Abstract
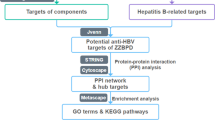
Sedum sarmentosum Bunge is a Traditional Chinese Medicine that is widely used in treating hepatitis, whereas the detailed mechanisms have not been fully interpreted. A systemic pharmacology method including absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination screening, drug targeting, interaction network plotting, and enrichment analysis was applied for exploring the underlying mechanisms of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge in the treatment of hepatitis. A total of 47 ingredients were identified in Sedum sarmentosum Bunge, and 5 active ingredients (DFV, isorhamnetin, beta-sitosterol, luteolin and quercetin) were screened out with the criteria of oral bioavailability (OB) ≥ 30% and drug-likeness (DL) ≥ 0.18. Those 5 ingredients interacted with 170 targets, 163 of which were hepatitis-related. By compound-target-disease network plotting, protein-protein interaction network plotting and enrichment analysis, the pathways that the 5 ingredients engaged in during hepatitis development and progression were investigated, such as threonine-protein kinase signaling. The integrated systemic pharmacology analysis facilitates the in-depth understanding of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge in the hepatitis treatment, which also paves the way for further knowledge of the molecular mechanism of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge in treating hepatitis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data are available.
References
Antunes-Ricardo M, Rodríguez-Rodríguez C, Gutiérrez-Uribe JA, Cepeda-Cañedo E, Serna-Saldívar SO (2017) Bioaccessibility, intestinal permeability and plasma stability of isorhamnetin glycosides from Opuntia ficus-indica (L.). Int J Mol Sci 18(8):1816
Bastard JP et al (2018) Elevated adiponectin and sTNFRII serum levels can predict progression to hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with compensated HCV1 cirrhosis. Eur Cytokine Netw 29(3):112–120
Chang XJ et al (2019) On-treatment monitoring of liver fibrosis with serum hepatitis B core-related antigen in chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 25(32):4764–4778
Chen T et al (2007) Absorption and excretion of luteolin and apigenin in rats after oral administration of Chrysanthemum morifolium extract. J Agric Food Chem 55(2):273–277
Choi YH (2019) Isorhamnetin induces ROS-dependent cycle arrest at G2/M phase and apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma Hep3B cells. Gen Physiol Biophys 38(6):473–484
Devaraj E, Roy A, Royapuram Veeraragavan G et al (2020) β-Sitosterol attenuates carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress and chronic liver injury in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393(6):1067–1075
Do A, Reau NS (2020) Chronic viral hepatitis: current management and future directions. Hepatol Commun 4(3):329–341
Du B et al (2020) Systems pharmacology uncovers multiple mechanisms of erxian decoction () for treatment of premature ovarian failure. Chin J Integr Med 26(2):106–113
Fadda LM et al (2018) Quercetin and idebenone ameliorate oxidative stress, inflammation, DNA damage, and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in rat liver. Dose Response 16(4):1559325818812188
Geng W et al (2020) Liquiritigenin suppresses the activation of hepatic stellate cells via targeting miR-181b/PTEN axis. Phytomedicine 66:153108
Gumede NM et al (2020) beta-Sitosterol mitigates the development of high-fructose diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in growing male Sprague-Dawley rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 98(1):44–50
Han YJ, Kang B, Yang EJ, Choi MK, Song IS (2019) Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic characterization of glycyrrhizin, isoliquiritigenin, liquiritigenin, and liquiritin in rat plasma following oral administration of glycyrrhizae radix extract. Molecules 24(9):1816
Hao L et al (2020) Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract ameliorates lipopolysaccharide- and D-galactosamine-induced acute liver injury by attenuating the hedgehog signaling pathway via regulation of miR-124 expression. BMC Complement Med Ther 20(1):88
Huang L et al (2018) Ameliorative effect of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge extract on Tilapia fatty liver via the PPAR and P53 signaling pathway. Sci Rep 8(1):8456
Huang Z et al (2019) Liquiritigenin and liquiritin alleviated monocrotaline-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome via inhibiting HSP60-induced inflammatory injury. Toxicology 428:152307
