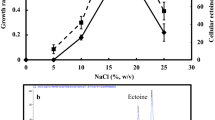
Abstract
Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) is a type of biopolymer produced by most bacteria and archaea, resembling thermoplastic with biodegradability and biocompatibility features. Here, we report the complete genome of a PHA producer, Aquitalea sp. USM4, isolated from Perak, Malaysia. This bacterium possessed a 4.2 Mb circular chromosome and a 54,370 bp plasmid. A total of 4067 predicted protein-coding sequences, 87 tRNA genes, and 25 rRNA operons were identified using PGAP. Based on ANI and dDDH analysis, the Aquitalea sp. USM4 is highly similar to Aquitalea pelogenes. We also identified genes, including acetyl-CoA (phaA), acetoacetyl-CoA (phaB), PHA synthase (phaC), enoyl-CoA hydratase (phaJ), and phasin (phaP), which play an important role in PHA production in Aquitalea sp. USM4. The heterologous expression of phaC1 from Aquitalea sp. USM4 in Cupriavidus necator PHB−4 was able to incorporate six different types of PHA monomers, which are 3-hydroxybutyrate (3HB), 3-hydroxyvalerate (3HV), 4-hydroxybutyrate (4HB), 5-hydroxyvalerate (5HV), 3-hydroxyhexanoate (3HHx) and isocaproic acid (3H4MV) with suitable precursor substrates. This is the first complete genome sequence of the genus Aquitalea among the 22 genome sequences from 4 Aquitalea species listed in the GOLD database, which provides an insight into its genome evolution and molecular machinery responsible for PHA biosynthesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (1990) Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 54(4):450–472. https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.54.4.450-472.1990
Ang SL, Shaharuddin B, Chuah J-A, Sudesh K (2020) Electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate)/silk fibroin film is a promising scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol 145:173–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.149
Arikawa H, Matsumoto K (2016) Evaluation of gene expression cassettes and production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) with a fine modulated monomer composition by using it in Cupriavidus necator. Microb Cell Fact 15(1):184. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0583-7
Bhubalan K, Chuah JA, Shozui F, Brigham CJ, Taguchi S, Sinskey AJ, Rha C, Sudesh K (2011) Characterization of the highly active polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase of Chromobacterium sp. strain USM2. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(9):2926–2933. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01997-10
Braunegg G, Sonnleitner B, Lafferty R (1978) A rapid gas chromatographic method for the determination of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6(1):29–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00500854
Brito C, Carvalho CB, Santos F, Gazzinelli RT, Oliveira SC, Azevedo V, Teixeira S (2004) Chromobacterium violaceum genome: molecular mechanisms associated with pathogenicity. Gen Mol Res 3(1):148–161
Budde CF, Mahan AE, Lu J, Rha C, Sinskey AJ (2010) Roles of multiple acetoacetyl coenzyme A reductases in polyhydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in Ralstonia eutropha H16. J Bacteriol 192(20):5319–5328. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00207-10
Budde CF, Riedel SL, Willis LB, Rha C, Sinskey AJ (2011) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from plant oil by engineered Ralstonia eutropha strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(9):2847–2854. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02429-10
Chee JY, Yoga SS, Lau N-S, Ling SC, Abed RM, Sudesh K (2010) Bacterially produced polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): converting renewable resources into bioplastics. Curr Res Technol Educ Top Appl Microbiol Microb Biotechnol 2:1395–1404
Chen I-MA, Chu K, Palaniappan K, Ratner A, Huang J, Huntemann M, Hajek P, Ritter S, Varghese N, Seshadri R, Roux S, Woyke T, Eloe-Fadrosh EA, Ivanova NN, Kyrpides NC (2020) The IMG/M data management and analysis system v.6.0: new tools and advanced capabilities. Nucl Acid Res 49(D1):D751–D763. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa939
Chuah J-A, Yamada M, Taguchi S, Sudesh K, Doi Y, Numata K (2013) Biosynthesis and characterization of polyhydroxyalkanoate containing 5-hydroxyvalerate units: effects of 5HV units on biodegradability, cytotoxicity, mechanical and thermal properties. Polym Degrad Stab 98(1):331–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2012.09.008
Doi Y (1990) Microbial polyesters: VCH, New York
Doi Y, Kitamura S, Abe H (1995) Microbial synthesis and characterization of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate). Macromolecules 28(14):4822–4828. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma00118a007
Ebadzadsahrai G, Soby S (2018) Draft genome sequence of Aquitalea sp. strain MWU14–2217, isolated from a wild cranberry bog in Provincetown, Massachusetts. Microbiol Resour Announ 7(21):e01493-e11418. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.01493-18
