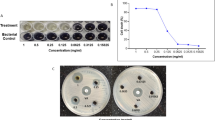
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a serious causative agent of infectious disease. Multidrug-resistant strains like methicillin-resistant S. aureus compromise treatment efficacy, causing significant morbidity and mortality. Active efflux represents a major antimicrobial resistance mechanism. The proton-driven multidrug efflux pump, LmrS, actively exports structurally distinct antimicrobials. To circumvent resistance and restore clinical efficacy of antibiotics, efflux pump inhibitors are necessary, and natural edible spices like cumin are potential candidates. The mode of cumin antibacterial action and underlying mechanisms behind drug resistance inhibition, however, are unclear. We tested the hypothesis that cumin inhibits LmrS drug transport. We found that cumin inhibited bacterial growth and LmrS ethidium transport in a dosage-dependent manner. We demonstrate that cumin is antibacterial toward a multidrug-resistant host and that resistance modulation involves multidrug efflux inhibition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allahghadri T, Rasooli I, Owlia P, Nadooshan MJ, Ghazanfari T, Taghizadeh M, Astaneh SD (2010) Antimicrobial property, antioxidant capacity, and cytotoxicity of essential oil from cumin produced in Iran. J Food Sci 75:H54–H61. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01467.x
Andersen JL, He GX, Kakarla P, Ranjana KC, Kumar S, Lakra WS, Mukherjee MM, Ranaweera I, Shrestha U, Tran T, Varela MF (2015) Multidrug efflux pumps from Enterobacteriaceae, Vibrio cholerae and Staphylococcus aureus bacterial food pathogens. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12:1487–1547. doi:10.3390/ijerph120201487
Ani V, Varadaraj MC, Naidu KA (2006) Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of polyphenolic compounds from bitter cumin (Cuminum nigrum L.). Eur Food Res Technol 224:117. doi:10.1007/s00217-006-0408-8
Arora JK (1999) Antimicrobial activity of spices. Int J Antimicrob Agents 12:257–262
Aruna K, Sivaramakrishnan VM (1996) Anticarcinogenic effects of the essential oils from cumin, Poppy and Basil. Phytother Res 10:577–580. doi:10.1002/(sici)1099-1573(199611)10:7<577:aid-ptr906>3.0.co;2-q
Behera S, Nagarajan S, Jagan Mohan Rao L (2004) Microwave heating and conventional roasting of cumin seeds (Cuminum cyminum L.) and effect on chemical composition of volatiles. Food Chem 87:25–29. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2003.10.012
Bhardwaj AK, Mohanty P (2012) Bacterial efflux pumps involved in multidrug resistance and their inhibitors: rejuvinating the antimicrobial chemotherapy. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov 7:73–89
Bing L (2013) Separation and analysis of bacteriostatic component from cumin essential oil. Food Ind 9:043
Blair JM, Piddock LJ (2016) How to measure export via bacterial multidrug resistance efflux pumps. MBio. doi:10.1128/mBio.00840-16
Bukhari S, Iqbal S, Bhanger MI (2009) Antioxidant potential of commercially available cumin (Cuminum cyminuml inn) in Pakistan. Int J Food Sci Nutr 60:240–247. doi:10.1080/09637480701695583
Costa SS, Viveiros M, Amaral L, Couto I (2013) Multidrug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: an update. Open Microbiol J 7:59–71. doi:10.2174/1874285801307010059
Derakhshan S, Sattari M, Bigdeli M (2010) Effect of cumin (Cuminum cyminum) seed essential oil on biofilm formation and plasmid Integrity of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pharmacogn Mag 6:57–61. doi:10.4103/0973-1296.59967
Dhandapani S, Subramanian VR, Rajagopal S, Namasivayam N (2002) Hypolipidemic effect of Cuminum cyminum L. on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Pharmacol Res Off J Ital Pharmacol Soc 46:251–255
Diaz MR, Sembrano JM (1985) A comparative study of the efficacy of garlic and eugenol as palliative agents against dental pain of pulpal origin. J Philipp Dent Assoc 35:3–10
Drysdale A (1950) Staphylococcus aureus food poisoning; an account of an outbreak in Khartoum. J Trop Med Hyg 53:12–14
Floyd JL, Smith KP, Kumar SH, Floyd JT, Varela MF (2010) LmrS is a multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:5406–5412. doi:10.1128/AAC.00580-10
