Abstract
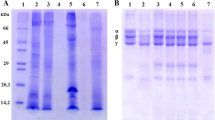
This paper describes two neurotoxic proteins obtained from the Caribbean sea anemone Lebrunia danae. To assess the neurotoxic activity of the venom of L. danae, several bioassays were carried out, and to evaluate the effect of the toxin, Median Lethal Doses (LD50) were determined in vivo using sea crabs (Ocypode quadrata) and Artemia salina nauplii with the crude extract of the proportion of 2.82 mg/m. The proteins with neurotoxic effects were isolated using low-pressure liquid chromatography. The fractions containing the neurotoxic activity were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and showed protein bands with an apparent molecular weight of 62.50 kDa (LdNt1) and 58 kDa (LdNt2). To demonstrate that these proteins were indeed responsible for the neurotoxic activity observed, we injected a small fraction of the purified protein into the third walking leg of a crab and observed the typical convulsions, paralysis and death provoked by neurotoxins. Hemolytic activity was also tested for 0.238 mg of crude extract; the hemolytic value was 39.5, 49.6 and 50.1% for cow, sheep and pig erythrocytes, respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Alsen C, Peters T, Scheufler E (1982) Studies on the mechanism of the positive inotropic effect of ATX II (Anemonia sulcata) on isolated guinea pig atria. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 4:63–69
Anderluh G, Maček P (2000) Review: cytolytic peptide and protein toxins from sea anemones (Anthozoa: Actinaria). Toxicon 40:111–124
Ayre DJ (1982) Inter-genotype aggression in solitary sea anemone Actinia tenebrosa. Mar Biol 68:199–205
Baslow MH (1977) Marine pharmacology: a study of toxins and other biologically active substances of marine origin. Krieger R E Publishing, Huntington, p 327
Béress L (1982) Biologically active compounds from coelenterates. Pure Appl Chem 54:1981–1994
Béress L, Zwick J (1980) Purification of two crab-paralyzing polypeptides from the sea anemone Bolocera tuediae. Marine Chem 8:333–338
Béress L, Béress R (1984) Biologically active compounds from marine invertebrates. Nova Acta Leopoldina. 56:153–159
Garateix A, Vega R, Salceda E, Cebada J, Aneiros A, Soto E (2000) BgK anemone toxin inhibits outward K+ currents in snail neurons. Brain Res 864:312–314
Hessinger DA (1988) Nematocyst Venoms and toxins. In: Hessinger DA, Lenhoff HM (eds) The biology of Nematocyst. Academic. San Diego pp 333–368
Kem WR, Parten B, Pennington MW, Dunn BM, Price D (1989) Isolation and characterization, and amino acid sequence of a polypeptide neurotoxin occurring in the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus. Biochemistry 28:3483–3489
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Maček P, Belmonte G, Pederzolli C, Menestrina G (1994) Mechanisms of action of Equinotoxin-II, a cytolysin from the sea anemone Actinia equina L. belonging to the family of actinosporins. Toxinology 87:205–227
Meyer BN, Ferrigni NR, Putnam JE, Jacobsen LB, Nicols D E, Mc Laughlin J L (1982) Brine shrimp: a convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. J Medicinal Plan Res. 45:31–34
Monastyrnaya MM, Zykova TA, Apalikova OV, Shwets TV, Kozlovskaya EP (2002) Biologically active polypeptides from the tropical sea anemone Radianthus macrodactylus. Toxicon 40:1197–1217
Norton RS (1991) Structure and structure-function relationship of sea anemone proteins that interact with the sodium channel. Toxicon 29:1051–1084
Norton RT, Kashiwagi M. Shibata S (1978) Anthopleurin A, B and C cardiotonic polypeptides from the sea anemone Anthopleura xanthogrammica (Brandt) and Anthopleura elegantissima (Brandt). In: Kaul PN, Sindermann CJ (eds) Drugs and food from the sea myth or reality? University of Oklahoma Press, Oklahoma, pp 37–50
Rottini GD, Dobrina A, Forgiarini O, Nardon E, Almirante G, Patriarca P (1990) Purification and properties of a cytolitic toxin in venom of the jellyfish Carybdea marsupialis. Toxicon. 33:315–326
Santamaría A, Sánches-Rodríguez J, Zugasti A, Martínez A, Galván-Arzate S, Segura-Puertas L (2002) A venoms extract from the sea anemone Bartholomea annulata produces haemolysis and lipid peroxidation in mouse erythrocytes. Toxicology 173:221–228
Terlau H, Olivera BM (2004) Conus venoms: a rich source of novel ion channel-targeted peptides. Physiol Rev 84:41–68
Wah ST (1993) Toxicity testing using the brine shrimp: Artemia salina. In: Colegate SM, Molyneux RJ (eds) Bioactive natural products, detection, isolation and structural determination. CRC London pp 441–456
Watson GM, Hessinger DA (1989) The three-dimensional structure of the neurotoxin ATX Ia from Anemonia sulcata in aqueous solution determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proteins 6:357–371
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Fernando Negrete-Soto, M.Sc., for his collection of sea anemones and Dr. Anastazia Banaszak for help with the English expressions in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez-Rodríguez, J., Cruz-Vazquez, K. Isolation and biological characterization of neurotoxic compounds from the sea anemone Lebrunia danae (Duchassaing and Michelotti, 1860). Arch Toxicol 80, 436–441 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0059-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0059-3