Abstract
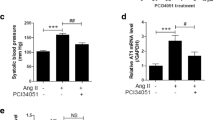
Inhibition of lysine deacetylase (KDAC) attenuated development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). We hypothesized that KDAC inhibition attenuates hypertension and is accompanied by acetylation of mineralocorticoid receptors (MR) instead of histone acetylation in SHRs. Valproate (VPA, 0.71 % wt/vol), an inhibitor of class I KDACs, was administered in drinking water to 7-week-old SHRs and Wistar Kyoto rats for 11 weeks. MR acetylation was determined by immunoprecipitation with anti-MR antibody followed by western blot with anti-acetyl-lysine antibody. Expression levels of acetylated histone H3, KDACs, MR target genes, or MR corepressors in the kidney cortex were measured by using western blot analysis or real-time PCR. Recruitment of MR and RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and histone modifications on promoters of target genes were analyzed by performing a chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. Treatment of SHR with VPA increased MR acetylation without affecting MR expression, which attenuated development of hypertension in SHR VPA decreased expression of KDAC class I but globally increased acetylated histone H3. Although VPA treatment increased histone 3 acetylation (H3Ac) and trimethylation of the fourth lysine (H3K4me3) in the promoter regions of MR target genes, it decreased the expression of target genes as well as recruitment of MR and Pol II. These results suggest that KDAC inhibition attenuates the development of hypertension in SHRs and is accompanied by acetylation of MR that is independent of histone acetylation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALDO:
-
Aldosterone
- ATP1a1:
-
Na+-K+-APTase subunit α1
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth-factor receptor
- ENaC:
-
Epithelial Na+ channel
- GILZ:
-
Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper protein
- GR:
-
Glucocorticoid receptor
- HAT:
-
Histone acetyltransferase
- HRE:
-
Hormone response element
- KDAC:
-
Lysine deacetylase
- MR:
-
Mineralocorticoid receptor
- Pol II:
-
RNA polymerase II
- SGK1:
-
Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1
- SHR:
-
Spontaneously hypertensive rats
- VPA:
-
Valproate
References
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW (2006) Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:769–784
Buchwald M, Kramer OH, Heinzel T (2009) HDACi—targets beyond chromatin. Cancer Lett 280:160–167
Cardinale JP, Sriramula S, Pariaut R, Guggilam A, Mariappan N, Elks CM, Francis J (2010) HDAC inhibition attenuates inflammatory, hypertrophic, and hypertensive responses in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 56:437–444
Chapman N, Dobson J, Wilson S, Dahlof B, Sever PS, Wedel H, Poulter NR (2007) Effect of spironolactone on blood pressure in subjects with resistant hypertension. Hypertension 49:839–845
Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML, Rehman M, Walther TC, Olsen JV, Mann M (2009) Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 325:834–840
Coffey K, Robson CN (2012) Regulation of the androgen receptor by post-translational modifications. J Endocrinol 215:221–237
Connell JM, MacKenzie SM, Freel EM, Fraser R, Davies E (2008) A lifetime of aldosterone excess: long-term consequences of altered regulation of aldosterone production for cardiovascular function. Endocr Rev 29:133–154
Daniel AR, Gaviglio AL, Czaplicki LM, Hillard CJ, Housa D, Lange CA (2010) The progesterone receptor hinge region regulates the kinetics of transcriptional responses through acetylation, phosphorylation, and nuclear retention. Mol Endocrinol 24:2126–2138
Galmozzi A, Mitro N, Ferrari A, Gers E, Gilardi F, Godio C, Cermenati G, Gualerzi A, Donetti E, Rotili D, Valente S, Guerrini U, Caruso D, Mai A, Saez E, De Fabiani E, Crestani M (2013) Inhibition of class I histone deacetylases unveils a mitochondrial signature and enhances oxidative metabolism in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Diabetes 62:732–742
Grossmann C, Ruhs S, Langenbruch L, Mildenberger S, Stratz N, Schumann K, Gekle M (2012) Nuclear shuttling precedes dimerization in mineralocorticoid receptor signaling. Chem Biol 19:742–751
