Abstract
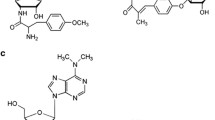
In Streptomyces davawensis roseoflavin is synthesized from GTP and ribulose-5-phosphate through riboflavin. As a first step towards the molecular analysis of flavin metabolism in S. davawensis the genes involved in riboflavin biosynthesis were cloned by hybridization of heterologous probes to a genomic library on a high-density colony-array. The genes ribB (riboflavin synthase, α-chain; EC 2.5.1.9), ribM (putative membrane protein), ribA (bifunctional GTP cyclohydrolase II/3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase; EC 3.5.4.25) and ribH (lumazine synthase; EC 2.5.1.9) are organized in an operon-like cluster. Northern blot analysis of this cluster revealed two transcripts of 1.7 and 3.1 kb, respectively. The gene ribB was overexpressed in Escherichia coli. The specific riboflavin synthase activity in a cell-free extract of a recombinant strain was 0.246 nmol mg−1 min−1. Overexpression of ribM enhanced the transport of riboflavin in the corresponding recombinant E. coli strain. Furthermore, overexpression of ribM increased roseoflavin sensitivity of E. coli. On another subgenomic fragment a putative S. davawensis ribG gene coding for the missing pyrimidine deaminase/reductase (EC 3.5.4.26 and EC 1.1.1.193) of the riboflavin biosynthetic pathway and ribY coding for a second (monofunctional) GTP cyclohydrolase II were identified.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacher A, Baur R, Eggers U, Harders HD, Otto MK, Schnepple H (1980) Riboflavin synthases of Bacillus subtilis. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem 255:632–637
Bacher A, Eberhardt S, Richter G (1996) Biosynthesis of riboflavin. In: Neidhardt FC (ed) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. ASM Press, Washington, pp 657–664
Bacher A, Eberhardt S, Fischer M, Kis K, Richter G (2000) Biosynthesis of vitamin B2 (riboflavin). Annu Rev Nutr 20:153–167
Bacher A et al (2001) Biosynthesis of riboflavin. Vitam Horm 61:1–49
Bandrin SV, Beburov M, Rabinovich PM, Stepanov AI (1979) [Riboflavin auxotrophs of Escherichia coli]. Genetika 15:2063–2065
Bentley SD et al (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Bereswill S, Hinkelmann S, Kist M, Sander A (1999) Molecular analysis of riboflavin synthesis genes in Bartonella henselae and use of the ribC gene for differentiation of Bartonella species by PCR. J Clin Microbiol 37:3159–3166
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Burgess CM, Slotboom DJ, Geertsma ER, Duurkens RH, Poolman B, van Sinderen D (2006) The riboflavin transporter RibU in Lactococcus lactis: molecular characterization of gene expression and the transport mechanism. J Bacteriol 188:2752–2760
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Eberhardt S, Richter G, Gimbel W, Werner T, Bacher A (1996) Cloning, sequencing, mapping and hyperexpression of the ribC gene coding for riboflavin synthase of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 242:712–719
Eberhardt S, Korn S, Lottspeich F, Bacher A (1997) Biosynthesis of riboflavin: an unusual riboflavin synthase of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol 179:2938–2943
Fassbinder F, Kist M, Bereswill S (2000) Structural and functional analysis of the riboflavin synthesis genes encoding GTP cyclohydrolase II (ribA), DHBP synthase (ribBA), riboflavin synthase (ribC), and riboflavin deaminase/reductase (ribD) from Helicobacter pylori strain P1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 191:191–197
Fischer M, Bacher A (2005) Biosynthesis of flavocoenzymes. Nat Prod Rep 22:324–350
Fuller TE, Mulks MH (1995) Characterization of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae riboflavin biosynthesis genes. J Bacteriol 177:7265–7270
Gusarov II et al (1997) Riboflavin biosynthetic genes in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens: primary structure, organization and regulation of activity. Mol Biol (Mosk) 31:446–453
Haase I, Mortl S, Kohler P, Bacher A, Fischer M (2003) Biosynthesis of riboflavin in archaea. 6,7-dimethyl-8-ribityllumazine synthase of Methanococcus jannaschii. Eur J Biochem 270:1025–1032
Hunkapiller MW, Hewick RM, Dreyer WJ, Hood LE (1983) High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol 91:399–413
