Abstract
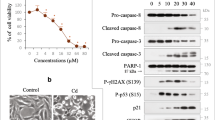
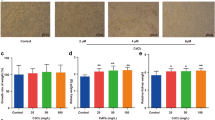
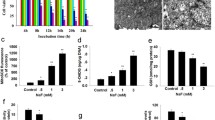
Cadmium (Cd), an occupational and environmental pollutant, induces nephrotoxicity by primarily damaging renal proximal tubular cells. In this study, we hypothesized that pyroptosis, a caspase-1-dependent inflammatory programmed cell death mechanism, mediates Cd-induced nephrotoxicity. Human proximal tubular epithelial HK-2 cells were treated with 0–10 µM CdCl2 for 48 h. We found that Cd dose-dependently caused cytotoxicity, which correlated with activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, increases in the expression and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulation of pyroptosis-related genes in HK-2 cells or/and in kidneys of Cd-treated mice. These effects were significantly abrogated by inhibiting caspase-1 activity with inhibitor YVAD or silencing NLRP3 with siRNA in vitro, suggesting that Cd induces caspase-1- and NLRP3-inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis. Moreover, Cd treatment also activated three branches (ATF6, PERK and IRE-1α) of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Selective inhibition of the IRE-1α/XBP-1s branch by a pharmacological inhibitor STF-083010 or by genetic silencing of XBP-1 significantly attenuated Cd-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. Mechanistically, Cd suppressed deacetylase Sirtuin-1 (SIRT-1) protein expression and activity leading to decrease in physical binding with XBP-1s protein, and thus the accumulation of acetylated XBP-1s levels. Activation of SIRT1 using a pharmacological agonist resveratrol or genetic SIRT1 overexpression significantly abolished Cd-induced activation of the IRE-1α/XBP-1s pathway and the NRLP3 inflammasome as well as pyroptosis, which were counteracted by co-overexpression of both SIRT1 and XBP-1s. Collectively, our findings indicate that SIRT1 activity protects against Cd-induced pyroptosis through deacetylating XBP-1s, and thus inhibiting the IRE-1α/XBP-1s pathway in HK-2 cells. These results provide a novel mechanism for Cd-induced nephrotoxicity.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATF6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- IRE-1α:
-
Inositol-requiring enzyme 1α
- NLRP3:
-
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization segment-like receptor family 3 inflammasome
- PERK:
-
Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
- XBP-1s:
-
Splice X-box binding protein-1
- SIRT1:
-
Sirtuin-1
References
Benham AM (2012) Protein secretion and the endoplasmic reticulum. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(8):a012872. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a012872
Bergsbaken T, Cookson BT (2007) Macrophage activation redirects yersinia-infected host cell death from apoptosis to caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis. PLoS Pathog 3(11):e161. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.0030161
Bergsbaken T, Fink SL, Cookson BT (2009) Pyroptosis: host cell death and inflammation. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(2):99–109. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2070
Blander G, Guarente L (2004) The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu Rev Biochem 73:417–435. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.73.011303.073651
Boonprasert K, Satarug S, Morais C et al (2016) The stress response of human proximal tubule cells to cadmium involves up-regulation of haemoxygenase 1 and metallothionein but not cytochrome P450 enzymes. Toxicol Lett 249:5–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.02.016
Brunet A, Sweeney LB, Sturgill JF et al (2004) Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 303(5666):2011–2015. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094637
Brzoska MM, Kaminski M, Supernak-Bobko D, Zwierz K, Moniuszko-Jakoniuk J (2003) Changes in the structure and function of the kidney of rats chronically exposed to cadmium. I. Biochemical and histopathological studies. Arch Toxicol 77(6):344–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-003-0451-1
Burrows JA, Willis LK, Perlmutter DH (2000) Chemical chaperones mediate increased secretion of mutant alpha 1-antitrypsin (alpha 1-AT) Z: a potential pharmacological strategy for prevention of liver injury and emphysema in alpha 1-AT deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(4):1796–1801 https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.97.4.1796
Cerqueira DM, Pereira MS, Silva AL, Cunha LD, Zamboni DS (2015) Caspase-1 but not caspase-11 is required for NLRC4-mediated pyroptosis and restriction of infection by flagellated Legionella species in mouse macrophages and in vivo. J Immunol 195(5):2303–2311. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1501223
Chen X, Zhu G (2018) The association between dietary cadmium exposure and renal dysfunction—the benchmark dose estimation of reference levels: the ChinaCad study. J Appl Toxicol 38(10):1365–1373. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3647
Chen H, Lu Y, Cao Z et al (2016) Cadmium induces NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis in vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett 246:7–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.01.014
