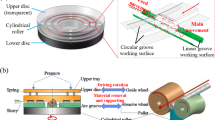
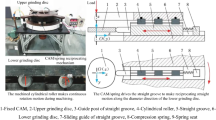
Abstract
Cylindrical roller bearings have been widely used in the mechanical industry due to the high radial load capacity. In some precision applications, high accuracy of cylindrical rollers, such as high profile accuracy and excellent surface quality, is strongly demanded and is even indispensable for the operational reliability of bearings. In this paper, on the basis of a lapping process, chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) technique was used to prepare cylindrical rollers with a low roundness and a nanoscale surface roughness R a on a double-side cylindrical ultra-precision processing device, which was developed by the Ultra-precision Machining Center of Zhejiang University of Technology. Firstly, the effects of the experimental conditions, such as the rotating speeds and the down force, on the processing performance were studied. The simulation results reveal that, using the optimized rotating speeds, with the processing time going, the processing trajectory gradually distributes uniformly on the cylindrical surface of the roller along both the circular and the axial directions, and thereby, the uniform material removal can be realized; with the increase of the down force, the material removal rate (MRR) of the cylindrical roller almost linearly increases. Specially, the down force of the CMP process was set to 20 N/roller to obtain a better polishing performance. Then, on the basis of a lapping process, CMP technique was used to further improve the surface quality of the cylindrical rollers to nanoscale roughness. The results show that, after a two-step CMP process including a rough polishing step and a fine polishing step, the cylindrical surface of the rollers changes from rough and uneven state into smooth and free of micro-scratches state, and the surface roughness R a decreases from initial 76 to 16.6 nm, and the roundness decreases from initial 0.97 to 0.40 μm. Finally, the material removal mechanism of the cylindrical rollers was investigated. During the lapping process, the material removal is predominantly driven by the mechanical abrasion from the α-alumina particles; while during the CMP process, the material removal is realized by the alternating cycles of “oxidation/complexation/passivation-abrasion-oxidation/complexation/passivation” process. In sequence, the mechanism of the roundness improvement was proposed. During the lapping and the CMP processes, the MRR at the protrudent point is larger than that at the recessed point due to the larger contact stress, and as a result, the actual surface profile of the circular section gradually reaches the average circle, and the roundness decreases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brändlein J, Eschmann P, Hasbargen L, Weigand K (1999) Ball and roller bearings: theory, design, and application, 3rd edn. Wiley
Harris TA, Kotzalas MN (2006) Advanced concepts of bearing technology: rolling bearing analysis. CRC Press
Hashimoto F, Gallego I, Oliveira JFG, Barrenetxea D, Takahashi M, Sakakibara K, Stålfelt H-O, Staadt G, Ogawa K (2012) Advances in centerless grinding technology. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61(2):747–770. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2012.05.003
Song M, Zou W (2014) Improvement of large cylindrical roller processing technology. J Harbin Bearing 35(2):65–69 (in Chinese)
Wang Y, Deng Q, Cheng L, Lv Y, Yuan J (2012) Generalization of cylindrical surface processing of cylindrical roller. Light Ind Mach 30(3):110–113 (in Chinese)
Jiang Q, Ge Z (2002) Simulation on topography of superfinished roller surfaces. Sci China Ser B: Chem 45(2):122–126. doi:10.1360/02yb9017
Nakayama K, Hashimoto H (1995) Experimental investigation of the superfinishing process. Wear 185(1–2):173–182. doi:10.1016/0043-1648(95)06609-8
El-Taweel T, Ebeid S (2007) Improvement of roundness of cylindrical parts using hybrid electrochemical smoothing and roller burnishing process. In: Proceedings of the 35th International MATADOR Conference. Springer, pp 85–88. doi:10.1360/02yb9017
Xu W, Wei Z, Sun J, Wei L, Yu Z (2012) Surface quality prediction and processing parameter determination in electrochemical mechanical polishing of bearing rollers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 63(1–4):129–136. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3891-4
Zhou W, Yao W, Feng M, Deng Q, Lv B, Yuan J (2014) Polishing process study of cylindrical rollers by using a double-side lapping machine. Light Ind Mach 32(4):36–38 (in Chinese)
Feng M, Yao W, Zhou W, Sun L, Deng Q, Lv B (2014) Process optimization of cylindrical roller lapping technology based on double-side lapping methods. Light Ind Mach 32(3):26–34 (in Chinese)
He X, Chen Y, Zhao H, Sun H, Lu X, Liang H (2013) Y2O3 nanosheets as slurry abrasives for chemical–mechanical planarization of copper. Friction 1(4):327–332. doi:10.1007/s40544-013-0035-x