Ikeda H et al (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol 21:526–531
Juri N, Kubo Y, Kasai S, Otani S, Kusunose M, Matsui K (1987) Formation of roseoflavin from 8-amino- and 8-methylamino-8-demethyl-d-riboflavin. J Biochem (Tokyo) 101:705–711
Kieser T, Bibb M, Buttner M, Chater K, Hodwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kreneva RA et al (2000) [Study of the phenotypic occurrence of ura gene inactivation in Bacillus subtilis]. Genetika 36:1166–1168
Lee CY, Szittner RB, Meighen EA (1991) The lux genes of the luminous bacterial symbiont, Photobacterium leiognathi, of the ponyfish. Nucleotide sequence, difference in gene organization, and high expression in mutant Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 201:161–167
Lee CY, Szittner RB, Miyamoto CM, Meighen EA (1993) The gene convergent to luxG in Vibrio fischeri codes for a protein related in sequence to RibG and deoxycytidylate deaminase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1143:337–339
Lee CY, O’Kane DJ, Meighen EA (1994) Riboflavin synthesis genes are linked with the lux operon of Photobacterium phosphoreum. J Bacteriol 176:2100–2104
Matsui K, Juri N, Kubo Y, Kasai S (1979) Formation of roseoflavin from guanine through riboflavin. J Biochem (Tokyo) 86:167–175
Otani S, Takatsu M, Nakano M, Kasai S, Miura R (1974) Letter: Roseoflavin, a new antimicrobial pigment from Streptomyces. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 27:86–87
Perkins J, Pero J (2002) Biosynthesis of riboflavin, biotin, folic acid, and cobalamin. In: Sonenshein A, Hoch J, Losick R (eds) Bacillus subtilis and its closest relatives: from genes to cells. ASM Press, Washington, pp 271–286
Richter G et al (1993) Biosynthesis of riboflavin: cloning, sequencing, mapping, and expression of the gene coding for GTP cyclohydrolase II in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 175:4045–4051
Richter G et al (1997) Biosynthesis of riboflavin: characterization of the bifunctional deaminase-reductase of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 179:2022–2028
Ritz H et al (2001) Biosynthesis of riboflavin: studies on the mechanism of GTP cyclohydrolase II. J Biol Chem 276:22273–22277
Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Sauer E, Merdanovic M, Mortimer AP, Bringmann G, Reidl J (2004) PnuC and the utilization of the nicotinamide riboside analog 3-aminopyridine in Haemophilus influenzae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:4532–4541
Spoonamore JE, Dahlgran AL, Jacobsen NE, Bandarian V (2006) Evolution of new function in the GTP cyclohydrolase II proteins of Streptomyces coelicolor. Biochemistry 45:12144–12155
Strohl WR (1992) Compilation and analysis of DNA sequences associated with apparent streptomycete promoters. Nucleic Acids Res 20:961–974
Stüber D, Matile H, Garotta G (1990) System for high-level production in Escherichia coli and rapid purification of recombinant proteins: application to epitope mapping, preparation of antibodies, and structure–function analysis. Immunol Methods 4:121–152
Vente A, Korn B, Zehetner G, Poustka A, Lehrach H (1999) Distribution and early development of microarray technology in Europe. Nat Genet 22:22
Vitreschak AG, Rodionov DA, Mironov AA, Gelfand MS (2002) Regulation of riboflavin biosynthesis and transport genes in bacteria by transcriptional and translational attenuation. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3141–3151
Winkler WC, Cohen-Chalamish S, Breaker RR (2002) An mRNA structure that controls gene expression by binding FMN. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15908–15913
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the Karl-Völker-Foundation and the German Research Foundation (DFG) for financial support and we thank John Clear for critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jean-Luc Pernodet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grill, S., Yamaguchi, H., Wagner, H. et al. Identification and characterization of two Streptomyces davawensis riboflavin biosynthesis gene clusters. Arch Microbiol 188, 377–387 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0258-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-007-0258-1