Floyd JL, Kumar S, Mukherjee MM, He G, Varela MF (2013) A review of the molecular mechanisms of drug efflux in pathogenic bacteria: A structure-function perspective. Recent Res Dev Membr Biol 3:15–66
Fridkin SK, Hageman JC, Morrison M, Sanza LT, Como-Sabetti K, Jernigan JA, Harriman K, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Farley MM (2005) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus disease in three communities. N Engl J Med 352(14):1436–1444
Gachkar L, Yadegari D, Rezaei M, Taghizadeh M, Astaneh S, Rasooli I (2007) Chemical and biological characteristics of Cuminum cyminum and Rosmarinus officinalis essential oils. Food Chem 102:898–904. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.06.035
Heidarian M, Vahideh Tyagi AK, Ebrahimi SH, Mohini M (2013) Effect of cumin (Cuminum cyminum) seed extract on milk fatty acid profile and methane emission in lactating goat. Small Rumin Res 113:66–72. doi:10.1016/j.smallrumres.2013.01.015
Holland TL, Arnold C, Fowler VG Jr (2014) Clinical management of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Rev JAMA 312:1330–1341. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.9743
Iacobellis NS, Lo Cantore P, Capasso F, Senatore F (2005) Antibacterial activity of Cuminum cyminum L. and Carum carvi L. essential oils. J Agric Food Chem 53:57–61. doi:10.1021/jf0487351
Jalali H, Zekavat B, Sereshti H (2007) Use of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with resolution methods to characterize the essential oil components of Iranian cumin and caraway. J Chromatogr A 1143:215–226. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.01.042
Janahmadi M, Niazi F, Danyali S, Kamalinejad M (2006) Effects of the fruit essential oil of Cuminum cyminum Linn. (Apiaceae) on pentylenetetrazol-induced epileptiform activity in F1 neurones of Helix aspersa. J Ethnopharmacol 104:278–282. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2005.09.019
Jarraud S (2002) Relationships between Staphylococcus aureus genetic background, virulence factors, agr groups (Alleles), and human disease. Infect Immun 70:631–641. doi:10.1128/iai.70.2.631-641.2002
Krieg PA, Melton DA (1987) In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol 155:397–415
Kumar S, Varela MF (2012) Biochemistry of bacterial multidrug efflux pumps. Int J Mol Sci 13:4484–4495. doi:10.3390/ijms13044484
Kumar S, Varela MF (2013) Molecular mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents. In: Méndez-Vilas A (ed) Microbial pathogens and strategies for combating them: science, technology and education. Formatex Research Center Inc, Badajoz, pp 522–534
Kumar S, Floyd JT, He G, Varela MF (2013a) Bacterial antimicrobial efflux pumps of the MFS and MATE transporter families: a review. Recent Res Dev Antimicrob Agents Chemother 7:1–21
Kumar S, Mukherjee MM, Varela MF (2013b) Modulation of bacterial multidrug resistance efflux pumps of the major facilitator superfamily. Int J Bacteriol. doi:10.1155/2013/204141
Kumar S, He G, Kakarla P, Shrestha U, Ranjana KC, Ranaweera I, Willmon TM, Barr SR, Hernandez AJ, Varela MF (2016) Bacterial multidrug efflux pumps of the major facilitator superfamily as targets for modulation. Infect Disord Drug Targets 16:28–43
Liu B (2013) Separation and analysis of bacteriostatic components from cumin essential oil. J Chem Pharm Res 5:358–363
Mageed MAAE, Mansour AF, El Massry KF, Ramadan MM, Shaheen MS, Shaaban H (2012) Effect of microwaves on essential oils of coriander and cumin seeds and on their antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. J Essent Oil Bear Plants 15:614–627. doi:10.1080/0972060x.2012.10644096
Martinez T, Jimenez AM, Ruggieri S, Frega N, Strabbioli R, Murcia MA (2001) Antioxidant properties of Mediterranean spices compared with common food additives. J Food Prot 64:1412–1419
Milan KM, Dholakia H, Tiku PK, Vishveshwaraiah P (2008) Enhancement of digestive enzymatic activity by cumin (Cuminum cyminum L.) and role of spent cumin as a bionutrient. Food Chem 110:678–683. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.062
