Abstract
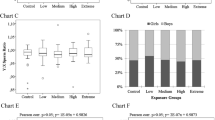
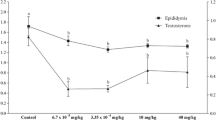
Boric acid and sodium borates are currently classified in the EU-CLP regulation as “toxic to reproduction” under “Category 1B”, with hazard statement of H360FD. However, so far field studies on male reproduction in China and in Turkey could not confirm such boron-associated toxic effects. As validation by another independent study is still required, the present study has investigated possible boron-associated effects on male reproduction in workers (n = 212) under different boron exposure conditions. The mean daily boron exposure (DBE) and blood boron concentration of workers in the extreme exposure group (n = 98) were 47.17 ± 17.47 (7.95–106.8) mg B/day and 570.6 ± 160.1 (402.6–1100) ng B/g blood, respectively. Nevertheless, boron-associated adverse effects on semen parameters, as well as on FSH, LH and total testosterone levels were not seen, even within the extreme exposure group. With this study, a total body of evidence has accumulated that allows to conclude that male reproductive effects are not relevant to humans, under any feasible and realistic conditions of exposure to inorganic boron compounds.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basaran N, Duydu Y, Bolt HM (2012) Reproductive toxicity in boron exposed workers in Bandirma, Turkey. J Trace Elem Med Biol 26(2–3):165–167
Bolt HM, Basaran N, Duydu Y (2012) Human environmental and occupational exposures to boric acid: reconciliation with experimental reproductive toxicity data. J Toxicol Environ Health A 75(8–10):508–514
Bolt HM, Duydu Y, Basaran N, Golka K (2017) Boron and its compounds: current biological research activities. Arch Toxicol 91:2719–2722
Conover WJ (1999) Practical nonparametric statistics, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Ustundag A, Aydin S, Undeger U et al (2011) Reproductive toxicity parameters and biological monitoring in occupationally and environmentally boron-exposed persons in Bandirma, Turkey. Arch Toxicol 85(6):589–600
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Bolt HM (2012a) Exposure assessment of boron in Bandirma boric acid production plant. J Trace Elem Med Biol 26(2–3):161–164
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Ustundag A, Aydin S, Undeger et al (2012b) Assessment of DNA integrity (COMET assay) in sperm cells of boron exposed workers. Arch Toxicol 86(1):27–35
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Bolt HM (2015) Risk assessment of borates in occupational settings, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 65–105
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Ustundag A, Aydin S, Undeger U et al (2016) Is boric acid toxic to reproduction in humans? Assessment of the animal reproductive toxicity data and epidemiological study results. Curr Drug Deliv 13(3):324–329
Duydu Y, Basaran N, Aydin S, Ustundag A, Yalcin CO, Goktas HG, Bacanli M, Aydos K, Atabekoglu CS, Golka K, Ickstadt K, Schwerdtle T, Werner M, Meyer S, Bolt HM (2018) Birth weight of newborns and pregnancy outcomes of environmentally boron- exposed females in Turkey. Arch Toxicol 92:2475–2485
EU Drinking Water Directive (1998) Council Directive 98/83/EC, of 3 November 1998, on the quality of water intended for human consumption, https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:1998:330:0032:0054:EN:PDF. Accessed 20 July 2018
Fail PA, Chapin RE, Price CJ, Heindel JJ (1998) General, reproductive, developmental and endocrine toxicity of boronated compounds. Reprod Toxicol 12(1):1–18
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70
Ku WW, Chapin RE, Wine RN, Gladen BC (1993) Testicular toxicity of boric acid (BA): relationship of dose to lesion development and recovery in F344 rat. Reprod Toxicol 7:305–319
R Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006
Robbins WA, Xun L, Jia J, Kennedy N, Elashoff DA, Ping L (2010) Chronic boron exposure and human semen parameters. Reprod Toxicol 29:184–190
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality, fourth edition, 2011. WHO Press, World Health Organization, Geneva. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/publications/drinking-water-quality-guidelines-4-including-1st-addendum/en/. Accessed 19 Mar 2018
World Health Organization (2010) WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen. 5th edn. WorldHealth Organization, Geneva
Xing X, Wu G, Wei F, Liu P, Wei H, Whang C, Xu J, Xun L, Jia J, Kennedy N, Elashoff D, Robbins W (2008) Biomarkers of environmental and workplace boron exposure. J Occup Environ Hyg 5:141–147
Acknowledgements
This study was a part of the “Boron Project II”, which was funded by Eti Mine Works General Management (2014–2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The project was funded by Eti Mine. Eti Mine had no influence on the conduct of the study and has not influenced the results and interpretation. Thus, the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duydu, Y., Başaran, N., Aydın, S. et al. Evaluation of FSH, LH, testosterone levels and semen parameters in male boron workers under extreme exposure conditions. Arch Toxicol 92, 3051–3059 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2296-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2296-7