Abstract
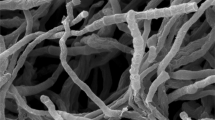
During the course of isolating rare actinobacteria from unexplored habitats, strain CH32T was obtained from an arid soil sample in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Polyphasic characterization and comprehensive genome analyses showed that the strain is a member of the genus Nonomuraea and it is closely related to Nonomuraea gerenzanensis ATCC 39727T, Nonomuraea polychroma DSM 43925T and Nonomuraea maritima FXJ7.203T with gene identity level of 98.7%, 98.2% and 98.1%, respectively. The whole-cell hydrolysates contain meso-diaminopimelic acid as diagnostic diaminoacid and glucose, ribose, galactose, mannose and madurose as whole cell sugars. The predominant menaquinones are MK-9(H4), MK-9(H6) and MK-9(H2) while MK-9 exists as minor component. The polar lipid profile consists of diphosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylinositol, glycolipid, glycophospholipids, phospholipids and unidentified lipids. The major cellular fatty acids are iso-C16:0 and C17:0 10-methyl. The total genome size is about 9.6 Mb and the G + C content is 71.0%. The genome contains biosynthetic gene clusters encoding for terpenes, siderophores, a type III polyketide synthase, a non-ribosomal polypeptide synthetase and a bacteriocin. The genome-based comparisons of the strain with its phylogenetic neighbours, as indicated by digital DNA–DNA hybridization and average nucleotide identity analyses, reveal that strain CH32T (= JCM 33876T = KCTC 49368T) is a novel member of the genus Nonomuraea, for which Nonomuraea terrae sp. nov. is proposed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alanjary M et al (2017) The antibiotic resistant target seeker (ARTS), an exploration engine for antibiotic cluster prioritization and novel drug target discovery. Nucleic Acids Res 45:W42–W48
Amin DH, Abolmaaty A, Borsetto C, Tolba S, Abdallah NA, Wellington EM (2019) In silico genomic mining reveals unexplored bioactive potential of rare actinobacteria isolated from Egyptian soil. Bull Natl Res Cent 43:78
Aryal N, Aziz S, Rajbhandari P, Gross H (2019) Draft genome sequence of Nonomuraea sp. strain C10, a producer of brartemicin, isolated from a mud dauber wasp nest in Nepal. Microbiol Resour Announc 8:45
Ay H, Saygin H, Sahin N (2020) Phylogenomic revision of the family Streptosporangiaceae, reclassification of Desertactinospora gelatinilytica as Spongiactinospora gelatinilytica comb. nov. and a taxonomic home for the genus Sinosporangium in the family Streptosporangiaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:2562–2572
Aziz RK et al (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9:75
Barka EA et al (2016) Taxonomy, physiology, and natural products of actinobacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 80:1–43
Blin K et al (2019) antiSMASH 5.0: updates to the secondary metabolite genome mining pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W81–W87
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL (2009) BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform 10:421
Collins MD (1985) 11 Analysis of isoprenoid quinones. Methods in microbiology, vol 18. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 329–36618
D’Argenio V et al (2016) The complete 12 Mb genome and transcriptome of Nonomuraea gerenzanensis with new insights into its duplicated “magic” RNA polymerase. Sci Rep 6:1–13
Dalmastri C, Gastaldo L, Marcone GL, Binda E, Congiu T, Marinelli F (2016) Classification of Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727, an actinomycete that produces the glycopeptide antibiotic A40926, as Nonomuraea gerenzanensis sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:912–921
Davis JJ et al (2016) PATtyFams: protein families for the microbial genomes in the PATRIC database. Front Microbiol 7:118
Derewacz DK et al (2014) Structure and stereochemical determination of hypogeamicins from a cave-derived actinomycete. J Nat Prod 77:1759–1763
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Farris JS (1972) Estimating phylogenetic trees from distance matrices. Am Nat 106:645–668
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA–DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Kämpfer P, Kroppenstedt RM (1996) Numerical analysis of fatty acid patterns of coryneform bacteria and related taxa. Can J Microbiol 42:989–1005
Komaki H, Ichikawa N, Tamura T, Oguchi A, Hamada M, Fujita N (2016) Genome-based survey of nonribosomal peptide synthetase and polyketide synthase gene clusters in type strains of the genus Microtetraspora. J Antibiot 69:712–718
Komaki H, Sakurai K, Hosoyama A, Kimura A, Igarashi Y, Tamura T (2018) Diversity of nonribosomal peptide synthetase and polyketide synthase gene clusters among taxonomically close Streptomyces strains. Sci Rep 8:1–11
Kreft Ł, Botzki A, Coppens F, Vandepoele K, Van Bel M (2017) PhyD3: a phylogenetic tree viewer with extended phyloXML support for functional genomics data visualization. Bioinformatics 33:2946–2947
Kroppenstedt RM, Goodfellow M (2006) The family Thermomonosporaceae: Actinocorallia, actinomadura, spirillospora and thermomonospora. The prokaryotes. Springer, New York, pp 682–724
Kurtz S, Phillippy A, Delcher AL, Smoot M, Shumway M, Antonescu C, Salzberg SL (2004) Versatile and open software for comparing large genomes. Genome Biol 5:R12
Küster E, Williams S (1964) Selection of media for isolation of streptomycetes. Nature 202:928–929
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108
Lechevalier MP, Lechevalier H (1970) Chemical composition as a criterion in the classification of aerobic actinomycetes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 20:435–443
Lefort V, Desper R, Gascuel O (2015) FastME 2.0: a comprehensive, accurate, and fast distance-based phylogeny inference program. Mol Biol Evol 32:2798–2800