Nalini N, Sabitha K, Viswanathan P, Menon VP (1998) Influence of spices on the bacterial (enzyme) activity in experimental colon cancer. J Ethnopharmacol 62:15–24
Naveed R, Hussain I, Tawab A, Tariq M, Rahman M, Hameed S, Mahmood MS, Siddique AB, Iqbal M (2013) Antimicrobial activity of the bioactive components of essential oils from Pakistani spices against Salmonella and other multi-drug resistant bacteria. BMC Complement Altern Med 13:265. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-13-265
Otsuka M, Yasuda M, Morita Y, Otsuka C, Tsuchiya T, Omote H, Moriyama Y (2005) Identification of essential amino acid residues of the NorM Na+/multidrug antiporter in Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol 187:1552–1558. doi:10.1128/JB.187.5.1552-1558.2005
Özkan G, Sağdiç O, Özcan M (2003) Note: inhibition of pathogenic bacteria by essential oils at different concentrations. Food Sci Technol Int 9:85–88. doi:10.1177/1082013203009002003
Ranaweera I, Shrestha U, Ranjana KC, Kakarla P, Willmon TM, Hernandez AJ, Mukherjee MM, Barr SR, Varela MF (2015) Structural comparison of bacterial multidrug efflux pumps of the major facilitator superfamily trends. Cell Mol Biol 10:131–140
Sağdıç O, Kuşçu A, Özcan M, Özçelik S (2002) Effects of Turkish spice extracts at various concentrations on the growth of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Food Microbiol 19:473–480. doi:10.1006/fmic.2002.0494
Schindler BD, Jacinto P, Kaatz GW (2013) Inhibition of drug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus: current status of potentiating existing antibiotics. Future Microbiol 8:491–507. doi:10.2217/fmb.13.16
Shetty RS, Singhal RS, Kulkarni PR (1994) Antimicrobial properties of cumin. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 10:232–233. doi:10.1007/BF00360896
Smith KP, Kumar S, Varela MF (2009) Identification, cloning, and functional characterization of EmrD-3, a putative multidrug efflux pump of the major facilitator superfamily from Vibrio cholerae O395. Arch Microbiol 191:903–911. doi:10.1007/s00203-009-0521-8
Sowbhagya H (2013) Chemistry, technology, and nutraceutical functions of cumin (Cuminum cyminum L): an overview. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 53:1–10. doi:10.1080/10408398.2010.500223
Stavri M, Piddock LJ, Gibbons S (2007) Bacterial efflux pump inhibitors from natural sources. J Antimicrob Chemother 59:1247–1260. doi:10.1093/jac/dkl460
Tajkarimi MM, Ibrahim SA, Cliver DO (2010) Antimicrobial herb and spice compounds in food. Food Control 21:1199–1218. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2010.02.003
Thippeswamy NB, Naidu KA (2005) Antioxidant potency of cumin varieties—cumin, black cumin and bitter cumin—on antioxidant systems. Eur Food Res Technol 220:472–476. doi:10.1007/s00217-004-1087-y
Tong SY, Davis JS, Eichenberger E, Holland TL, Fowler VG Jr (2015) Staphylococcus aureus infections: epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev 28:603–661. doi:10.1128/cmr.00134-14
Varela MF, Kumar S, He G (2013) Potential for inhibition of bacterial efflux pumps in multidrug-resistant Vibrio cholerae. Indian J Med Res 138:285–287
Venter H, Mowla R, Ohene-Agyei T, Ma S (2015) RND-type drug efflux pumps from Gram-negative bacteria: molecular mechanism and inhibition. Front Microbiol 6:1–11. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2015.00377
Wang Y, Venter H, Ma S (2015) Efflux pump inhibitors: a novel approach to combat efflux-mediated drug resistance in bacteria. Curr Drug Targets 17:702–719
Willatgamuwa SA, Platel K, Saraswathi G, Srinivasan K (1998) Antidiabetic influence of dietary cumin seeds (Cuminum cyminum) in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Nutr Res 18:131–142. doi:10.1016/S0271-5317(97)00207-8
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an Internal Research Grant (ENMU) and by the US Department of Education, HSI STEM, P031C110114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kakarla, P., Floyd, J., Mukherjee, M. et al. Inhibition of the multidrug efflux pump LmrS from Staphylococcus aureus by cumin spice Cuminum cyminum . Arch Microbiol 199, 465–474 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1314-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1314-5