Fiedler S, Steinbüchel A, Rehm BH (2002) The role of the fatty acid β-oxidation multienzyme complex from Pseudomonas oleovorans in polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis: molecular characterization of the fadBA operon from P. oleovorans and of the enoyl-CoA hydratase genes phaJ from P. oleovorans and Pseudomonas putida. Arch Microbiol 178(2):149–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-002-0444-0
Foong CP, Lakshmanan M, Abe H, Taylor TD, Foong SY, Sudesh K (2017) A novel and wide substrate specific polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase from unculturable bacteria found in mangrove soil. J Polym Res 25(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1403-4
Friedrich B, Hogrefe C, Schlegel HG (1981) Naturally occurring genetic transfer of hydrogen-oxidizing ability between strains of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 147(1):198–205. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.147.1.198-205.1981
Fukui T, Doi Y (1997) Cloning and analysis of the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) biosynthesis genes of Aeromonas caviae. J Bacteriol 179(15):4821–4830. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.15.4821-4830.1997
Fukui T, Kichise T, Iwata T, Doi Y (2001) Characterization of 13 kDa granule-associated protein in Aeromonas caviae and biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates with altered molar composition by recombinant bacteria. Biomacromol 2(1):148–153. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm0056052
Fukui T, Ohsawa K, Mifune J, Orita I, Nakamura S (2011) Evaluation of promoters for gene expression in polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing Cupriavidus necator H16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89(5):1527–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3100-2
Gamal RF, Abdelhady HM, Khodair TA, El-Tayeb TS, Hassan EA, Aboutaleb KA (2013) Semi-scale production of PHAs from waste frying oil by Pseudomonas fluorescens S48. Braz J Microbiol 44(2):539–549. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822013000200034
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA–DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities 57(1): 81–91. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0
Haft DH, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Brover V, Chetvernin V, O’Neill K, Li W, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Gonzales NR (2018) RefSeq: an update on prokaryotic genome annotation and curation. Nucl Acids Res 46(D1):D851–D860. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1068
Hassan MA, Yee L-N, Yee PL, Ariffin H, Raha AR, Shirai Y, Sudesh K (2013) Sustainable production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from renewable oil-palm biomass. Biomass Bioenerg 50:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.10.014
Huisman GW, de Leeuw O, Eggink G, Witholt B (1989) Synthesis of poly-3-hydroxyalkanoates is a common feature of fluorescent pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol 55(8):1949–1954. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.55.8.1949-1954.1989
Ishizawa H, Kuroda M, Ike M (2017) Draft genome sequence of Aquitalea magnusonii strain H3, a plant growth-promoting bacterium of duckweed (Lemna minor). Genom Announ. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00812-17
Jendrossek D, Handrick R (2002) Microbial degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:403–432. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.micro.56.012302.160838
Kajitani R, Toshimoto K, Noguchi H, Toyoda A, Ogura Y, Okuno M, Yabana M, Harada M, Nagayasu E, Maruyama H (2014) Efficient de novo assembly of highly heterozygous genomes from whole-genome shotgun short reads. Genome Res 24(8):1384–1395. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.170720.113
Kajitani R, Noguchi H, Gotoh Y, Ogura Y, Yoshimura D, Okuno M, Toyoda A, Kuwahara T, Hayashi T, Itoh T (2021) MetaPlatanus: a metagenome assembler that combines long-range sequence links and species-specific features. Nucl Acids Res 49(22):e130–e130. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab831
Kolibachuk D, Miller A, Dennis D (1999) Cloning, molecular analysis, and expression of the polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase (phaC) gene from Chromobacterium violaceum. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(8):3561–3565. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.8.3561-3565.1999
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Steven Hill D, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166(1):175–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(95)00584-1
Lakshmanan M, Foong CP, Abe H, Sudesh K (2019) Biosynthesis and characterization of co and ter-polyesters of polyhydroxyalkanoates containing high monomeric fractions of 4-hydroxybutyrate and 5-hydroxyvalerate via a novel PHA synthase. Polym Degrad Stab 163:122–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.03.005