Lipun K, Teo WFA, Tongpan J, Matsumoto A, Duangmal K (2019) Nonomuraea suaedae sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil of Suaeda maritima (L.) Dumort. J Antibiot 72:518–523
Malik A, Kim YR, Jang IH, Hwang S, Oh D-C, Kim SB (2020) Genome-based analysis for the bioactive potential of Streptomyces yeochonensis CN732, an acidophilic filamentous soil actinobacterium. BMC Genom 21:118
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M (2019) TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat Commun 10:2182
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013a) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M, Spröer C, Klenk H-P (2013b) When should a DDH experiment be mandatory in microbial taxonomy? Arch Microbiol 195:413–418
Meier-Kolthoff JP et al (2014) Complete genome sequence of DSM 30083 T, the type strain (U5/41 T) of Escherichia coli, and a proposal for delineating subspecies in microbial taxonomy. Stand Genom Sci 9:2
Minnikin D, O'donnell A, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett J (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Nazari B, Forneris CC, Gibson MI, Moon K, Schramma KR, Seyedsayamdost MR (2017) Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 55076 harbours the largest actinomycete chromosome to date and the kistamicin biosynthetic gene cluster. MedChemComm 8:780–788
Niemhom N, Chutrakul C, Suriyachadkun C, Thawai C (2017) Nonomuraea stahlianthi sp. nov., an endophytic actinomycete isolated from the stem of Stahlianthus campanulatus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2879–2884
Ondov BD, Treangen TJ, Melsted P, Mallonee AB, Bergman NH, Koren S, Phillippy AM (2016) Mash: fast genome and metagenome distance estimation using MinHash. Genome Biol 17:132
Primahana G, Risdian C, Mozef T, Sudarman E, Köck M, Wink J, Stadler M (2020) Nonocarbolines A–E, β-carboline antibiotics produced by the rare actinobacterium Nonomuraea sp. from Indonesia. Antibiotics 9:126
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Oliver Glöckner F, Peplies J (2015) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinformatics 32:929–931
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria through fatty acid analysis. In: Klement Z, Rudolph K, Sands D (eds) Methods in phytobacteriology. Akademiai Kiado, Budapest, pp 199–204
Saygin H, Nouioui I, Ay H, Guven K, Cetin D, Klenk HP, Goodfellow M, Sahin N (2020) Polyphasic classification of Nonomuraea strains isolated from the Karakum Desert and description of Nonomuraea deserti sp. nov., Nonomuraea diastatica sp. nov., Nonomuraea longispora sp. nov. and Nonomuraea mesophila sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:636–647
Shaaban KA et al (2019) Karamomycins A–C: 2-Naphthalen-2-yl-thiazoles from Nonomuraea endophytica. J Nat Prod 82:870–877
Shirling ET, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16:313–340
Sosio M, Stinchi S, Beltrametti F, Lazzarini A, Donadio S (2003) The gene cluster for the biosynthesis of the glycopeptide antibiotic A40926 by Nonomuraea species. Chem Biol 10:541–549
Sripreechasak P, Phongsopitanun W, Supong K, Pittayakhajonwut P, Kudo T, Ohkuma M, Tanasupawat S (2017) Nonomuraea rhodomycinica sp. nov., isolated from peat swamp forest soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1683–1687
Staneck JL, Roberts GD (1974) Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol 28:226–231
Sungthong R, Nakaew N (2015) The genus Nonomuraea: a review of a rare actinomycete taxon for novel metabolites. J Basic Microbiol 55:554–565
Supong K, Sripreechasak P, Phongsopitanun W, Tanasupawat S, Danwisetkanjana K, Bunbamrung N, Pittayakhajonwut P (2019) Antimicrobial substances from the rare actinomycete Nonomuraea rhodomycinica NR4-ASC07T. Nat Prod Res 33:2285–2291
Terui Y, Chu Y-w, Li J-y, Ando T, Fukunaga T, Aoki T, Toda Y (2008) New cyclic tetrapeptides from Nonomuraea sp. TA-0426 that inhibit glycine transporter type 1 (GlyT1). Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:6321–6323
Tocchetti A et al (2015) A genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic look at the GE2270 producer Planobispora rosea, an uncommon actinomycete. PLoS One 10:e0133705. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133705
Wang F et al (2011) Nonomuraea wenchangensis sp. nov., isolated from mangrove rhizosphere soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1304–1308
Wattam AR et al (2016) Improvements to PATRIC, the all-bacterial bioinformatics database and analysis resource center. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D535–D542
Weyland H (1969) Actinomycetes in North Sea and Atlantic ocean sediments. Nature 223:858–858
Williams S, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Wellington E, Sneath P, Sackin M (1983) Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J Gen Microbiol 129:1743–1813
Xi L, Zhang L, Ruan J, Huang Y (2011) Nonomuraea maritima sp. nov., isolated from coastal sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2740–2744
Yoon S-H, Ha S-M, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Yushchuk O, Andreo-Vidal A, Marcone GL, Bibb M, Marinelli F, Binda E (2020) New molecular tools for regulation and improvement of A40926 glycopeptide antibiotic production in Nonomuraea gerenzanensis ATCC 39727. Front Microbiol 11:8
Acknowledgements
Genome sequencing was provided by MicrobesNG (https://www.microbesng.uk) which is supported by the BBSRC (Grant number BB/L024209/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants and/or animals performed by the author. The formal consent is not required in this study.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ay, H. Nonomuraea terrae sp. nov., isolated from arid soil. Arch Microbiol 202, 2197–2205 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01941-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-01941-9