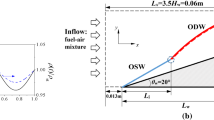
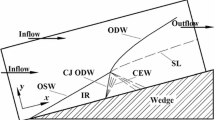
Abstract
The prompt oblique detonation wave (PODW) sustained by a finite-length wedge is investigated by numerical simulation. The numerical results show that it is possible to stabilize a PODW on a finite-length wedge shorter than the induction length of the mixture behind the inert shock by numerically imposing a premature initiation of combustion in the initial flow field. The fully coupled and the partially coupled PODWs are observed in the numerical results. For the fully coupled PODW, the upstream facing transverse waves (UF TW) are swept downstream and consequently a fully coupled PODW can persist. For the partially coupled PODW, the UF TWs propagate upstream and the downstream facing transverse waves are weakened by the expansion wave emanating from the corner. As a result, a partially coupled PODW forms. Further, it is found that the stability of the partially coupled PODW is weak. The configuration of the partially coupled PODW can be altered by local explosions occurring downstream.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashford, S.A., Emanuel, G.: Oblique detonation wave engine performance prediction. J. Propuls. Power 12(2), 322–327 (1996)
Hertzberg, A., Bruckner, A.P., Bogdanoff, D.W.: Ram accelerator: a new chemical method for accelerating projectile to ultrahigh velocities. AIAA J. 26(2), 195–203 (1988)
Fugueira da Silva, L.F., Deshaies, B.: Stabilization of an oblique detonation wave by a wedge: a parametric numerical study. Combust. Flame. 121, 152–166 (2000)
Verreault, J., Higgins, A.J.: Initiation of detonation by conical projectiles. Proc. Combust. Inst. 33, 2311–2318 (2011)
Lefebvre, M.H., Fujiwara, T.: Numerical modeling of combustion processes induced by a supersonic conical blunt body. Combust. Flame. 100, 85–93 (1995)
Liu, Y., Dan, W., Yao, S.-B., Wang, J.-P.: Analytical and numerical investigations of wedge-induced oblique detonation waves at low inflow Mach number. Combust. Sci. Tech. 187(6), 843–856 (2015)
Li, C., Kailasanath, K., Oran, E.S.: Detonation structures behind oblique shocks. Phys. Fluids. 6, 1600–1611 (1994)
Liu, Y., Liu, Y.S., Wu, D., Wang, J.P.: Structure of an oblique detonation wave induced by a wedge. Shock Waves (2016). doi:10.1007/s00193-015-0600-5 (in press)
Papalexandris, M.V.: A numerical study of wedge-induced detonations. Combust. Flame. 120, 526–538 (2000)
Teng, H.-H., Jiang, Z.-L.: On the transition pattern of the oblique detonation structure. J. Fluid Mech. 713, 659–669 (2012)
Teng, H.-H., Jiang, Z.-L., Ng, H.D.: Numerical study on unstable surfaces of oblique detonations. J. Fluid Mech. 744, 111–128 (2014)
Choi, J.-Y., Kim, D.-W., Jeung, I.-S., Ma, F., Yang, V.: Cell-like structure of unstable oblique detonation wave from high-resolution numerical simulation. Proc. Combust. Inst. 31(2), 2473–2480 (2007)
Teng, H.-H., Ng, H.D., Li, K., Luo, C.-T., Jiang, Z.-L.: Evolution of cellular structures on oblique detonation surfaces. Combust. Flame. 162, 470–477 (2015)
Verreault, J., Higgins, A.J., Stowe, R.A.: Formation of transverse waves in oblique detonations. Proc. Combust. Inst. 34(2), 1913–1920 (2013)
Gui, M.-Y., Fan, B.-C., Dong, G.: Periodic oscillation and fine structure of wedge-induced oblique detonation waves. Acta Mech. Sin. 27, 922–928 (2011)
Walter, M.A.T., Figueira da Silva, L.F.: Numerical study of detonation stabilization by finite length wedges. AIAA J. 44(2), 353–361 (2006)
Pimentel, C.A.R., Azevedo, J.L.F., Figueira da Silva, L.F.: Numerical study of wedge supported oblique shock wave-oblique detonation wave transitions. J. Braz. Soc. Mechan. Sci. XXIV, 149–157 (2002)
Kasahara, J., Takeishi, A., Kuroda, H., Horiba, M., Matsukawa, K., Leblanc, J.E., Endo, T., Fujiwara, T.: Experimental observation of oblique detonation waves around hypersonic free projectiles. In: Takayama, K., Sasoh, A. (eds.) Ram Accelerators, pp. 263–270. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, Germany (1998)
Kasahara, J., Arai, T., Chiba, S., Takazawa, K., Tanahashi, Y., Matsuo, A.: Criticality for stabilized oblique detonation waves around spherical bodies in acetylene/oxygen/krypton mixtures. Proc. Combust. Inst. 29, 2817–2824 (2002)
Kasahara, J., Fujiwara, T., Endo, T., Arai, T.: Chapman-Jouguet oblique detonation structure around hypersonic projectiles. AIAA J. 39, 1553–1561 (2001)
Kasahara, J., Arai, T., Matsuo, A., Akai, N., Takazawa, K.: Experimental investigation of steady-state oblique detonation waves generated around hypersonic projectiles. AIAA-2001-1800
Maeda, S., Inada, R., Kasahara, J., Matsuo, A.: Visualization of the non-steady state oblique detonation wave phenomena around hypersonic spherical projectile. Proc. Combust. Inst. 33, 2343–2349 (2011)
Korobeinikov, V.P., Levin, V.A., Markov, V.V., Chernyi, G.G.: Propagation of blast waves in a combustible gas. Astronaut. Acta 17(4–5), 529–537 (1972)
Liu, Y.-F.: Numerical Studies on Detonation and Pulse Detonation Engines (in Chinese). College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing (2004)
Steger, J.L., Warming, R.F.: Flux vector splitting of the inviscid gasdynamic equations with application to finite-difference methods. J. Comput. Phys. 40(2), 263–293 (1981)
Balsara, D.S., Shu, C.-W.: Monotonicity preserving weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes with increasingly high order of accuracy. J. Comput. Phys. 160(2), 405–452 (2000)
Radulescu, M.I., Lee, J.H.S.: The failure mechanism of gaseous detonations: experiments in porous wall tubes. Combust. Flame 131, 29–46 (2002)
Maeda, S., Sumiya, S., Kasahara, J., Matsuo, A.: Initiation and sustaining mechanisms of stabilized oblique detonation waves around projectiles. Proc. Combust. Inst. 34, 1973–1980 (2013)
Jones, D.A., Kemister, G., Tonello, N.A., Oran, E.S., Sichel, M.: Numerical simulation of detonation reignition in H\(_2\)–O\(_2\) mixtures in area expansions. Shock Waves 10, 33–41 (2000)
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 91441110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Higgins.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Han, X., Yao, S. et al. A numerical investigation of the prompt oblique detonation wave sustained by a finite-length wedge. Shock Waves 26, 729–739 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-016-0626-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-016-0626-3