Abstract
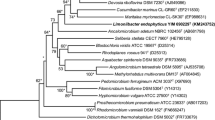
Three yellow-colored strains, NC2-4-308T, NC3-4-326 and NA3-4-109, were isolated from the rhizosphere soil of Larix gmelinii in Nanwenghe Nature Reserve, Great Khingan, China. These strains were oxidase- and catalase-positive and Gram-staining-negative. The cells were non-motile short rods that were aerobic and non-spore-forming. Growth occurred at pH values of 5.0–8.0 and at 0–4% (w/v) NaCl. The three strains were resistant to low temperature and grew at 2–35 °C. The principal fatty acids (> 5%) were summed feature 9, iso-C15:0, iso-C17:0 and anteiso-C15:0. The predominant quinone was ubiquinone-8. The polar lipids consisted of phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylcholine, two unidentified phospholipids, three unidentified lipids and three unidentified aminophospholipids. The DNA G + C content of the type species was 64.0 mol%. The 16S rRNA gene sequence similarities among the three strains are more than 99.9%, indicating they belong to the same species. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene, whole-genome sequences, the low ANI (74.2–75.5%) and dDDH (19.3–20.1%) hybridization values enabled differentiation of strains NC2-4-308T, NC3-4-326 and NA3-4-109 from the members of related genera. The combined data from the morphological, physiological, biochemical and chemotaxonomic tests indicate the three strains as a novel genus and a novel species in the family Rhodanobacteraceae. Therefore, we propose a novel genus with the name Pinirhizobacter soli gen. nov., sp. nov., for which the type strain is NC2-4-308T (= CFCC 14693T = KCTC 72394T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abedinzadeh M, Etesami H, Alikhani HA (2018) Characterization of rhizosphere and endophytic bacteria from roots of maize (Zea mays L.) plant irrigated with wastewater with biotechnological potential in agriculture. Biotechnol Rep 20:e00305
Akter S, Huq MA (2018) Luteibacter pinisoli sp. nov., a casein degrading bacterium isolated from rhizospheric soil of Pinus koraiensis. Arch Microbiol 7:1017–1023
Amos B, Rolf A (2000) The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res 28:45–48
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477
Besemer J, Lomsadze A, Borodovsky M (2001) GeneMarkS: a self-training method for prediction of gene starts in microbial genomes. Implications for finding sequence motifs in regulatory regions. Nucleic Acids Res 29:2607–2618
Bing X, Ke H, Inouye M (2001) Acquirement of cold sensitivity by quadruple deletion of the cspa family and its suppression by PNPase S1 domain in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 40:179–188
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Bernard H (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37(suppl 1):233–238
Chen MH, Xia F, Lv YY, Zhou XY, Qiu LH (2017) Dyella acidisoli sp. nov., D. flagellata sp. nov. and D. nitratireducens sp. nov., isolated from forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:736–743
Claus D (1992) A standardized Gram staining procedure. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 8:451–452
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Feng GD, Yang SZ, Xiong X, Li HP, Zhu HH (2017) Sphingomonas spermidinifaciens sp. nov., a novel bacterium containing spermidine as the major polyamine, isolated from an abandoned lead-zinc mine and emended descriptions of the genus Sphingomonas and the species Sphingomonas yantingensis and Sphingomonas japonica. Int J Syst Bacteriol 67:2160–2165
Galperin MY, Makarova KS, Wolf YI et al (2015) Expanded microbial genome coverage and improved protein family annotation in the COG database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:261–269
Johansen JE, Binnerup SJ, Kroer N, Mølbak L (2005) Luteibacter rhizovicinus gen. nov., sp. nov., a yellow-pigmented gammaproteobacterium isolated from the rhizosphere of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2285–2291
Kämpfer P, Lodders N, Falsen E et al (2009) 2006 as Luteibacter yeojuensis comb. nov., isolated from human blood, and reclassification of Dyella yeojuensis Kim et al. 2006 as Luteibacter yeojuensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2884–2887
Kandror O, Deleon A, Goldberg AL (2002) Trehalose synthesis is induced upon exposure of Escherichia coli to cold and is essential for viability at low temperatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9727–9732
Kates M (1986) Techniques of Lipidology, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lee DW, Lee SD (2009) Dyella marensis sp. nov., isolated from cliff soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1397–400
Lundberg DS, Lebeis SL, Paredes SH, Yourstone S, Gehring J (2012) Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature 488:86–90
Luo R, Liu B, Xie Y, Li Z, Huang W et al (2012) SOAPdenovo2: an empirically improved memory-efficient short-read de novo assembler. Gigascience 1:18
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-basedspecies delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Minnikin DE, O’Donnel AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M et al (1984) An intergrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid uinines and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Naushad S, Adeolu M, Wong S, Sohail M, Schellhorn HE et al (2015) A phylogenomic and molecular marker based taxonomic framework for the order Xanthomonadales: proposal to transfer the families Algiphilaceae and Solimonadaceae to the order Nevskiales ord. nov. and to create a new family within the order Xanthomonadales, the family Rhodanobacteraceae fam. nov., containing the genus Rhodanobacter and its closest relatives. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 107:467–485
Reiner J, Pisani L, Qiao WQ, Singh R, Yang Y et al (2018) Cytogenomic identification and long-read single molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing of a Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 9 (BBS9) deletion. Npj Genom Med 3:3
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1993) Theoretical foundation of the minimum-evolution method of phylogenetic inference. Mol Biol Evol 10:1073–1095
Saha S, Bridges S, Magbanua ZV, Peterson DG (2008) Empirical comparison of ab initio repeat finding programs. Nucleic Acids Res 36:2284–2294
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1997) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Biochemistry 74:5463–5467
Stackebrandt E, Päuker O, Steiner U, Schumann P, Sträubler B et al (2007) Taxonomic characterization of members of the genus Corallococcus: molecular divergence versus phenotypic coherency. Syst Appl Microbiol 30:109–118
Stanke M, Diekhans M, Baertsch R, Haussler D (2008) Using native and syntenically mapped cDNA alignments to improve de novo gene finding. Bioinformatics 24:637–644
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M et al (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Won KH, Singh H, Yi T, Kook M, Kim K et al (2015) Rhodanobacter koreensis sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from tomato rhizosphere. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1180–1185
Wu LK, Chen J, Xiao ZG, Zhu XC, Wang JY et al (2018) Barcoded pyrosequencing reveals a shift in the bacterial community in the rhizosphere and rhizoplane of Rehmannia glutinosa under consecutive monoculture. Int J Mol Sci 19:850
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y et al (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: A taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA and whole genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Zuo G, Hao B (2015) CVTree3 web server for whole-genome-based and alignment-free prokaryotic phylogeny and taxonomy. Genom Proteom Bioinform 13:321–331
Funding
This work was funded by the National Infrastructure of Microbial Resources (NIMR-2020-7) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant NO. 31570603).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there is no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, H., Piao, Cg., Lin, Yh. et al. Pinirhizobacter soli gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel low temperature resistant gammaproteobacterium in the family Rhodanobacteraceae isolated from rhizospheric soil of Larix gmelinii. Arch Microbiol 204, 283 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02867-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02867-0