Lau H-T, Faryna J, Triplett EW (2006) Aquitalea magnusonii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel Gram-negative bacterium isolated from a humic lake. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 56(4):867–871. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64089-0
Lee SY, Choi J-i (1999) Production and degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates in waste environment. Waste Manage 19(2):133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(99)00005-7
Lee W-H, Loo C-Y, Nomura CT, Sudesh K (2008) Biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymers from mixtures of plant oils and 3-hydroxyvalerate precursors. Biores Technol 99(15):6844–6851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.01.051
Lee C-M, Weon H-Y, Kim Y-J, Son J-A, Yoon S-H, Koo B-S, Kwon S-W (2009) Aquitalea denitrificans sp. Nov., isolated from a Korean wetland. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 59(5):1045–1048. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.002840-0
Lee I, Ouk Kim Y, Park S-C, Chun J. (2016). OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. 66(2), 1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
Ling SC, Tsuge T, Sudesh K (2011) Biosynthesis of novel polyhydroxyalkanoate containing 3-hydroxy-4-methylvalerate by Chromobacterium sp. USM2. J Appl Microbiol 111(3):559–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05084.x
Lopez-Llorca L, Valiente MC, Gascon A (1993) A study of biodegradation of poly-β-hydroxyalkanoate (PHA) films in soil using scanning electron microscopy. Micron 24(1):23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-4328(93)90012-P
Maehara A, Taguchi S, Nishiyama T, Yamane T, Doi Y (2002) A repressor protein, PhaR, regulates polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthesis via its direct interaction with PHA. J Bacteriol 184(14):3992–4002. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.184.14.3992-4002.2002
McCool GJ, Cannon MC (2001) PhaC and PhaR are required for polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthase activity in Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol 183(14):4235–4243. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.14.4235-4243.2001
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14(1):60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Mukherjee S, Stamatis D, Bertsch J, Ovchinnikova G, Sundaramurthi Jagadish C, Lee J, Kandimalla M, Chen I-MA, Kyrpides NC, Reddy TBK (2020) Genomes OnLine Database (GOLD) vol 8: overview and updates. Nucl Acids Res 49(D1):D723–D733. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa983
Neoh SZ, Chek MF, Tan HT, Linares-Pastén JA, Nandakumar A, Hakoshima T, Sudesh K (2022) Polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase (PhaC): the key enzyme for biopolyester synthesis. Curr Res Biotechnol 4:87–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crbiot.2022.01.002
Ng LM, Sudesh K (2016) Identification of a new polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) producer Aquitalea sp. USM4 (JCM 19919) and characterization of its PHA synthase. J Biosci Bioeng 122(5):550–557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2016.03.024
Ngo HT, Kim H, Trinh H, Yi T-H (2020) Aquitalea aquatilis sp. Nov., isolated from Jungwon waterfall. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 70(9):4903–4907. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004351
Peoples OP, Sinskey AJ (1989) Poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) biosynthesis in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16: identification and characterization of the PHB polymerase gene (phbC). J Biol Chem 264(26):15298–15303. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)84825-1
Reddy C, Ghai R, Kalia VC (2003) Polyhydroxyalkanoates: an overview. Biores Technol 87(2):137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(02)00212-2
Rehm BHA (2003) Polyester synthases: natural catalysts for plastics. Biochem J 376(1):15–33. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20031254
Rehm BHA, Steinbüchel A (1999) Biochemical and genetic analysis of PHA synthases and other proteins required for PHA synthesis. Int J Biol Macromol 25(1):3–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-8130(99)00010-0
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(45):19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Oliver Glöckner F, Peplies J (2015) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32(6):929–931. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv681
Riedel SL, Bader J, Brigham CJ, Budde CF, Yusof ZA, Rha C, Sinskey AJ (2012) Production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) by Ralstonia eutropha in high cell density palm oil fermentations. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(1):74–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23283