Jing C et al (2019) Network pharmacology-based identification of the key mechanism of Qinghuo Rougan Formula acting on uveitis. Biomed Pharmacother 120:109381
Kim D et al (2016) Simultaneous determination of beta-sitosterol, campesterol, and stigmasterol in rat plasma by using LC-APCI-MS/MS: application in a pharmacokinetic study of a titrated extract of the unsaponifiable fraction of Zea mays L. J Sep Sci 39(21):4060–4070
Kim MY, Park JY, Park HS (2019) Akt1-mediated phosphorylation of RBP-Jk controls Notch1 Signaling. Biochemistry (Mosc) 84(12):1537–1546
Liu H et al (2013) Systems approaches and polypharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines: an example using licorice. J Ethnopharmacol 146(3):773–793
Liu J et al (2016) Systems pharmacology uncovers the multiple mechanisms of Xijiao Dihuang decoction for the treatment of viral hemorrhagic fever. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016:1–17
Liu N et al (2019) Isorhamnetin inhibits liver fibrosis by reducing autophagy and inhibiting extracellular matrix formation via the TGF-beta1/Smad3 and TGF-beta1/p38 MAPK pathways. Mediat Inflamm 2019:6175091
Liu N et al (2020a) Traditional Chinese medicine combined with chemotherapy and cetuximab or bevacizumab for metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Front Pharmacol 11:478
Liu W et al (2020b) Systems pharmacology-based study of Tanreqing injection in airway mucus hypersecretion. J Ethnopharmacol 249:112425
Nguyen N et al (2019) Challenges in management of autoimmune hepatitis with concurrent graves thyrotoxicosis. ACG Case Rep J 6(11):e00277
Park CM, Song YS (2019) Luteolin and luteolin-7-O-glucoside protect against acute liver injury through regulation of inflammatory mediators and antioxidative enzymes in GalN/LPS-induced hepatitic ICR mice. Nutr Res Pract 13(6):473–479
Pei T et al (2016) Systematic understanding the mechanisms of vitiligo pathogenesis and its treatment by Qubaibabuqi formula. J Ethnopharmacol 190:272–287
Penalva R et al (2019) Casein nanoparticles in combination with 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin improves the oral bioavailability of quercetin. Int J Pharm 570:118652
Peng Z, Aggarwal R, Zeng N et al (2020) AKT1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and mediates the adaptive response of pancreatic β cells. Mol Cell Biol 40(11):e00031–20
Qi W et al (2020) The implementation of drug reposition for alcoholic hepatitis based on a sub-pathway integration strategy. Ann Transl Med 8(5):208
Remmler J et al (2018) Increased level of interleukin 6 associates with increased 90-day and 1-year mortality in patients with end-stage liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(5):730–737
Reyes-Gordillo K, Shah R, Arellanes-Robledo J, Cheng Y, Ibrahim J, Tuma PL (2019) Akt1 and Akt2 isoforms play distinct roles in regulating the development of inflammation and fibrosis associated with alcoholic liver disease. Cells 8(11):1337
Ru J et al (2014) TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform 6:13
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2018) Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 68(1):7–30
Wang D et al (2012) The role of AKT1 and autophagy in the protective effect of hydrogen sulphide against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Autophagy 8(6):954–962
Wang X, Lin H, Zhang R (2017) The clinical efficacy and adverse effects of interferon combined with matrine in chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytother Res 31(6):849–857
Xie Y et al (2014) Phytic acid enhances the oral absorption of isorhamnetin, quercetin, and kaempferol in total flavones of Hippophae rhamnoides L. Fitoterapia 93:216–225
Yang K et al (2019) Induction of interleukin 6 impairs the anti-HBV efficiency of IFN-alpha in human hepatocytes through upregulation of SOCS3. J Med Virol 91(5):803–812
Zeng H et al (2019) Quercetin alleviates ethanol-induced liver steatosis associated with improvement of lipophagy. Food Chem Toxicol 125:21–28
Acknowledgments
Thanks to my colleagues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CMZ and SQ conceived and designed the research, CMZ conducted the experiments, and SQ wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript, and all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(XLSX 630 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Sun, Q. Systemic pharmacology understanding of the key mechanism of Sedum sarmentosum Bunge in treating hepatitis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 421–430 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01952-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-020-01952-9