Abstract
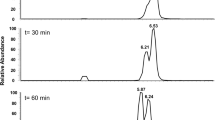
The naturally occurring sulfonate N-acetyltaurine was synthesized chemically and its identity was confirmed. Aerobic enrichment cultures for bacteria able to utilize N-acetyltaurine as sole source of fixed nitrogen or as sole source of carbon were successful. One representative isolate, strain NAT, which was identified as a strain of Delftia acidovorans, grew with N-acetyltaurine as carbon source and excreted stoichiometric amounts of sulfate and ammonium. Inducible enzyme activities were measured in crude extracts of this organism to elucidate the degradative pathway. Cleavage of N-acetyltaurine by a highly active amidase yielded acetate and taurine. The latter was oxidatively deaminated by taurine dehydrogenase to ammonium and sulfoacetaldehyde. This key intermediate of sulfonate catabolism was desulfonated by the known reaction of sulfoacetaldehyde acetyltransferase to sulfite and acetyl phosphate, which was further degraded to enter central metabolism. A degradative pathway including transport functions is proposed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergmeyer HU, Graßl M, Walter E-M (1983) Phosphotransacetylase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 295–296
Beutler H-O (1984) Acetate: determination with acetyl-CoA synthase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymic analysis, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 639–645
Brüggemann C, Denger K, Cook AM, Ruff J (2004) Enzymes and genes of taurine and isethionate dissimilation in Paracoccus denitrificans. Microbiology (Reading UK) 150:805–816
Clayden J, Greeves N, Warren S, Wothers P (2001) Organic chemistry. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 420–425
Cook AM (1987) Biodegradation of s-triazine xenobiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 46:93–116
Cook AM, Denger K (2002) Dissimilation of the C2 sulfonates. Arch Microbiol 179:1–6
Cook AM, Denger K (2006) Metabolism of taurine in microorganisms: a primer in molecular diversity? Adv Exp Med Biol 583:3–13
Cook AM, Hütter R (1981) s-Triazines as nitrogen sources for bacteria. J Agric Food Chem 29:1135–1143
Cunningham C, Tipton KF, Dixon HBF (1998) Conversion of taurine into N-chlorotaurine (taurine chloramine) and sulphoacetaldehyde in response to oxidative stress. Biochem J 330:939–945
Denger K, Ruff J, Rein U, Cook AM (2001) Sulfoacetaldehyde sulfo-lyase [EC 4.4.1.12] from Desulfonispora thiosulfatigenes: purification, properties and primary sequence. Biochem J 357:581–586
Denger K, Ruff J, Schleheck D, Cook AM (2004a) Rhodococcus opacus expresses the xsc gene to utilize taurine as a carbon source or as a nitrogen source but not as a sulfur source. Microbiology (Reading UK) 150:1859–1867
Denger K, Smits THM, Cook AM (2006) L-Cysteate sulfo-lyase, a widespread, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-coupled desulfonative enzyme purified from Silicibacter pomeroyi DSS-3T. Biochem J 394:657–664
Denger K, Weinitschke S, Hollemeyer K, Cook AM (2004b) Sulfoacetate generated by Rhodopseudomonas palustris from taurine. Arch Microbiol 182:254–258
Dixon GH, Kornberg HL (1959) Assay methods for key enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle. Biochem J 72:3P
Fujimoto D, Koyama T, Tamiya N (1968) N-Acetyl-β-alanine deacetylase in hog kidney. Biochim Biophys Acta 167:407–413
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (1994) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington
Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker (1996) German standard methods for the laboratory examination of water, waste water and sludge. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim
Gorzynska AK, Denger K, Cook AM, Smits THM (2006) Inducible transcription of genes involved in taurine uptake and dissimilation by Silicibacter pomeroyi DSS-3T. Arch Microbiol 182:402–406
Hayashi T, Yamamoto K, Matsuo A, Otsubo K, Muramatsu S, Matsuda A, Komatsu K-E (1997) Characterization and cloning of an enantioselective amidase from Comamonas acidovorans KPO-2771–4. J Ferment Bioeng 83:139–145
