Abstract
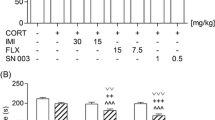
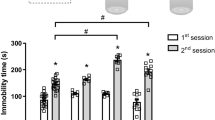
The dopamine D2/D3 receptor agonist pramipexole has clinically been proven to improve depression or treatment-resistant depression. However, the involvement of the dopamine receptor system on the effect of pramipexole on depression remains unclear. We examined the influence of pramipexole on the duration of immobility during the forced swim test in normal and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)-treated rats and further analyzed the possible role of dopamine receptors in this effect. Additionally, the mechanism by which pramipexole acts in this model was explored specifically in relation to the site of action through the use of microinjections into the intramedial prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens. Pramipexole (0.3–1 mg/kg) significantly decreased the duration of immobility in normal and ACTH-treated rats. This effect was blocked by L-741,626, a D2 receptor antagonist, and nafadotride, a D3 receptor antagonist, in normal rats. Furthermore, infusions of pramipexole into the intranucleus accumbens, but not the medial prefrontal cortex, decreased the immobility of normal and ACTH-treated rats during the forced swim test. Taken together, the results of these experiments suggested that pramipexole, administered into the intranucleus accumbens rather than the medial prefrontal cortex, exerted an antidepressant-like effect on ACTH-treated rats via the dopaminergic system. The immobility-decreasing effect of pramipexole may be mediated by dopamine D2 and D3 receptors.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brocco M, Dekeyne A, Papp M, Millan M (2006) Antidepressant-like properties of the anti-Parkinson agent, piribedil, in rodents: mediation by dopamine D2 receptors. Behav Pharmacol 17:559–572
Carroll BJ, Curtis GC, Mendels J (1976) Neuroendocrine regulation in depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 33:1039–1044
Cassano P, Lattanzi L, Soldani F, Navari S, Battistini G, Gemignani A, Cassano GB (2004) Pramipexole in treatment-resistant depression: an extended follow-up. Depress Anxiety 20:131–138
Cassano P, Lattanzi L, Fava M, Navari S, Battistini G, Abelli M, Cassano GB (2005) Ropinirole in treatment-resistant depression: a 16-week pilot study. Can J Psychiatry 50:357–360
Cervo L, Samanin R (1987) Evidence that dopamine mechanisms in the nucleus accumbens are selectively involved in the effect of desipramine in the forced swimming test. Neuropharmacology 26:1469–1472
Cervo L, Samanin R (1988) Repeated treatment with imipramine and amitriptyline reduced the immobility of rats in the swimming test by enhancing dopamine mechanisms in the nucleus accumbens. J Pharm Pharmacol 40:155–156
D’Aquila PS, Collu M, Pani L, Gessa GL, Serra G (1994) Antidepressant-like effect of selective dopamine D1 receptor agonists in the behavioural despair animal model of depression. Eur J Pharmacol 262:107–111
Fink M (1990) How does convulsive therapy work? Neuropsychopharmacology 3:73–82
Gutierrez-Garcia AG, Contreras CM, Diaz-Meza JL, Bernal-Morales B, Rodriguez-Landa JF, Saavedra M (2003) Intraaccumbens dopaminergic legion suppresses desipramine effects in the forced swim test but not in the neuronal activity of lateral septal nucleus. Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 20:1427–1434
Inoue T, Tsuchiya K, Miura J, Sakakibara S, Denda K, Kasahara T, Koyama T (1996) Bromocriptine treatment of tricyclic and heterocyclic antidepressant-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 40:151–153
Izumi T, Inoue T, Kitagawa N, Nishi N, Shimanaka S, Takahashi Y, Kusumi I, Odagaki Y, Denda K, Ohmori T, Koyama T (2000) Open pergolide treatment of tricyclic and heterocyclic antidepressant-resistant depression. J Affect Disorders 61:127–132
Jordan S, Kramer GL, Zukas PK, Moeller M, Petty F (1994) In vivo biogenic amine efflux in medial prefrontal cortex with imipramine, fluoxetine, and fluvoxamine. Synapse 18:294–297
Kapur S, Mann J (1992) Role of the dopaminergic system in depression. Biol Psychiatry 32:1–17
Kelly WF, Checkley SA, Bender DA (1980) Cushing’s syndrome, tryptophan and depression. Br J Psychiatry 136:125–32
