragalus membranaceus, has shown attractive anti-cancer effects in certain malignancies. Oxidative stress (OS) is considered as a crucial factor in promoting the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In response to OS, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) upregulates and induces heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) to combat oxidative damages. The phosphorylation of the COOH-terminal of Smad3 (pSmad3C) activates p21 to resist HCC progression, while the phosphorylation of the linker region of Smad3 (pSmad3L) up-regulates c-Myc transcription to exert promoting effect towards HCC. This study aimed to explore whether AS-IV suppresses migration and invasion of human hepatoma HuH-7 cells by regulating Nrf2/HO-1 and TGF-β1/Smad3 pathways. HuH-7 cells were induced with TGF-β1 (9 or 40 pM) to establish HCC model in vitro and pretreated with AS-IV at different concentration (5, 10, and 20 μM) for 24 h. Cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) of HuH-7 cells were measured. The expression of Nrf2, pSmad3C, Nrf2/pNrf2, HO-1, pSmad3C/3L, c-Myc, and p21 were detected. Exposure of HuH-7 cells to TGF-β1 enhanced the cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and ROS production. Pretreatment with AS-IV (5, 10, and 20 μM) significantly reduced the cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and ROS production in HuH-7 cells. Furthermore, AS-IV increased the expressions of Nrf2/pNrf2, HO-1, pSmad3C, and p21, meanwhile reduced the expressions of pSmad3L and c-Myc. In conclusion, our study suggested that AS-IV inhibit HuH-7 cells migration and invasion, which related to activate Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, up-regulation pSmad3C/p21 pathway, and down-regulation pSmad3L/c-Myc pathway. The present research supports the notion that AS-IV may be a latent agent for the treatment of HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Brahma MK, Gilglioni EH, Zhou L, Trépo E, Chen P, Gurzov EN (2021) Oxidative stress in obesity-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: sources, signaling and therapeutic challenges. Oncogene 40:5155–5167
Cheng X, Gu J, Zhang M, Yuan J, Zhao B, Jiang J, Jia X (2014) Astragaloside IV inhibits migration and invasion in human lung cancer A549 cells via regulating PKC-α-ERK1/2-NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 23:304–313
Choi YJ, Kim DH, Kim SJ, Kim J, Jeong SI, Chung CH, Yu KY, Kim SY (2014) Decursin attenuates hepatic fibrogenesis through interrupting TGF-beta-mediated NAD(P)H oxidase activation and Smad signaling in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci 108:94–103
Cui X, Jiang X, Wei C, Xing Y, Tong G (2020) Astragaloside IV suppresses development of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating miR-150–5p/β-catenin axis. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 78:103397
Dituri F, Mancarella S, Cigliano A, Chieti A, Giannelli G (2019) TGF-β as multifaceted orchestrator in HCC progression: signaling, EMT, immune microenvironment, and novel therapeutic perspectives. Semin Liver Dis 39:53–69
Globocan (2020) Liver. Cancer today web. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/11-Liver-fact-sheet.pdf. Accessed 10 Sept 2021
Gong Y, Li D, Li L, Yang J, Ding H, Zhang C, Wen G, Wu C, Fang Z, Hou S, Yang Y (2021) Smad3 C-terminal phosphorylation site mutation attenuates the hepatoprotective effect of salvianolic acid B against hepatocarcinogenesis. Food Chem Toxicol 147:111912
Hui L, Zatloukal K, Scheuch H, Stepniak E, Wagner EF (2008) Proliferation of human HCC cells and chemically induced mouse liver cancers requires JNK1-dependent p21 downregulation. J Clin Invest 118:3943–3953
Jiang K, Lu Q, Li Q, Ji Y, Chen W, Xue X (2017) Astragaloside IV inhibits breast cancer cell invasion by suppressing Vav3 mediated Rac1/MAPK signaling. Int Immunopharmacol 42:195–202
Kaneko J, Inagaki Y, Ishizawa T, Gao J, Tang W, Aoki T, Sakamoto Y, Hasegawa K, Sugawara Y, Kokudo N (2014) Photodynamic therapy for human hepatoma-cell-line tumors utilizing biliary excretion properties of indocyanine green. J Gastroenterol 49:110–116
Kasai F, Hirayama N, Ozawa M, Satoh M, Kohara A (2018) HuH-7 reference genome profile: complex karyotype composed of massive loss of heterozygosity. Hum Cell 31:261–267
Keleku-Lukwete N, Suzuki M, Yamamoto M (2018) an overview of the advantages of KEAP1-NRF2 system activation during inflammatory disease treatment. Antioxid Redox Signal 29:1746–1755
Li L, Hou X, Xu R, Liu C, Tu M (2017) Research review on the pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 31:17–36
Li Y, Ye Y, Chen H (2018b) Astragaloside IV inhibits cell migration and viability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via suppressing long noncoding RNA ATB. Biomed Pharmacother 99:134–141
Li L, Huang W, Wang S, Sun K, Zhang W, Ding Y, Zhang L, Tumen B, Ji L, Liu C (2018) Astragaloside IV attenuates acetaminophen-induced liver injuries in mice by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Molecules 23
Lin J, Schyschka L, Mühl-Benninghaus R, Neumann J, Hao L, Nussler N, Dooley S, Liu L, Stöckle U, Nussler AK, Ehnert S (2012) Comparative analysis of phase I and II enzyme activities in 5 hepatic cell lines identifies Huh-7 and HCC-T cells with the highest potential to study drug metabolism. Arch Toxicol 86:87–95
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz A, Dulak J (2016) Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci 73:3221–3247