Haberland M, Montgomery RL, Olson EN (2009) The many roles of histone deacetylases in development and physiology: implications for disease and therapy. Nat Rev Genet 10:32–42
Hargovan M, Ferro A (2014) Aldosterone synthase inhibitors in hypertension: current status and future possibilities. JRSM Cardiovasc Dis 3:2048004014522440
Iyer A, Fenning A, Lim J, Le GT, Reid RC, Halili MA, Fairlie DP, Brown L (2010) Antifibrotic activity of an inhibitor of histone deacetylases in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Br J Pharmacol 159:1408–1417
Kouzarides T (2007) Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128:693–705
Le Menuet D, Isnard R, Bichara M, Viengchareun S, Muffat-Joly M, Walker F, Zennaro MC, Lombes M (2001) Alteration of cardiac and renal functions in transgenic mice overexpressing human mineralocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem 276:38911–38920
Lee HA, Lee DY, Cho HM, Kim SY, Iwasaki Y, Kim IK (2013) Histone deacetylase inhibition attenuates transcriptional activity of mineralocorticoid receptor through its acetylation and prevents development of hypertension. Circ Res 112:1004–1012
McGraw AP, McCurley A, Preston IR, Jaffe IZ (2013) Mineralocorticoid receptors in vascular disease: connecting molecular pathways to clinical implications. Curr Atheroscler Rep 15:340
Morrell MJ, Isojarvi J, Taylor AE, Dam M, Ayala R, Gomez G, O’Neill F, Tennis P, Messenheimer J (2003) Higher androgens and weight gain with valproate compared with lamotrigine for epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 54:189–199
Nader N, Chrousos GP, Kino T (2009) Circadian rhythm transcription factor CLOCK regulates the transcriptional activity of the glucocorticoid receptor by acetylating its hinge region lysine cluster: potential physiological implications. FASEB J 23:1572–1583
Nagai Y, Miyata K, Sun GP, Rahman M, Kimura S, Miyatake A, Kiyomoto H, Kohno M, Abe Y, Yoshizumi M, Nishiyama A (2005) Aldosterone stimulates collagen gene expression and synthesis via activation of ERK1/2 in rat renal fibroblasts. Hypertension 46:1039–1045
Nakagaki T, Hirooka Y, Matsukawa R, Nishihara M, Nakano M, Ito K, Hoka S, Sunagawa K (2012) Activation of mineralocorticoid receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla is involved in hypertensive mechanisms in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res 35:470–476
Nightingale KP, Gendreizig S, White DA, Bradbury C, Hollfelder F, Turner BM (2007) Cross-talk between histone modifications in response to histone deacetylase inhibitors: MLL4 links histone H3 acetylation and histone H3K4 methylation. J Biol Chem 282:4408–4416
Perico N, Benigni A, Remuzzi G (2008) Present and future drug treatments for chronic kidney diseases: evolving targets in renoprotection. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:936–953
Pinto V, Pinho MJ, Silva E, Simao S, Igreja B, Afonso J, Serrao MP, Gomes P, Soares-da-Silva P (2012) Long-term food restriction attenuates age-related changes in the expression of renal aldosterone-sensitive sodium transporters in Wistar-Kyoto rats: a comparison with SHR. Exp Gerontol 47:644–653
Pitt B, Remme W, Zannad F, Neaton J, Martinez F, Roniker B, Bittman R, Hurley S, Kleiman J, Gatlin M (2003) Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 348:1309–1321
Qiu Y, Zhao Y, Becker M, John S, Parekh BS, Huang S, Hendarwanto A, Martinez ED, Chen Y, Lu H, Adkins NL, Stavreva DA, Wiench M, Georgel PT, Schiltz RL, Hager GL (2006) HDAC1 acetylation is linked to progressive modulation of steroid receptor-induced gene transcription. Mol Cell 22:669–679
Rice JC, Allis CD (2001) Histone methylation versus histone acetylation: new insights into epigenetic regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:263–273
Rossig L, Li H, Fisslthaler B, Urbich C, Fleming I, Forstermann U, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (2002) Inhibitors of histone deacetylation downregulate the expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and compromise endothelial cell function in vasorelaxation and angiogenesis. Circ Res 91:837–844