Kitamura Y, Araki H, Gomita Y (2002) Influence of ACTH on the effects of imipramine, desipramine and lithium on duration of immobility of rats in the forced swim test. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:63–69
Klimek V, Maj J (1989) Repeated administration of antidepressants enhances agonist affinity for mesolimbic D3-receptors. J Pharm Pharmacol 41:555–558
Levant B, Nichole R, Vansell BA (1997) In vivo occupancy of D2 dopamine receptors by nafadotride. Neuropsychopharmacol 17:67–71
Li B, Suemaru K, Kitamura Y, Cui R, Gomita Y, Araki H (2007) Strategy to develop a new drug for treatment-resistant depression—role of electroconvulsive stimuli and BDNF. Yakugaku Zasshi 127:735–742
Maj J, Rogoz Z, Margas W, Kata M, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M (2000) The effect of repeated treatment with pramipexole on the central dopamine D3 system. J Neural Transm 107:1369–1379
Mierau J, Schneider FJ, Ensinger HA, Chio CL, Lajiness ME, Huff RM (1995) Pramipexole binding and activation of cloned and expressed dopamine D2, D3 and D4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 290:29–36
Murphy BEP, Dhar V, Ghadirian AM, Chouinard G, Keller R (1991) Response to steroid suppression in major depression on resistant to antidepressant therapy. J Clin Psychopharmacol 11:121–126
Muscat R, Papp M, Willner P (1992) Antidepressant-like effects of dopamine agonist in an animal model of depression. Biol Psychiatry 31:937–946
Plaznik A, Kostowski W (1987) The effects of antidepressants and electroconvulsive shocks on the functioning of the mesolimbic dopaminergic system: a behavioral study. Eur J Pharmacol 135:389–396
Plaznik A, Danysz W, Lostowski W (1985) A stimulatory effect of intraaccumbens injections of noradrenaline on the behavior of rats in the forced swim test. Psychopharmacology 87:119–123
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N (1987) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47:379–391
Rogoz R, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska MD (1999) Effect of antidepressant drugs on the dopamine D2/D3 receptors in the rat brain differentiated by agonist and antagonist binding—an autoradiographic analysis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 359:178–186
Rogoz Z, Skuza G, Klodzinska A (2004) Anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of 7-OH-DPAT, preferential dopamine D3 receptor agonist in rats. Pol J Pharmacol 56:519–526
Serra G, Collu M, D’Aquila PS, De Montis GM, Gessa GL (1990) Possible role of dopamine D1 receptor in the behavioural supersensitivity to dopamine agonists induced by chronic treatment with antidepressants. Brain Res 527:234–243
Siuciak JA, Fujiwara RA (2004) The activity of pramipexole in the forced swim test is mediated by D2 rather than D3 receptors. Psychopharmacology 175:163–169
Sonino N, Boscaro M, AmbrosoG Merola G, Mantero F (1986) Prolonged treatment of Cushing’s disease with metyrapone and aminoglutethimide. IRCS J Med Sci 14:485–486
Swanson CJ, Heath S, Stratford TR, Kelley AE (1997) Differential behavioral responses to dopaminergic stimulation of nucleus accumbens subregions in the rat. Pharmcol Biochem Behav 58:933–945
Tanda G, Carboni E, Frau R, Di Chiara G (1994) Increase of extracellular dopamine in the prefrontal cortex: a trait of drugs with antidepressant potential? Psychopharmacology 93:193–200
Vaugeois J, Pouhe D, Zuccaro F, Costentin J (1996) Indirect dopamine agonists effects on despair test: dissociation from hyperactivity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 54:235–239
Willner P (1997) The mesolimbic dopamine system as a target for rapid antidepressant action. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 12(Suppl 3):S7–S14
Willner P, Lappas S, Cheeta S, Muscat R (1994) Reversal of stress-induced anhedonia by the dopamine receptor agonist, pramipexole. Psychopharmacology 115:454–462
Acknowledgment
This study was supported in part by a grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (No. 19590535).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitagawa, K., Kitamura, Y., Miyazaki, T. et al. Effects of pramipexole on the duration of immobility during the forced swim test in normal and ACTH-treated rats. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 380, 59–66 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-009-0405-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-009-0405-0