Medina MV, Sapochnik D, Garcia SM, Coso O (2020) Regulation of the expression of heme oxygenase-1: signal transduction, gene promoter activation, and beyond. Antioxid Redox Signal 32:1033–1044
Murata M, Yoshida K, Yamaguchi T, Matsuzaki K (2014) Linker phosphorylation of Smad3 promotes fibro-carcinogenesis in chronic viral hepatitis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 20:15018–15027
Ooshima A, Park J, Kim SJ (2019) Phosphorylation status at Smad3 linker region modulates transforming growth factor-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer progression. Cancer Sci 110:481–488
Oura K, Tadokoro T, Fujihara S, Morishita A, Chiyo T, Samukawa E, Yamana Y, Fujita K, Sakamoto T, Nomura T, Yoneyama H, Kobara H, Mori H, Iwama H, Okano K, Suzuki Y, Masaki T (2017) Telmisartan inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation in vitro by inducing cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep 38:2825–2835
Pisoschi AM, Pop A (2015) The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: a review. Eur J Med Chem 97:55–74
Qu Z, Li D, Xu H, Zhang R, Li B, Sun C, Dong W, Zhang Y (2016) CUL4B, NEDD4, and UGT1As involve in the TGF-β signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Hepatol 15:568–576
Roberts AB, Tian F, Byfield SD, Stuelten C, Ooshima A, Saika S, Flanders KC (2006) Smad3 is key to TGF-beta-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, fibrosis, tumor suppression and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17:19–27
Sies H (2015) Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol 4:180–183
Suwa K, Yamaguchi T, Yoshida K, Murata M, Ichimura M, Tsuneyama K, Seki T, Okazaki K (2020) Smad phospho-isoforms for hepatocellular carcinoma risk assessment in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Cancers (Basel) 12
Wang J, Guo HM (2019) Astragaloside IV ameliorates high glucose-induced HK-2 cell apoptosis and oxidative stress by regulating the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med 17:4409–4416
Wang Z, Li Z, Ye Y, Xie L, Li W (2016) Oxidative stress and liver cancer: etiology and therapeutic targets. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:7891574
Wang ZF, Ma DG, Zhu Z, Mu YP, Yang YY, Feng L, Yang H, Liang JQ, Liu YY, Liu L, Lu HW (2017) Astragaloside IV inhibits pathological functions of gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts. World J Gastroenterol 23:8512–8525
Wu C, Chen W, Ding H, Li D, Wen G, Zhang C, Lu W, Chen M, Yang Y (2019) Salvianolic acid B exerts anti-liver fibrosis effects via inhibition of MAPK-mediated phospho-Smad2/3 at linker regions in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci 239:116881
Wu C, Chen W, Fang M, Boye A, Tao X, Xu Y, Hou S, Yang Y (2019b) Compound Astragalus and Salvia miltiorrhiza extract inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression via miR-145/miR-21 mediated Smad3 phosphorylation. J Ethnopharmacol 231:98–112
Xu F, Cui WQ, Wei Y, Cui J, Qiu J, Hu LL, Gong WY, Dong JC, Liu BJ (2018) Astragaloside IV inhibits lung cancer progression and metastasis by modulating macrophage polarization through AMPK signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:207
Yamaguchi T, Yoshida K, Murata M, Matsuzaki K (2014) Smad3 phospho-isoform signaling in hepatitis C virus-related chronic liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol 20:12381–12390
Yoshida K, Murata M, Yamaguchi T, Matsuzaki K (2014) TGF-β/Smad signaling during hepatic fibro-carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol 45:1363–1371
Yoshida K, Matsuzaki K, Murata M, Yamaguchi T, Suwa K, Okazaki K (2018) Clinico-pathological importance of TGF-β/Phospho-Smad signaling during human hepatic fibrocarcinogenesis. Cancers (Basel) 10
Zhang C, Li L, Hou S, Shi Z, Xu W, Wang Q, He Y, Gong Y, Fang Z, Yang Y (2021) Astragaloside IV inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by continually suppressing the development of fibrosis and regulating pSmad3C/3L and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 279:114350
Zhu J, Wen K (2018) Astragaloside IV inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in gastric cancer cells. Phytother Res 32:1289–1296
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. K.Matsuzaki for presenting us with rabbit polyclonal anti-pSmad3L (Ser208/213) antibody.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No 81874354; 82074073) and the Fund support by Anhui Medical University (No:2019GQFY13; 2020xkj035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LLL and YY conceived and designed the research. LLL conducted experiments and wrote the manuscript. QW contributed to new reagents and analytical tools. YHH provided the methodology and analyzed data. YY and XNP were responsible for the supervision and funding acquisition. XNP contributed to writing, reviewing, and editing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript, and all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the manuscript to be published.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1
(RAR 8.94 MB)
Supplementary file2
(RAR 1.66 MB)
Supplementary file3
(RAR 4.46 MB)
Supplementary file4
(RAR 4.16 MB)
Supplementary file5
(RAR 3.49 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Wang, Q., He, Y. et al. Astragaloside IV suppresses migration and invasion of TGF-β1-induced human hepatoma HuH-7 cells by regulating Nrf2/HO-1 and TGF-β1/Smad3 pathways. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 395, 397–405 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02199-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02199-8