Chen A, Chen Z, Xia Y et al (2018a) Liraglutide attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis via regulating SIRT1/NOX4/ROS pathway in H9c2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 499(2):267–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.142
Chen X, Wang Z, Zhu G, Nordberg GF, Ding X, Jin T (2018b) The association between renal tubular dysfunction and zinc level in a Chinese population environmentally exposed to cadmium. Biol Trace Elem Res 186(1):114–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1304-3
Ellgaard L, Helenius A (2003) Quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4(3):181–191. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1052
Fan Y, Xiao W, Li Z et al (2015) RTN1 mediates progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress. Nat Commun 6:7841. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8841
Fantuzzi G, Dinarello CA (1999) Interleukin-18 and interleukin-1 beta: two cytokine substrates for ICE (caspase-1). J Clin Immunol 19(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020506300324
Faroon O, Ashizawa A, Wright S et al (2012) Toxicological profile for cadmium. Agency for Toxic Substance and Disease Registry (US), Atlanta
Fink SL, Bergsbaken T, Cookson BT (2008) Anthrax lethal toxin and Salmonella elicit the common cell death pathway of caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis via distinct mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(11):4312–4317. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0707370105
Fu Y, Wang Y, Du L et al (2013) Resveratrol inhibits ionising irradiation-induced inflammation in MSCs by activating SIRT1 and limiting NLRP-3 inflammasome activation. Int J Mol Sci 14(7):14105–14118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140714105
Ge Z, Diao H, Ji X, Liu Q, Zhang X, Wu Q (2018) Gap junctional intercellular communication and endoplasmic reticulum stress regulate chronic cadmium exposure induced apoptosis in HK-2 cells. Toxicol Lett 288:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.02.013
Gu J, Dai S, Liu Y et al (2018) Activation of Ca(2+)-sensing receptor as a protective pathway to reduce cadmium-induced cytotoxicity in renal proximal tubular cells. Sci Rep 8(1):1092. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19327-9
Guo P, Pi H, Xu S et al (2014) Melatonin Improves mitochondrial function by promoting MT1/SIRT1/PGC-1 alpha-dependent mitochondrial biogenesis in cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity in vitro. Toxicol Sci 142(1):182–195. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfu164
Guo R, Liu W, Liu B, Zhang B, Li W, Xu Y (2015) SIRT1 suppresses cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy: an insight into endoplasmic reticulum stress response mechanism. Int J Cardiol 191:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.04.245
Haigis MC, Sinclair DA (2010) Mammalian sirtuins: biological insights and disease relevance. Annu Rev Pathol 5:253–295. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092250
Hasnain SZ, Lourie R, Das I, Chen AC, McGuckin MA (2012) The interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation. Immunol Cell Biol 90(3):260–270. https://doi.org/10.1038/icb.2011.112
He WT, Wan H, Hu L et al (2015) Gasdermin D is an executor of pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1beta secretion. Cell Res 25(12):1285–1298. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2015.139
Huo J, Huang Z, Li R et al (2018) Dietary cadmium exposure assessment in rural areas of Southwest China. PLoS One 13(8):e0201454. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201454
Jarup L, Akesson A (2009) Current status of cadmium as an environmental health problem. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):201–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.04.020
Kang X, Yang W, Wang R et al (2018) Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) stimulates growth-plate chondrogenesis by attenuating the PERK-eIF-2alpha-CHOP pathway in the unfolded protein response. J Biol Chem 293(22):8614–8625. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.809822
Kato H, Nakajima S, Saito Y, Takahashi S, Katoh R, Kitamura M (2012) mTORC1 serves ER stress-triggered apoptosis via selective activation of the IRE1-JNK pathway. Cell Death Differ 19(2):310–320. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.98
Klaassen CD, Liu J, Diwan BA (2009) Metallothionein protection of cadmium toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.03.026
Kriss CL, Pinilla-Ibarz JA, Mailloux AW et al (2012) Overexpression of TCL1 activates the endoplasmic reticulum stress response: a novel mechanism of leukemic progression in mice. Blood 120(5):1027–1038. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-11-394346
Lebeaupin C, Proics E, de Bieville CH et al (2015) ER stress induces NLRP3 inflammasome activation and hepatocyte death. Cell Death Dis 6:e1879. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.248
Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Glimcher LH (2003) XBP-1 regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol 23(21):7448–7459. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.23.21.7448-7459.2003
Lerner AG, Upton JP, Praveen PV et al (2012) IRE1alpha induces thioredoxin-interacting protein to activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and promote programmed cell death under irremediable ER stress. Cell Metab 16(2):250–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.07.007
