Abstract
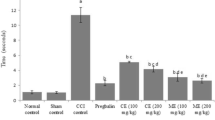
Derangement of electrolyte in the sensory nervous system has been attributed to the development and maintenance of hyperalgesic and allodynic symptoms in painful neuropathy. This study investigated the effect of bromelain on electrolyte imbalance in chronically constricted sciatic nerve of rats (a model of neuropathic pain). Forty Wistar rats, divided into five groups of eight animals each were used for this study. von Frey filaments, tail immersion and acetone spray tests were used to assessed allodynic and thermal hyperalgesic symptoms in the Wistar rats. Sodium ion (Na+), potassium ion (K+), calcium ion (Ca2+) and chloride ion (Cl−) concentrations as well as sodium-potassium and calcium electrogenic pump (Na-K ATPase and Ca ATPase, respectively) activities were estimated using spectrophotometry techniques. Bromelain significantly (p < 0.05) reversed elevation of Na+ and Ca2+ concentration compared with sciatic nerve chronic constriction injury (snCCI) group (35.68 ± 1.71 vs 44.46 ± 1.24 mg/ml/mg protein and 1.06 ± 0.19 vs 6.66 ± 0.03 mg/ml/mg protein, respectively). There were also significant (p < 0.05) increases in the level of K+ (0.84 ± 0.02 vs 0.36 ± 0.05 mg/ml/mg protein) and Cl− (18.51 ± 0.29 vs 15.82 ± 0.21 mg/ml/mg protein). Bromelain reduced the activities of Ca2+ electrogenic pumps significantly compared with snCCI. This study therefore suggests that bromelain mitigated electrolyte imbalance in chronic constricted injury of the sciatic nerve implying that this may be an important mechanism for the anti-nociceptive effect of bromelain.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
André S, Puech-Mallié S, Desmadryl G, Valmier J, Scamps F (2003) Axotomy differentially regulates voltage-gated calcium currents in mice sensory neurones. NeuroReport. 14(1):147–150. https://doi.org/10.1097/00001756-200301200-00027
Bain JR, Mackinnon SE, Hunter DA (1989) Functional evaluation of complete sciatic, peroneal, and posterior tibial nerve lesions in the rat. Plast Reconstr Surg 83(1):129–138
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 33(1):87–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(88)90209-6
Bonin RP, Bories C, De Koninck Y (2014) A simplified up-down method (SUDO) for measuring mechanical nociception in rodents using von Frey filaments. Mol Pain 10(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-10-26
Coull JAM, Boudreau D, Bachand K et al (2003) Trans-synaptic shift in anion gradient in spinal lamina I neurons as a mechanism of neuropathic pain. Nature. 424(6951):938–942. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01868
Gemes G, Bangaru MLY, Wu H-E et al (2011) Store-operated Ca2+ entry in sensory neurons: functional role and the effect of painful nerve injury. J Neurosci 31(10):3536–3549. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5053-10.2011
Gemes G, Oyster KD, Pan B et al (2012) Painful nerve injury increases plasma membrane Ca 2 + -ATPase activity in axotomized sensory neurons. Mol Pain 8(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-8-46
Ghosh B, Li Y, Thayer SA (2011) Inhibition of the plasma membrane Ca 2 ϩ pump by CD44 receptor activation of tyrosine kinases increases the action potential afterhyperpolarization in sensory neurons. J Neurosci 31(7):2361–2370. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5764-10.2011
Jang Y, Cho PS, Yang YD, Hwang SW (2018) Nociceptive roles of TRPM2 ion channel in pathologic pain. Mol Neurobiol 55(8):6589–6600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0862-2
Jin X, John RH, David AP (2005) Impaired Cl− extrusion in layer V pyramidal neurons of chronically injured epileptogenic neocortex. J Neurophysiol 93(4):2117–2126. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00728.2004
Malan TP, Mata HP, Porreca F (2002) Spinal GABA A and GABA B receptor pharmacology in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200205000-00020
Paul D, Soignier RD, Minor L, Tau H, Songu-mize E, Gould HJ (2014) Regulation and pharmacological blockade of sodium-potassium ATPase: a novel pathway to neuropathy. J Neurol Sci 340(1-2):139–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2014.03.012
Price TJ, Cervero F, Gold MS, Hammond DL, Prescott SA (2009) Chloride regulation in the pain pathway. Brain Res Rev 60(1):149–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.015
Schoffnegger D, Ruscheweyh R (2008) Spread of excitation across modality borders in spinal dorsal horn of neuropathic rats. Pain. 135:300–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2007.12.016
St. John Smith E (2018) Advances in understanding nociception and neuropathic pain. J Neurol 265(2):231–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8641-6
Sudjarwo SA (2005) Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of bromelain. Universa Medicina 24(4):155–160
Thiagarajan VRK, Shanmugam P (2014) Ameliorative potential of Vernonia cinerea on chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve induced neuropathic pain in rats. An Acad Bras Cienc 86:1435–1449
Thomas AM, Atkinson TJ (2018) Old friends with new faces: are sodium channel blockers the future of adjunct pain medication management? J Pain 19(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2017.08.001
Zhang MT, Wang B, Jia YN et al (2017) Neuroprotective effect of liquiritin against neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 95:186–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.07.167
Acknowledgements
Our special appreciation goes to Mr. Sodiq Ishola and Mr. Bakare Habeeb for their immense technical support during the course of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors listed were involved in carrying out the laboratory works and contributed to the writing of the manuscripts.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental protocols were carried out in accordance with the International Ethical Guidelines (International Association for the Study of Pain). Ethical clearance was obtained from the University of Ilorin Ethical Review Committee (UERC/ASN/2017/936).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakare, A.O., Owoyele, B.V. Bromelain reversed electrolyte imbalance in the chronically constricted sciatic nerve of Wistar rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 457–467 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01744-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01744-w