Sedláček I, Kwon S-W, Švec P, Mašlanˇová I, Kýrová K, Holochová P, Černohlávková J, Busse H-J. (2016). Aquitalea pelogenes sp nov, isolated from mineral peloid. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 66(2), 962–967. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000819
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat Biotechnol 1(9):784–791
Slater SC, Voige WH, Dennis DE (1988) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 poly-β-hydroxybutyrate biosynthetic pathway. J Bacteriol 170(10):4431–4436. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.170.10.4431-4436.1988
Steinbüchel A, Valentin HE (1995) Diversity of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. FEMS Microbiol Lett 128(3):219–228. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1995.tb07528.x
Steinbüchel A, Debzi E-M, Marchessault RH, Timm A (1993) Synthesis and production of poly(3-hydroxyvaleric acid) homopolyester by Chromobacterium violaceum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39(4):443–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00205030
Sudesh K, Abe H, Doi Y (2000) Synthesis, structure and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates: biological polyesters. Prog Polym Sci 25(10):1503–1555. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6700(00)00035-6
Tan HT, Chek MF, Lakshmanan M, Foong CP, Hakoshima T, Sudesh K (2020) Evaluation of BP-M-CPF4 polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase on the production of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) from plant oil using Cupriavidus necator transformants. Int J Biol Macromol 159:250–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.064
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucl Acids Res 44(14):6614–6624. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw569
Thinagaran L, Sudesh K (2019) Evaluation of sludge palm oil as feedstock and development of efficient method for its utilization to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate. Waste Biomass Valorization 10:709–720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0078-8
Tsuge T, Fukui T, Matsusaki H, Taguchi S, Kobayashi G, Ishizaki A, Doi Y (2000) Molecular cloning of two (R)-specific enoyl-CoA hydratase genes from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and their use for polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 184(2):193–198. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2000.tb09013.x
Ushimaru K, Motoda Y, Numata K, Tsuge T, Parales RE (2014) Phasin proteins activate Aeromonas caviae polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase but not Ralstonia eutropha PHA synthase. Appl Environ Microbiol 80(9):2867–2873. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.04179-13
Varghese NJ, Mukherjee S, Ivanova N, Konstantinidis KT, Mavrommatis K, Kyrpides NC, Pati A (2015) Microbial species delineation using whole genome sequences. Nucl Acids Res 43(14):6761–6771. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv657
Wang H, Zhang K, Zhu J, Song W, Zhao L, Zhang X (2013) Structure reveals regulatory mechanisms of a MaoC-like hydratase from Phytophthora capsici involved in biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs). PLoS ONE 8(11):e80024. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080024
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110(10):1281–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4
Zain N-AA, Ng L-M, Foong CP, Tai YT, Nanthini J, Sudesh K (2020) Complete genome sequence of a novel polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) producer, Jeongeupia sp. USM3 (JCM 19920) and characterization of its PHA synthases. Curr Microbiol 77(3):500–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01852-z
Zhao H, Wei H, Liu X, Yao Z, Xu M, Wei D, Wang J, Wang X, Chen G-Q (2016) Structural insights on PHA binding protein PhaP from Aeromonas hydrophila. Sci Rep 6(1):39424. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep39424
Acknowledgements
JHW and SZN acknowledge the Graduate Student Financial Assistance (GRA‐Assist) awarded by Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM).
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia, titled “Soil analysis and value-addition to oil palm trunk (OPT) and sap through biotechnology” (203/PBIOLOGI/67811001 to KS) as well as Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JHW and LMN were involved in conceptualization. JHW, LMN, and RK designed and performed the experiment. JHW, LMN, and SZN were involved in formal analysis and wrote the original draft. KS and SK provided supervision. KS provided the funding. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This manuscript does not report data collected from humans or animals.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, J.H., Ng, LM., Neoh, S.Z. et al. Complete genome sequence of Aquitalea pelogenes USM4 (JCM19919), a polyhydroxyalkanoate producer. Arch Microbiol 205, 66 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03406-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03406-1