Abstract
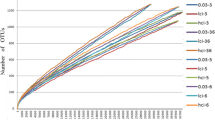
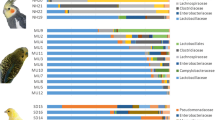
The goal of this study is to compare the gut microbiota of domestic blue fox (Alopex lagopus) and raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides) to provide better understanding of their intestinal gut microbiota. We analyzed the structure of fecal microbes in 40 blue foxes and 40 raccoon dogs that were raised under same conditions, using high-throughput Illumina sequencing targeting the V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene. In total, 295,146 sequence reads were obtained. The average number of operational taxonomical units in the two group samples was 194 to 286. Firmicutes (blue fox 73.40%, raccoon dog 46.90%) and Bacteroidetes (blue fox 21.92%, raccoon dog 44.25%) were the most abundant phyla in the gut of blue fox and raccoon dog. At the genus level, Prevotella (blue fox 16.89%, raccoon dog 36.22%), Blautia (blue fox 9.02%, raccoon dog 13.72%), and Peptostreptococcaeae_incertae_sedi (blue fox 22.41%, raccoon dog 2.84%) were commonly presented in the gut of two kinds of animal. Principal coordinates analysis showed that the microbial communities were different between blue fox and raccoon dog. The Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes ratio was higher in blue foxes (3:1) than in raccoon dogs (1:1). Moreover, Peptostreptococcaeae_incertae_sedi and Prevotella, were more abundant in the gut of blue fox, whereas the abundance of Prevotella and Blautia were higher in the gut of raccoon dog. In conclusion, the present study revealed the difference of the gut microbial composition between blue fox and raccoon dog under the same diet conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amato KR, Yeoman CJ, Kent A, Righini N, Carbonero F, Estrada A, Gaskins HR, Stumpf RM, Yildirim S, Torralba M, Gillis M, Wilson BA, Nelson KE, White BA, Leigh SR (2013) Habitat degradation impacts black howler monkey (Alouatta pigra) gastrointestinal microbiomes. ISME J 7:1344–1353
An C, Okamoto Y, Xu S, Ko KY, Kimura J, Yamamoto N (2017) Comparison of fecal microbiota of three captive carnivore species inhabiting Korea. J Vet Med Sci 79:542–546
Arsene-Ploetze F, Nicoloff H, Bringel F (2005) Lactobacillus plantarum ccl gene is non-essential, arginine-repressed and codes for a conserved protein in Firmicutes. Arch Microbiol 183:307–316
Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2005) Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307:1915–1920
Becker AA, Hesta M, Hollants J, Janssens GP, Huys G (2014) Phylogenetic analysis of faecal microbiota from captive cheetahs reveals underrepresentation of Bacteroidetes and Bifidobacteriaceae. BMC Microbiol 14:43
Bekele AZ, Koike S, Kobayashi Y (2010) Genetic diversity and diet specificity of ruminal Prevotella revealed by 16S rRNA gene-based analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 305:49–57
Bermingham EN, Kittelmann S, Young W, Kerr KR, Swanson KS, Roy NC, Thomas DG (2013) Post-weaning diet affects faecal microbial composition but not selected adipose gene expression in the cat (Felis catus). PLoS ONE 8:e80992
Bermingham EN, Maclean P, Thomas DG, Cave NJ, Young W (2017) Key bacterial families (Clostridiaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae and Bacteroidaceae) are related to the digestion of protein and energy in dogs. PeerJ 5:e3019
Bernini LJ, Simao AN, Alfieri DF, Lozovoy MA, Mari NL, de Souza CH, Dichi I, Costa GN (2016) Beneficial effects of Bifidobacterium lactis on lipid profile and cytokines in patients with metabolic syndrome: a randomized trial. Effects of probiotics on metabolic syndrome. Nutrition 32:716–719
Berry D (2016) The emerging view of Firmicutes as key fibre degraders in the human gut. Environ Microbiol 18:2081–2083
Bervoets L, Van Hoorenbeeck K, Kortleven I, Van Noten C, Hens N, Vael C, Goossens H, Desager KN, Vankerckhoven V (2013) Differences in gut microbiota composition between obese and lean children: a cross-sectional study. Gut Pathog 5:10
Bian G, Ma L, Su Y, Zhu W (2013) The microbial community in the feces of the white rhinoceros (Ceratotherium simum) as determined by barcoded pyrosequencing analysis. PLoS ONE 8:e70103