Li Y, Xu S, Giles A et al (2011) Hepatic overexpression of SIRT1 in mice attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and insulin resistance in the liver. FASEB J 25(5):1664–1679. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.10-173492
Li PC, Wang BR, Li CC et al (2018) Seawater inhalation induces acute lung injury via ROS generation and the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Int J Mol Med 41(5):2505–2516. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3486
Liu Y, Liu J, Habeebu SM, Waalkes MP, Klaassen CD (2000) Metallothionein-I/II null mice are sensitive to chronic oral cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 57(1):167–176. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/57.1.167
Liu F, Li ZF, Wang ZY, Wang L (2016) Role of subcellular calcium redistribution in regulating apoptosis and autophagy in cadmium-exposed primary rat proximal tubular cells. J Inorg Biochem 164:99–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.09.005
Liu YG, Chen JK, Zhang ZT et al (2017) NLRP3 inflammasome activation mediates radiation-induced pyroptosis in bone marrow-derived macrophages. Cell Death Dis 8(2):e2579. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.460
Lu A, Magupalli VG, Ruan J et al (2014) Unified polymerization mechanism for the assembly of ASC-dependent inflammasomes. Cell 156(6):1193–1206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.008
Lu Y, Xu S, Chen H et al (2016) CdSe/ZnS quantum dots induce hepatocyte pyroptosis and liver inflammation via NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biomaterials 90:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.03.003
Luo B, Lin Y, Jiang S et al (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum stress eIF2alpha-ATF4 pathway-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction regulates cadmium-induced autophagy in kidney. Cell Death Dis 7(6):e2251. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.78
Ma Q (2013) Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011112-140320
Morigi M, Perico L, Benigni A (2018) Sirtuins in renal health and disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 29(7):1799–1809. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2017111218
Olszowski T, Baranowska-Bosiacka I, Gutowska I, Chlubek D (2012) Pro-inflammatory properties of cadmium. Acta Biochim Pol 59(4):475–482
Oslowski CM, Hara T, O’Sullivan-Murphy B et al (2012) Thioredoxin-interacting protein mediates ER stress-induced beta cell death through initiation of the inflammasome. Cell Metab 16(2):265–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.07.005
Papandreou I, Denko NC, Olson M et al (2011) Identification of an Ire1alpha endonuclease specific inhibitor with cytotoxic activity against human multiple myeloma. Blood 117(4):1311–1314. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-08-303099
Prola A, Pires Da Silva J, Guilbert A et al (2017) SIRT1 protects the heart from ER stress-induced cell death through eIF2alpha deacetylation. Cell Death Differ 24(2):343–356. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2016.138
Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(7):519–529. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2199
Sabolic I, Breljak D, Skarica M, Herak-Kramberger CM (2010) Role of metallothionein in cadmium traffic and toxicity in kidneys and other mammalian organs. Biometals 23(5):897–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9351-z
Satarug S (2018) Dietary cadmium intake and its effects on kidneys. Toxics https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics6010015
Schroder M (2008) Endoplasmic reticulum stress responses. Cell Mol Life Sci 65(6):862–894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7383-5
Schroder K, Tschopp J (2010) The inflammasomes. Cell 140(6):821–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.040
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K et al (2015) Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 526(7575):660–665. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15514
Simard JC, Vallieres F, de Liz R, Lavastre V, Girard D (2015) Silver nanoparticles induce degradation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor activating transcription factor-6 leading to activation of the NLRP-3 inflammasome. J Biol Chem 290(9):5926–5939. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.610899
Sui DM, Xie Q, Yi WJ et al (2016) Resveratrol protects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy and inhibits the NLRP3/IL-1beta axis in microglia. Mediat Inflamm 2016:1045657. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1045657
Takahashi M (2014) NLRP3 inflammasome as a novel player in myocardial infarction. Int Heart J 55(2):101–105. https://doi.org/10.1536/ihj.13-388
Thijssen S, Lambrichts I, Maringwa J, Van Kerkhove E (2007a) Changes in expression of fibrotic markers and histopathological alterations in kidneys of mice chronically exposed to low and high Cd doses. Toxicology 238(2–3):200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2007.06.087
Thijssen S, Maringwa J, Faes C, Lambrichts I, Van Kerkhove E (2007b) Chronic exposure of mice to environmentally relevant, low doses of cadmium leads to early renal damage, not predicted by blood or urine cadmium levels. Toxicology 229(1–2):145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2006.10.011
Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Ng Eaton E et al (2001) hSIR2(SIRT1) functions as an NAD-dependent p53 deacetylase. Cell 107(2):149–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00527-X
Wang FM, Chen YJ, Ouyang HJ (2011a) Regulation of unfolded protein response modulator XBP1s by acetylation and deacetylation. Biochem J 433(1):245–252. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20101293
Wang FM, Galson DL, Roodman GD, Ouyang H (2011b) Resveratrol triggers the pro-apoptotic endoplasmic reticulum stress response and represses pro-survival XBP1 signaling in human multiple myeloma cells. Exp Hematol 39(10):999–1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2011.06.007
Wilmes A, Crean D, Aydin S, Pfaller W, Jennings P, Leonard MO (2011) Identification and dissection of the Nrf2 mediated oxidative stress pathway in human renal proximal tubule toxicity. Toxicol In Vitro 25(3):613–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2010.12.009
Wu KC, Liu JJ, Klaassen CD (2012) Nrf2 activation prevents cadmium-induced acute liver injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 263(1):14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2012.05.017
Xiao W, Sarsour EH, Wagner BA et al (2016) Succinate dehydrogenase activity regulates PCB3-quinone-induced metabolic oxidative stress and toxicity in HaCaT human keratinocytes. Arch Toxicol 90(2):319–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1407-3
Xiao W, Wang RS, Handy DE, Loscalzo J (2018) NAD(H) and NADP(H) redox couples and cellular energy metabolism. Antioxid Redox Signal 28(3):251–272. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2017.7216
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B, Reed JC (2005) Endoplasmic reticulum stress: cell life and death decisions. J Clin Investig 115(10):2656–2664. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci26373
Yam GH, Gaplovska-Kysela K, Zuber C, Roth J (2007) Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate acts as a chemical chaperone on misfolded myocilin to rescue cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48(4):1683–1690. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.06-0943
Yang SJ, Lim Y (2014) Resveratrol ameliorates hepatic metaflammation and inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Metabolism 63(5):693–701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.02.003
Yang H, Shu Y (2015) Cadmium transporters in the kidney and cadmium-induced nephrotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 16(1):1484–1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16011484
Yang JR, Yao FH, Zhang JG et al (2014) Ischemia-reperfusion induces renal tubule pyroptosis via the CHOP-caspase-11 pathway. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 306(1):F75–F84. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00117.2013
Yokouchi M, Hiramatsu N, Hayakawa K et al (2007) Atypical, bidirectional regulation of cadmium-induced apoptosis via distinct signaling of unfolded protein response. Cell Death Differ 14(8):1467–1474. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4402154
Zeng X, Jin T, Zhou Y, Nordberg GF (2003) Changes of serum sex hormone levels and MT mRNA expression in rats orally exposed to cadmium. Toxicol 186(1–2):109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00725-4
Zhang C, Liang Y, Lei L et al (2013) Hypermethylations of RASAL1 and KLOTHO is associated with renal dysfunction in a Chinese population environmentally exposed to cadmium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 271(1):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.04.025
Zhang Y, Tao X, Yin L et al (2017) Protective effects of dioscin against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via the microRNA-34a/sirtuin 1 signalling pathway. Br J Pharmacol 174(15):2512–2527. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13862
Zheng X, Xu F, Liang H et al (2017) SIRT1/HSF1/HSP pathway is essential for exenatide-alleviated, lipid-induced hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress. Hepatology 66(3):809–824. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29238
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant (no. 21277033) from the national Natural Science Foundation of China; Grant (no. 14DZ2260200, the Project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Kidney and Blood Purification) from the Scienceand Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality; Program of China-Sri Lanka Joint Research and Demonstration Center for Water Technology and China-Sri Lanka Joint Center for Education and Research by Chinese Academy of Sciences, China and Grant (no. 15GWZK0202) from the Fourth Round of Three-year Public Health Action Plan of Shanghai. The authors thank Dr. Wusheng Xiao for his critical language editing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, X., Ding, F., Zhang, X. et al. Sirtuin-1 ameliorates cadmium-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis through XBP-1s deacetylation in human renal tubular epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol 93, 965–986 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02415-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02415-8