Abstract
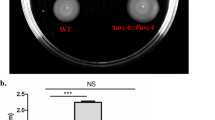
Vibrio parahaemolyticus expresses one major virulence determinant T6SS2, which is constituted into three putative operons, i.e., VPA1027-1024, VPA1043-1028, and VPA1044-1046. CalR, a LysR-type transcriptional regulator, was originally identified as a repressor of the swarming motility and T3SS1 gene expression. As shown in this study, CalR binds to the promoter-proximal region of each of the three operons to activate their transcription, and moreover, CalR activates the adhesion of V. parahaemolyticus to HeLa cells. In addition, competitive EMSAs demonstrated that CalR acts as an antagonist of H–NS in V. parahaemolyticus. Collectively, these studies confirmed a new physiological role for CalR in V. parahaemolyticus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ante VM, Bina XR, Bina JE (2015a) The LysR-type regulator LeuO regulates the acid tolerance response in Vibrio cholerae. Microbiology 161:2434–2443
Ante VM, Bina XR, Howard MF, Sayeed S, Taylor DL, Bina JE (2015b) Vibrio cholerae leuO transcription is positively regulated by ToxR and contributes to bile resistance. J Bacteriol 197:3499–3510
De la Cruz MA, Fernandez-Mora M, Guadarrama C, Flores-Valdez MA, Bustamante VH, Vazquez A et al (2007) LeuO antagonizes H–NS and StpA-dependent repression in Salmonella enterica ompS1. Mol Microbiol 66:727–743
Dillon SC, Espinosa E, Hokamp K, Ussery DW, Casadesus J, Dorman CJ (2012) LeuO is a global regulator of gene expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol Microbiol 85:1072–1089
Gao H, Zhang Y, Yang L, Liu X, Guo Z, Tan Y et al (2011) Regulatory effects of cAMP receptor protein (CRP) on porin genes and its own gene in Yersinia pestis. BMC Microbiol 11:40
Gode-Potratz CJ, Chodur DM, McCarter LL (2010) Calcium and iron regulate swarming and type III secretion in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol 192:6025–6038
Hernandez-Lucas I, Calva E (2012) The coming of age of the LeuO regulator. Mol Microbiol 85:1026–1028
Hernandez-Lucas I, Gallego-Hernandez AL, Encarnacion S, Fernandez-Mora M, Martinez-Batallar AG, Salgado H et al (2008) The LysR-type transcriptional regulator LeuO controls expression of several genes in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. J Bacteriol 190:1658–1670
Hertzberg KM, Gemmill R, Jones J, Calvo JM (1980) Cloning of an EcoRI-generated fragment of the leucine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. Gene 8:135–152
Ma L, Zhang Y, Yan X, Guo L, Wang L, Qiu J et al (2012) Expression of the type VI secretion system 1 component Hcp1 is indirectly repressed by OpaR in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Sci World J 2012:982140
Makino K, Oshima K, Kurokawa K, Yokoyama K, Uda T, Tagomori K et al (2003) Genome sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a pathogenic mechanism distinct from that of V cholerae. Lancet 361:743–749
Moorthy S, Watnick PI (2005) Identification of novel stage-specific genetic requirements through whole genome transcription profiling of Vibrio cholerae biofilm development. Mol Microbiol 57:1623–1635
Parales RE, Harwood CS (1993) Construction and use of a new broad-host-range lacZ transcriptional fusion vector, pHRP309, for gram- bacteria. Gene 133:23–30
Philippe N, Alcaraz JP, Coursange E, Geiselmann J, Schneider D (2004) Improvement of pCVD442, a suicide plasmid for gene allele exchange in bacteria. Plasmid 51:246–255
Raghunath P (2014) Roles of thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) and TDH-related hemolysin (TRH) in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front Microbiol 5:805
Records AR (2011) The type VI secretion system: a multipurpose delivery system with a phage-like machinery. Molecular plant-microbe interactions. MPMI 24:751–757
Salomon D, Gonzalez H, Updegraff BL, Orth K (2013) Vibrio parahaemolyticus type VI secretion system 1 is activated in marine conditions to target bacteria, and is differentially regulated from system 2. PloS one 8:e61086
Sun F, Zhang Y, Qiu Y, Yang H, Yang W, Yin Z et al (2014) H–NS is a repressor of major virulence gene loci in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Front Microbiol 5:675
Wang L, Zhou D, Mao P, Zhang Y, Hou J, Hu Y et al (2013) Cell density- and quorum sensing-dependent expression of type VI secretion system 2 in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. PloS one 8:e73363
Whitaker WB, Parent MA, Boyd A, Richards GP, Boyd EF (2012) The Vibrio parahaemolyticus ToxRS regulator is required for stress tolerance and colonization in a novel orogastric streptomycin-induced adult murine model. Infect Immun 80:1834–1845
Yang L, Zhan L, Han H, Gao H, Guo Z, Qin C et al (2010) The low-salt stimulon in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Int J Food Microbiol 137:49–54
Yu Y, Yang H, Li J, Zhang P, Wu B, Zhu B et al (2012) Putative type VI secretion systems of Vibrio parahaemolyticus contribute to adhesion to cultured cell monolayers. Arch Microbiol 194:827–835
Zhou D, Yan X, Qu F, Wang L, Zhang Y, Hou J et al (2013) Quorum sensing modulates transcription of cpsQ-mfpABC and mfpABC in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Int J Food Microbiol 166:458–463
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20160505), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471184), and the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Pathogen and Biosecurity of China (SKLPBS1517).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Djamel DRIDER.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Osei-Adjei, G., Zhang, Y. et al. CalR is required for the expression of T6SS2 and the adhesion of Vibrio parahaemolyticus to HeLa cells. Arch Microbiol 199, 931–938 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1361-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1361-6