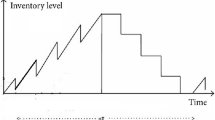
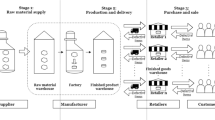
Abstract
Improving the performance of supply chains is imperative in the contemporary competitive business environment. Integrated decision models incorporating various important aspects and decision variables into a single model are desired towards this end. An important issue lacking in the supply chain literature relates to the incorporation of such quintessential and omnipresent supply chain practices as repairing or replacing non-conforming items supplied by the vendor. Specifically, this paper proposes two integrated models. The first model incorporates the notion of repairing non-conforming items supplied by the vendor at the site of the buyer/manufacturer. The second model incorporates the notion of replacing non-conforming items supplied by the vendor through local purchases at the site of the buyer/manufacturer. Illustrative examples and sensitivity analyses are provided to demonstrate the model application, efficacy, and managerial insights. Some very interesting and challenging future research directions are also provided.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad A (1997) Integrated mathematical models for production, quality, & maintenance in multi-stage production-inventory systems. MS Thesis, King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals, Saudi Arabia
Ben-Daya M (1999) Multi-stage lot sizing models with imperfect processes and inspection errors. Production Planning & Control 10:118–126
Ben-Daya M, Darwish M, Rahim A (2003) Two-stage imperfect production systems with inspection errors. Int J Oper Quantitative Manage 9:117–132
Ben-Daya M, Rahim A (2003) Optimal lot-sizing, quality improvement and inspection errors for multistage production systems. Int J Prod Res 41:65–79
Cárdenas-Barrón LE (2012) A complement to “a comprehensive note on: an economic order quantity with imperfect quality and quantity discounts”. Appl Math Model 36:6338–6340
Chang H (2011) A comprehensive note on: an economic order quantity with imperfect quality and quantity discounts. Appl Math Model 35:5208–5216
Chiu YP (2003) Determining the optimal lot size for the finite production model with random defective rate, the rework process, and backlogging. Eng Optim 35:427–437
Chung K (2013) The EOQ model with defective items and partially permissible delay in payments linked to order quantity derived analytically in the supply chain management. Appl Math Model 37:2317–2326
Duffuaa S, Khan M (2002) An optimal repeat inspection plan with several classifications. J Oper Res Soc 53:1016–1026
Harris FW (1990) How many parts to make at once. Oper Res 38:947–950
Gerchak Y, Vickson RG, Parlar M (1988) Periodic review production models with variable yield and uncertain demand∗. IIE Trans 20:144–150
Goyal SK, Cárdenas-Barrón LE (2002) Note on: economic production quantity model for items with imperfect quality—a practical approach. Int J Prod Econ 77:85–87
Goyal SK, Huang C, Chen K (2003) A simple integrated production policy of an imperfect item for vendor and buyer. Prod Plan Cont 14:596–602
Hsu J, Hsu L (2013) An EOQ model with imperfect quality items, inspection errors, shortage backordering, and sales returns. Int J Prod Econ 143:162–170
Huang C (2004) An optimal policy for a single-vendor single-buyer integrated production–inventory problem with process unreliability consideration. Int J Prod Econ 91:91–98
Jaber MY, Zanoni S, Zavanella LE (2014) Economic order quantity models for imperfect items with buy and repair options. Int J Prod Econ 155:126–131
Jaber M, Goyal S, Imran M (2008) Economic production quantity model for items with imperfect quality subject to learning effects. Int J Prod Econ 115:143–150
Khan M, Jaber M, Wahab M (2010) Economic order quantity model for items with imperfect quality with learning in inspection. Int J Prod Econ 124:87–96
Khan M, Jaber MY, Bonney M (2011) An economic order quantity (EOQ) for items with imperfect quality and inspection errors. Int J Prod Econ 133:113–118
Khan M, Jaber M, Guiffrida A (2012) The effect of human factors on the performance of a two level supply chain. Int J Prod Res 50:517–533
Khan M, Jaber M, Guiffrida A, Zolfaghari S (2011) A review of the extensions of a modified EOQ model for imperfect quality items. Int J Prod Econ 132:1–12
Khan M, Jaber MY, Ahmad A (2014) An integrated supply chain model with errors in quality inspection and learning in production. Omega 42:16–24
Lee HL, Rosenblatt MJ (1987) Simultaneous determination of production cycle and inspection schedules in a production system. Manag Sci 33:1125–1136
Liao J (2007) A note on an EOQ model for deteriorating items under supplier credit linked to ordering quantity. Appl Math Model 31:1690–1699
Lin T (2010) An economic order quantity with imperfect quality and quantity discounts. Appl Math Model 34:3158–3165
Nodem FID, Kenne J, Gharbi A (2011) Production planning and repair/replacement switching policy for deteriorating manufacturing systems. Int J Adv Manf Tech 57:827–840
Papachristos S, Konstantaras I (2006) Economic ordering quantity models for items with imperfect quality. Int J Prod Econ 100:148–154
Porteus EL (1986) Optimal lot sizing, process quality improvement and setup cost reduction. Oper Res 34:137–144
Rahim M (1985) Economic model of X-chart under non-normality and measurement errors. Comput Oper Res 12:291–299
Raouf A, Jain J, Sathe P (1983) A cost-minimization model for multicharacteristic component inspection. AIIE Trans 15:187–194
Rosenblatt MJ, Lee HL (1986) Economic production cycles with imperfect production processes. IIE Trans 18:48–55
Salameh M, Jaber M (2000) Economic production quantity model for items with imperfect quality. Int J Prod Econ 64:59–64
Shapiro JF (2006) Modeling the supply chain. Nelson Education
Simchi-Levi D, Kaminsky P, Simchi-levi E (2003) Designing and managing the supply chain: concepts, strategies and case studies. McGraw Hills, Mass
Zhou Y, Chen J, Wu Y, Zhou W (2014) EPQ models for items with imperfect quality and one-time-only discount. Appl Math Model 39:1000–1018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M., Ahmad, AR. & Hussain, M. Integrated decision models for a vendor–buyer supply chain with inspection errors and purchase and repair options. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 104, 3221–3228 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1137-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-017-1137-9