Cabre E, Manosa M, Gassull MA (2012) Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory bowel diseases—a systematic review. Br J Nutr 107(Suppl 2):S240–252
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Clemente JC, Ursell LK, Parfrey LW, Knight R (2012) The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view. Cell 148:1258–1270
Cole JR, Wang Q, Cardenas E, Fish J, Chai B, Farris RJ, Kulam-Syed-Mohideen AS, McGarrell DM, Marsh T, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM (2009) The ribosomal database project: improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D141–D145
Deusch O, O'Flynn C, Colyer A, Morris P, Allaway D, Jones PG, Swanson KS (2014) Deep illumina-based shotgun sequencing reveals dietary effects on the structure and function of the fecal microbiome of growing kittens. PLoS ONE 9:e101021
Deusch O, O'Flynn C, Colyer A, Swanson KS, Allaway D, Morris P (2015) A longitudinal study of the feline faecal microbiome identifies changes into early adulthood irrespective of sexual development. PLoS ONE 10:e0144881
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10(10):996–998
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
Fischer MM, Kessler AM, Kieffer DA, Knotts TA, Kim K, Wei A, Ramsey JJ, Fascetti AJ (2017) Effects of obesity, energy restriction and neutering on the faecal microbiota of cats. Brit J Nutr 118:513–524
Geng YY, Yang FH, Xing XM, Gao XH (2012) Effects of dietary fat levels on nutrient digestibility and production performance of growing-furring blue foxes (Alopex lagopus). J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 96:610–617
Grześkowiak Ł, Endo A, Beasley S, Salminen S (2015) Microbiota and probiotics in canine and feline welfare. Anaerobe 34:14–23
Handl S, Dowd SE, Garcia-Mazcorro JF, Steiner JM, Suchodolski JS (2011) Massive parallel 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing reveals highly diverse fecal bacterial and fungal communities in healthy dogs and cats. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 76:301–310
Huang S, Zhang H (2013) The impact of environmental heterogeneity and life stage on the hindgut microbiota of Holotrichia parallela larvae (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). PLoS ONE 8:e57169
Lee SM, Han HW, Yim SY (2015) Beneficial effects of soy milk and fiber on high cholesterol diet-induced alteration of gut microbiota and inflammatory gene expression in rats. Food Funct 6:492–500
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI (2006) Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444:1022–1023
Ley RE, Hamady M, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Ramey RR, Bircher JS, Schlegel ML, Tucker TA, Schrenzel MD, Knight R, Gordon J (2008) Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 320:1647–1651
Liu H, Li G, Zhong W, Li D, Liu F, Sun W (2012) Supplemental dietary methionine affects the pelt quality and nutrient metabolism of raccoon dogs (Nyctereutes procyonoides). Asian J Anim Vet Adv 7:61–67
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8228–8235
Mazmanian SK, Round JL, Kasper DL (2008) A microbial symbiosis factor prevents intestinal inflammatory disease. Nature 453:620–625
McGrosky A, Navarrete A, Isler K, Langer P, Clauss M (2016) Gross intestinal morphometry and allometry in Carnivora. Eur J Wildlife Res 62:395–405
Middelbos IS, Boler BMV, Qu A, White BA, Swanson KS, Fahey GC (2010) Phylogenetic characterization of fecal microbial communities of dogs fed diets with or without supplemental dietary fiber using 454 pyrosequencing. PLoS ONE 5:e9768
Million M, Lagier JC, Yahav D, Paul M (2013) Gut bacterial microbiota and obesity. Clin Microbiol Infect 19:305–313
Muegge BD, Kuczynski J, Knights D, Clemente JC, Gonzalez A, Fontana L, Henrissat B, Knight R, Gordon JI (2011) Diet drives convergence in gut microbiome functions across mammalian phylogeny and within humans. Science 332:970–974
Nagy-Szakal D, Hollister EB, Luna RA, Szigeti R, Tatevian N, Smith CW, Versalovic J, Kellermayer R (2013) Cellulose supplementation early in life ameliorates colitis in adult mice. PLoS ONE 8:e56685
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590–D596
