Abstract
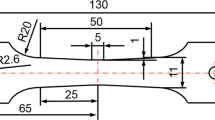
The study aims to obtain the effect of forming parameters on multi-stage cold forging with 20MnTiB steel by performing a series of physical simulation and then verified by producing experiment of high-strength bolt. Physical simulation was performed through Gleeble 3500 compression tests; the mainly forming parameters such as strain rate (100∼101), deformation degree (20∼80 %), and number of stages were discussed. The results showed that the strain rate has little effect on the microstructure and the mechanical property. However, the number of stages and the deformation degree have an appreciable effect on the sample microstructure, of which the pearlite grain is fined and ferrite grain is elongated as fiber. The adiabatic thermal temperature rises from 20 to 142 °C with a 60 % deformation degree at a strain rate of 10 s−1. Finally, the deformation properties of bolts can compare with the physical simulation results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kazeminezhad M (2013) Prediction of the mechanical properties of rods after cold forging and heat treatment. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69:2071–2079
Ku TW, Kang BS (2014) Tool design and experimental verification for multi-stage cold forging process of the outer race. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 15:1995–2004
İnce U, Güden M (2013) An iterative numerical method for determination of temperature dependent friction coefficients in thermo-mechanical model analysis of cold bolt forging. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68:2133–2144
Ku TW, Kim LH, Kang BS (2013) Multi-stage cold forging and experimental investigation for the outer race of constant velocity joints. Mater Des 49:368–85
Lee M, Chung S, Joun M (2009) Automatic and precise simulation of multistage automatic cold-forging processes by combined analyses of two- and three-dimensional approaches. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 41:1–7
Sun MC, Tzou GY, Zheng LA (2013) Processing animation simulation and FEM analysis of multi-stage cold forging of stainless automotive battery fastener. Indian J Eng Mater Sci 20:219–224
Danno A, Berner S, Fong KS, Yap WT (2014) Multi-stage cold forging of thin-walled components. Procedia Eng 81:407–412
Schiemann T, Liewald M, Beiermeister C, Till M (2014) Influence of process chain on fold formation during flange upsetting of tubular cold forged parts. Procedia Eng 81:352–357
Ince U, Güden M (2013) An iterative numerical method for determination of temperature dependent friction coefficients in thermo mechanical model analysis of cold bolt forging. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68:2133–2144
Zhao Q, Wu G, Sha W (2010) Deformation of titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V under dynamic compression. Comput Mater Sci 50:516–526
Song PW (2012) Microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-4Al-4Si magnesium alloy by reciprocating extrusion. Chin J Nonferrous Metals 22:1863–1871
Ghosh SK, Mallick P, Chattopadhyay PP (2012) Effect of cold deformation on phase evolution and mechanical properties in an austenitic stainless steel for structural and safety applications. J Iron Steel Res Int 19:63–68
Fang F, Hu XJ, Zhang BM, Xie ZH, Jiang JQ (2013) Deformation of dual-structure medium carbon steel in cold drawing. Mater Sci Eng A 583:78–83
Shi XF, Hussain G, Zha GC, Wu ML, Kong FX (2014) Study on formability of vertical parts formed by multi-stage incremental forming. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 75:1049–1053
Li DZ, Wei YH, Liu CY, Hou LF, Liu DF, Jin XZ (2010) Effects of high strain rate on properties and microstructure evolution of TWIP steel subjected to impact loading. J Iron Steel Res Int 2010(17):67–73
CMES (1993) Press association. Forging handbook. China Machine Press, Beijing
WangW LM, He C, Wei X, Wang D, Du H (2013) Experimental study on high strain rate behavior of high strength 600–1000 MPa dual phase steels and 1200 MPa fully martensitic steels. Mater Des 47:510–521
Kannana AR, Pandey KS, Shanmugam S (2008) Some investigation on the cold deformation behaviour of sintered iron–0.8% carbon alloy powder preforms. J Mater Process Technol 203:542–547
Mahadevan P, Dixit U, Robi P (2007) Analysis of cold rigid-plastic axisymmetric forging problem by radial basis function collocation method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34:464–473
Ananthanarayanan R (2010) Deformation behaviour of sintered silicon–copper steel preforms of various aspect ratios during cold upsetting. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50:509–515
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhiling Xiao and Hua Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Z., Liu, H., Liu, B. et al. The effect of forming parameter on multi-stage cold forging with 20MnTiB steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83, 1189–1197 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7659-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7659-0