Higgins LE, Townley MA, Tillinghast EK, Rankin MA (2001) Variation in the chemical composition of orb webs built by the spider Nephila clavipes (Araneae, Tetragnathidae). J Arachnol 29:82–94
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 9th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Hughes GJ, Frutiger S, Fonck C (1987) Quantitative high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of Dabsyl-amino acids within 14 min. J Chromatogr 389:327–333
Huxtable RJ (1992) Physiological actions of taurine. Physiol Rev 72:101–163
Kim G-B, Miyamoto CM, Meighen EA, Lee BH (2004) Cloning and characterization of the bile salt hydrolase genes (bsh) from Bifidobacterium bifidum strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5603–5612
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nat Lond 227:680–685
Laue H, Denger K, Cook AM (1997) Taurine reduction in anaerobic respiration of Bilophila wadsworthia RZATAU. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2016–2021
Palleroni NJ (1984) Pseudomonadaceae. In: Krieg NR (ed) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 141–199
Patron NJ, Waller RF, Archibald JM, Keeling PJ (2005) Complex protein targeting to dinoflagellate plastids. J Mol Biol 348:1015–1024
Racker E (1962) Fructose-6-phosphate phosphoketolase from Acetobacter xylinum. Methods Enzymol 5:276–280
Reichenbecher W, Kelly DP, Murrell JC (1999) Desulfonation of propanesulfonic acid by Comamonas acidovorans strain P53: evidence for an alkanesulfonate sulfonatase and an atypical sulfite dehydrogenase. Arch Microbiol 172:387–392
Rein U, Gueta R, Denger K, Ruff J, Hollemeyer K, Cook AM (2005) Dissimilation of cysteate via 3-sulfolactate sulfo-lyase and a sulfate exporter in Paracoccus pantotrophus NKNCYSA. Microbiology (Reading UK) 151:737–747
Ruff J, Denger K, Cook AM (2003) Sulphoacetaldehyde acetyltransferase yields acetyl phosphate: purification from Alcaligenes defragrans and gene clusters in taurine degradation. Biochem J 369:275–285
Sörbo B (1987) Sulfate: turbidimetric and nephelometric methods. Methods Enzymol 143:3–6
Teraoka M (1925) Methylation and acylation of taurine. Hoppe-Seyler’s Z Physiol Chem 145:238–243
Tholey A, Wittmann C, Kang MJ, Bungert D, Hollemeyer K, Heinzle E (2002) Derivatization of small biomolecules for optimized matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 37:963–973
Thurnheer T, Köhler T, Cook AM, Leisinger T (1986) Orthanilic acid and analogues as carbon sources for bacteria: growth physiology and enzymic desulphonation. J Gen Microbiol 132:1215–1220
Vollrath F, Fairbrother WJ, Williams RJP, Tillinghast EK, Bernstein DT, Gallagher KS, Townley MA (1990) Compounds in the droplets of the orb spider’s viscid spiral. Nat Lond 345:526–528
Webb EC (1992) Enzyme nomenclature 1992: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Academic, San Diego, p 306
Weinitschke S, Denger K, Smits THM, Hollemeyer K, Cook AM (2006) The sulfonated osmolyte N-methyltaurine is dissimilated by Alcaligenes faecalis and by Paracoccus versutus with release of methylamine. Microbiology (Reading UK) 152:1179–1186
Weinitschke S, Styp von Rekowski K, Denger K, Cook AM (2005) Sulfoacetaldehyde is excreted quantitatively by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus SW1 during growth with taurine as sole source of nitrogen. Microbiology (Reading UK) 151:1285–1290
Wen A, Fegan M, Hayward C, Chakraborty S, Sly LI (1999) Phylogenetic relationships among members of the Comamonadaceae, and description of Delftia acidovorans (den Dooren de Jong 1926 and Tamaoka et al. 1987) gen nov, comb nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:567–576
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by funds from the University of Konstanz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayer, J., Denger, K., Smits, T.H.M. et al. N-Acetyltaurine dissimilated via taurine by Delftia acidovorans NAT. Arch Microbiol 186, 61–67 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0123-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0123-7