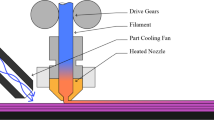
Abstract
Additive manufacturing has the potential to provide novel solutions for fabricating complex structures. However, one of the main obstacles for such methods is the anisotropic mechanical properties of the manufactured product, which hinder the popularization of additive manufacturing in modern industries. Here, a simple yet versatile algorithm is introduced to produce isotropic products via optimizing the printing path. In this method, the workpiece is first separated into distinct areas in terms of the printing sequence, which increases the efficiency of the fabrication process. Subsequently, the printing path is schemed in each sub-region to allow a short extrusion length and low number of start-stop processes. Finally, this maze-like printing path is revised through a series of tensile tests and fracture surface analyses to validate the isotropy. Bending and indentation tests demonstrate that the samples present distinguished properties in terms of strength and isotropy in mechanical properties. Moreover, numerical and physical tests are implemented for validating the advantage of this maze-like pattern in preventing warping caused by residual stress. This work may play a significant role in printing molds that require isotropic properties.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vishwas M, Basavaraj CK (2017) Studies on optimizing process parameters of fused deposition modelling technology for abs. Materials Today Proceedings 4(10):10994–11003
Rayna T, Striukova L (2016) From rapid prototyping to home fabrication: How 3d printing is changing business model innovation. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 102:214–224
Bose S, Ke D, Sahasrabudhe H, Bandyopadhyay A (2018) Additive manufacturing of biomaterials. Prog Mater Sci 93:45–111
Lin S, Xie YM, Li Q, Huang X, Zhou S (2015) Buckling-induced retraction of spherical shells: A study on the shape of aperture. Sci Rep 5(11309):11309
Lin S, Xie YM, Li Q, Huang X, Zhou S (2016) On the shape transformation of cone scales. Soft Matter 12:9797–9802
Zarek M, Layani M, Cooperstein I, Sachyani E, Cohn D, Magdassi S (2015) 3d printing: 3d printing of shape memory polymers for flexible electronic devices (adv. mater. 22/2016). Adv Mater 28(22):4166–4166
Lin S, Xie YM, Li Q, Huang X, Zhou S (2016) A kirigami approach to forming a synthetic buckliball. Sci Rep 6:33016
Turner BN, Gold SA (2015) A review of melt extrusion additive manufacturing processes: Ii. materials, dimensional accuracy, and surface roughness. Rapid Prototyp J 21(3):250– 261
Go J, Hart AJ (2017) Fast desktop-scale extrusion additive manufacturing. Addit Manuf 18:276–284
Zhang J, Wang XZ, Yu WW, Deng YH (2017) Numerical investigation of the influence of process conditions on the temperature variation in fused deposition modeling. Mater Des 130:59–68
Ding D, Pan Z, Cuiuri D, Li H (2015) A practical path planning methodology for wire and arc additive manufacturing of thin-walled structures. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 34:8–19
Casavola C, Cazzato A, Moramarco V, Pappalettera G (2017) Residual stress measurement in fused deposition modelling parts. Polym Test 58:249–255
Kok Y, Tan X, Wang P, Nai M, Loh N, Liu E, Tor S (2018) Anisotropy and heterogeneity of microstructure and mechanical properties in metal additive manufacturing: A critical review. Mater Des 139:565–586
Dolen M, Yaman U (2014) New morphological methods to generate two-dimensional curve offsets. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 71(9-12):1687–1700
Jin GQ, Li WD, Gao L (2013) An adaptive process planning approach of rapid prototyping and manufacturing. Robot Comput Integr Manuf 29(1):23–38
Zhang Y, Chou K (2008) A parametric study of part distortions in fused deposition modelling using three-dimensional finite element analysis. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 222(8):959–968
Yang J, Bin H, Zhang X, Liu Z (2003) Fractal scanning path generation and control system for selective laser sintering (sls). Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(3):293–300
Lu Y, Wu S, Gan Y, Huang T, Yang C, Lin J, Lin J (2015) Study on the microstructure, mechanical property and residual stress of slm inconel-718 alloy manufactured by differing island scanning strategy. Opt Laser Technol 75:197–206
Boschetto A, Bottini L, Veniali F (2016) Integration of fdm surface quality modeling with process design. Addit Manuf 12:334–344
Sang CP, Yun CC, Choi BK (2003) Contour-parallel offset machining without tool-retractions. Comput Aided Des 35(9):841–849
Zhao H, Huang Q X, Huang Q X, Garcia J, Chen Y, Tu C, Benes B, Zhang H, Cohen-Or D, Chen B (2016) Connected fermat spirals for layered fabrication. ACM Trans Graph 35(4):100