Sasaki S, Nakata T, Kawasaki S, Hayashi J, Oguro M, Takeda K, Nakagawa M (1990) Chronic central GABAergic stimulation attenuates hypothalamic hyperactivity and development of spontaneous hypertension in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 15:706–713
Seo M, Song M, Seok YM, Kang SH, Lee HA, Sohn UD, Kim IK (2015) Lysine acetyltransferases cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding binding protein and acetyltransferase p300 attenuate transcriptional activity of the mineralocorticoid receptor through its acetylation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 42:559–566
Shibata H, Ando T, Suzuki T, Kurihara I, Hayashi K, Hayashi M, Saito I, Murai M, Saruta T (1998) COUP-TFI expression in human adrenocortical adenomas: possible role in steroidogenesis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:4520–4523
Singh BN, Zhang G, Hwa YL, Li J, Dowdy SC, Jiang SW (2010) Nonhistone protein acetylation as cancer therapy targets. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 10:935–954
Stockand JD (2002) New ideas about aldosterone signaling in epithelia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F559–F576
Strahl BD, Allis CD (2000) The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403:41–45
Tao H, Shi KH, Yang JJ, Huang C, Zhan HY, Li J (2014) Histone deacetylases in cardiac fibrosis: current perspectives for therapy. Cell Signal 26:521–527
van der Laan S, Sarabdjitsingh RA, Van Batenburg MF, Lachize SB, Li H, Dijkmans TF, Vreugdenhil E, de Kloet ER, Meijer OC (2008) Chromatin immunoprecipitation scanning identifies glucocorticoid receptor binding regions in the proximal promoter of a ubiquitously expressed glucocorticoid target gene in brain. J Neurochem 106:2515–2523
Verrotti A, D’Egidio C, Mohn A, Coppola G, Chiarelli F (2011) Weight gain following treatment with valproic acid: pathogenetic mechanisms and clinical implications. Obes Rev 12:e32–e43
Viengchareun S, Le Menuet D, Martinerie L, Munier M, Pascual-Le Tallec L, Lombes M (2007) The mineralocorticoid receptor: insights into its molecular and (patho)physiological biology. Nucl Recept Signal 5:e012
Wang C, Fu M, Angeletti RH, Siconolfi-Baez L, Reutens AT, Albanese C, Lisanti MP, Katzenellenbogen BS, Kato S, Hopp T, Fuqua SA, Lopez GN, Kushner PJ, Pestell RG (2001) Direct acetylation of the estrogen receptor alpha hinge region by p300 regulates transactivation and hormone sensitivity. J Biol Chem 276:18375–18383
Wang C, Tian L, Popov VM, Pestell RG (2011) Acetylation and nuclear receptor action. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 123:91–100
Yang XJ, Seto E (2008) Lysine acetylation: codified crosstalk with other posttranslational modifications. Mol Cell 31:449–461
Yang J, Young MJ (2009) The mineralocorticoid receptor and its coregulators. J Mol Endocrinol 43:53–64
Zhao L, Chen CN, Hajji N, Oliver E, Cotroneo E, Wharton J, Wang D, Li M, McKinsey TA, Stenmark KR, Wilkins MR (2012) Histone deacetylation inhibition in pulmonary hypertension: therapeutic potential of valproic acid and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid. Circulation 126:455–467
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2013R1A1A2058145 and 2013R1A2A2A01005155), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, and the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI13C1527).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This investigation was conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kyungpook National University (KNU 2012–116), and every effort was made to minimize both the number of animals used and their suffering.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Young Mi Seok and Hae Ahm Lee contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PPTX 111 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seok, Y.M., Lee, H.A., Park, K.M. et al. Lysine deacetylase inhibition attenuates hypertension and is accompanied by acetylation of mineralocorticoid receptor instead of histone acetylation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 389, 799–808 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1246-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1246-2