Roggenbuck M, Schnell IB, Blom N, Baelum J, Bertelsen MF, Sicheritz-Ponten T, Sorensen SJ, Gilbert MT, Graves GR, Hansen LH (2015) Corrigendum: the microbiome of New World vultures. Nat Commun 6:8774
Salyers AA, West SE, Vercellotti JR, Wilkins TD (1977) Fermentation of mucins and plant polysaccharides by anaerobic bacteria from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol 34:529–533
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Shen W, Gaskins HR, McIntosh MK (2014) Influence of dietary fat on intestinal microbes, inflammation, barrier function and metabolic outcomes. J Nutr Biochem 25:270–280
Song C, Wang B, Tan J, Zhu L, Lou D, Cen X (2017) Comparative analysis of the gut microbiota of black bears in China using high-throughput sequencing. Mol Genet Genomics 292:407–414
Suchodolski JS, Camacho J, Steiner JM (2008) Analysis of bacterial diversity in the canine duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and colon by comparative 16S rRNA gene analysis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:567–578
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444:1027–1031
Turnbaugh PJ, Backhed F, Fulton L, Gordon JI (2008) Diet-induced obesity is linked to marked but reversible alterations in the mouse distal gut microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 3:213–223
Ussar S, Griffin NW, Bezy O, Fujisaka S, Vienberg S, Softic S, Deng LX, Bry L, Gordon JI, Kahn CR (2015) Interactions between Gut microbiota, host genetics and diet modulate the predisposition to obesity and metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab 22:516–530
Wu XY, Zhang HH, Chen J, Shang S, Wei QG, Yan JK, Tu XY (2016) Comparison of the fecal microbiota of dholes high-throughput Illumina sequencing of the V3–V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:3577–3586
Zhang H, DiBaise JK, Zuccolo A, Kudrna D, Braidotti M, Yu Y, Parameswaran P, Crowell MD, Wing R, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R (2009) Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2365–2370
Zhang CH, Li SF, Yang L, Huang P, Li WJ, Wang SY, Zhao GP, Zhang MH, Pang XY, Yan Z, Liu Y, Zhao LP (2013) Structural modulation of gut microbiota in life-long calorie-restricted mice. Nat Commun 4
Zhang HH, Zhou N, Zhang TT, Bao K, Xu C, Song XC, Li GY (2014) Effects of different dietary manganese levels on growth performance and N balance of growing mink (Neovision vision). Biol Trace Elem Res 160:206–211
Zhang JY, Zhu BC, Xu C, Ding X, Li JF, Zhang XG, Lu ZH (2015a) Strategy of selecting 16S rRNA hypervariable regions for metagenome-phylogenetic marker genes based analysis. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 26:3545–3553
Zhang Q, Pan Y, Yan RQ, Zeng BH, Wang HF, Zhang XW, Li WX, Wei H, Liu ZH (2015b) Commensal bacteria direct selective cargo sorting to promote symbiosis. Nat Immunol 16:918–926
Zhu L, Wu Q, Dai J, Zhang S, Wei F (2011) Evidence of cellulose metabolism by the giant panda gut microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:17714–17719
Zhu L, Wu Q, Deng C, Zhang M, Zhang C, Chen H, Lu G, Wei F (2018) Adaptive evolution to a high purine and fat diet of carnivorans revealed by gut microbiomes and host genomes. Environ Microbiol 20:1711–1722
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS-ASTIP-2017-ISAPS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt .
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1.
Rarefaction analysis of V3/V4 MiSeq sequencing reads of the 16S rRNA gene in different fecal ecosystems. Rarefaction curves at a cutoff level of 3 % were constructed at a 97 % sequence similarity cutoff value in mothur (PDF 18 kb)
Table S1.
Major phyla of the microbiota of blue fox and raccoon dog, and their percentage composition (DOC 32 kb)
Table S2.
Differences of the fecal microbiota of blue fox and raccoon dog at class level (DOC 35 kb)
Table S3
. Differences of the fecal microbiota of blue fox and raccoon dog at genus level (DOC 54 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Li, Z., Si, H. et al. Comparative analysis of the gut microbiota of the blue fox (Alopex lagopus) and raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides). Arch Microbiol 202, 135–142 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01721-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01721-0