Lin Z, Fu J, He Y, Gan W (2013) A robust 2d point-sequence curve offset algorithm with multiple islands for contour-parallel tool path. Comput Aided Des 45(3):657–670
Kim HC (2010) Optimum tool path generation for 2.5d direction-parallel milling with incomplete mesh model. J Mech Sci Technol 24(5):1019–1027
Ċwikła G, Grabowik C, Kalinowski K, Paprocka I, Ociepka P (2017) The influence of printing parameters on selected mechanical properties of fdm/fff 3d-printed parts. In: Materials science and engineering conference series
Zaldivar RJ, Witkin DB, Mclouth T, Patel DN, Schmitt K, Nokes JP (2017) Influence of processing and orientation print effects on the mechanical and thermal behavior of 3d-printed ultem; 9085 material. Addit Manuf 13:71–80
Ahn S, Montero M, Dan O, Roundy S, Wright PK (2016) Anisotropic material properties of fused deposition modeling abs. Rapid Prototyp J 8(4):248–257(10)
Tam K-MM, Mueller C T (2017) Additive manufacturing along principal stress lines. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing 4(2):63–81
Jiang BG, Lei L, Hu J (2012) Tool path generation algorithm based on the double spiral filling curve. Appl Mech Mater 190-191:790–793
Choi SH, Samavedam S (2002) Modelling and optimisation of rapid prototyping. Comput Ind 47(1):39–53
Giberti H, Sbaglia L, Urgo M (2017) A path planning algorithm for industrial processes under velocity constraints with an application to additive manufacturing. J Manuf Syst 43:160–167
Zhao J (2005) Determination of optimal build orientation based on satisfactory degree theory for rpt. In: International conference on computer aided design and computer graphics, pp 225–230
Qian B, Zhang L, Shi Y, Liu G (2013) Support fast generation algorithm based on discrete-marking in rapid prototyping. Rapid Prototyp J 17(6):451–457
Jin YA, He Y, Fu JZ, Gan WF, Lin ZW (2014) Optimization of tool-path generation for material extrusion-based additive manufacturing technology. Addit Manuf 1-4:32–47
Zhang Y (2017) Multi-slicing strategy for the three-dimensional discontinuity layout optimization (3D DLO). Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 41:488–507
Zhang Y, Zhuang X (2018) Stability analysis of shotcrete supported crown of NATM tunnels with discontinuity layout optimization. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2775
Liu J, To AC (2017) Deposition path planning-integrated structural topology optimization for 3d additive manufacturing subject to self-support constraint. Comput Aided Des 91:27– 45
Dreifus G, Goodrick K, Giles S, Patel M, Foster RM, Williams C, Lindahl J, Post B, Roschli A, Love L, Kunc V (2017) Path optimization along lattices in additive manufacturing using the chinese postman problem. 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing 4(2):98–104
Isayev AI, Shyu GD, Li CT (2006) Residual stresses and birefringence in injection molding of amorphous polymers: Simulation and comparison with experiment. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 44(3):622–639
Li X, Yu W, Liu C (2016) Geometry-aware partitioning of complex domains for parallel quad meshing. Comput Aided Des 85:20–33
Singh R (2013) Some investigations for small sized product fabrication with fdm for plastic components. Rapid Prototyp J 19(1):58–63
Wu S, Zhao Z, Wang CY, Xie Y, Ma W (2016) Optimization of toolpath with circular cycle transition for sharp corners in pocket milling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(9-12):1–11
Mei G, Tipper JC, Xu N (2012) Ear-clipping based algorithms of generating high-quality polygon triangulation. In: Proceedings of the 2012 international conference on information technology and software engineering, vol 212, pp 979–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-34531-9_105
Dorigo M, Birattari M, Stutzle T (2007) Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput Intell Mag 1(4):28–39
Bonet B, Geffner H (2006) Learning in depth-first search: A unified approach to heuristic search in deterministic, non-deterministic, probabilistic, and game tree settings, Proceedings of Icaps, pp 3–23
Ahn S, Montero M, Dan O, Roundy S, Wright PK (2002) Anisotropic material properties of fused deposition modeling abs. Rapid Prototyp J 8(4):248–257(10)
Zhang Y, Zhuang X (2018) Cracking elements: a self-propagating strong discontinuity embedded approach for quasi-brittle fracture. Finite Elem Anal Des 144:84–100
Funding
This paper is sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 11802082), Hebei Science and Technology Department (18391203D), and by Hebei University of Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, S., Xia, L., Ma, G. et al. A maze-like path generation scheme for fused deposition modeling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 104, 1509–1519 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03986-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-03986-7