Zhang W, Lei H (2013) Abrasive-free polishing of hard disk substrate with H2O2-C4H10O2-Na2S2O5 slurry. Friction 1(4):359–366. doi:10.1007/s40544-013-0032-0
Zhao D, Lu X (2013) Chemical mechanical polishing: theory and experiment. Friction 1(4):306–326. doi:10.1007/s40544-013-0035-x
Jiang L, He Y, Luo J (2015) Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using colloidal silica-based slurries. Appl Surf Sci 330:487–495. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.01.016
Sohn I-S, Moudgil B, Singh R, Park C-W (1999) Hydrodynamics of a chemical–mechanical planarization process. In: Babu SV, Danyluk S, Kirshnan M, Tsujimura T (eds) 1999 MRS Spring Meeting, San Francisco, California, USA, April 5–7, 1999. Materials Research Society, pp 181–184
Lin Y-Y, Lo S-P (2003) A study on the stress and nonuniformity of the wafer surface for the chemical–mechanical polishing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 22(5–6):401–409. doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1544-y
Qin K, Moudgil B, Park C-W (2004) A chemical mechanical polishing model incorporating both the chemical and mechanical effects. Thin Solid Films 446(2):277–286. doi:10.1016/j.tsf.2003.09.060
Lin T-R (2007) An analytical model of the material removal rate between elastic and elastic–plastic deformation for a polishing process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32(7–8):675–681. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-0391-4
Zhou P, Guo D, Kang R, Jin Z (2013) A mixed elastohydrodynamic lubrication model with layered elastic theory for simulation of chemical mechanical polishing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(5–8):1009–1016. doi:10.1007/s00170-013-5108-5
Tsai MY, Wang SM, Tsai CC, Yeh TS (2015) Investigation of increased removal rate during polishing of single-crystal silicon carbide. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-7023-4
Zhong ZW, Tian YB, Ang YJ, Wu H (2012) Optimization of the chemical mechanical polishing process for optical silicon substrates. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 60(9–12):1197–1206. doi:10.1007/s00170-011-3668-9
Chang K-Y, Song Y-H, Lin T-R (2002) Analysis of lapping and polishing of a gauge block. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 20(6):414–419. doi:10.1007/s001700200171
Kao MJ, Hsu FC, Peng DX (2014) Synthesis and characterization of SiO2 nanoparticles and their efficacy in chemical mechanical polishing steel substrate. Adv Mater Sci Eng 1–8. doi:10.1155/2014/691967
Peng D-X (2014) Chemical mechanical polishing of steel substrate using aluminum nanoparticles abrasive slurry. Ind Lubr Tribol 66(1):124–130. doi:10.1108/ILT-10-2011-0078
Jiang L, He Y, Luo J (2014) Effects of pH and oxidizer on chemical mechanical polishing of AISI 1045 steel. Tribol Lett 56(2):327–335. doi:10.1007/s11249-014-0412-2
Jiang L, He Y, Yang Y, Luo J (2015) Chemical mechanical polishing of stainless steel as solar cell substrate. ECS J Solid State Sci Technol 4(5):P162–P170. doi:10.1149/2.0171505jss
Yuan J, Yao W, Zhao P, Lyu B, Chen Z, Zhong M (2015) Kinematics and trajectory of both-sides cylindrical lapping process in planetary motion type. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 92:60–71. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2015.02.004
Yuan JL, Zhao P, Ruan J, Cao ZX, Zhao WH, Xing T (2003) Lapping and polishing process for obtaining super-smooth surfaces of quartz crystal. J Mater Process Technol 138(1–3):116–119. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00058-X
Tam HY, Cheng HB, Wang YW (2007) Removal rate and surface roughness in the lapping and polishing of RB-SiC optical components. J Mater Process Technol 192–193:276–280. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.04.091
Deshpande S, Kuiry S, Klimov M, Obeng Y, Seal S (2004) Chemical mechanical planarization of copper: role of oxidants and inhibitors. J Electrochem Soc 151(11):G788–G794. doi:10.1149/1.1806395
Deshpande S, Kuiry S, Klimov M, Seal S (2005) Elucidating Cu-glycine and BTA complexations in Cu-CMP using SIMS and XPS. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 8(4):G98–G101. doi:10.1149/1.1869112
Zhang M, Wang X, Fu X, Xia Y (2009) Performance and anti-wear mechanism of CaCO3 nanoparticles as a green additive in poly-alpha-olefin. Tribol Int 42(7):1029–1039. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2009.02.012
Seal S, Kuiry SC, Heinmen B (2003) Effect of glycine and hydrogen peroxide on chemical–mechanical planarization of copper. Thin Solid Films 423(2):243–251. doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(02)00989-6
Yu L, Cui Y-L, Guan H-Y, Xu M-H, Mao J-W (2013) Synthesis and Characterization of ferrous glycinate monohydrate. J Zhejiang Univ (Sci Ed) 40(3):291–296 (in Chinese)
Hu P (2011) The synthesis of glycine iron and the influence of weaning piglets growth performance. Master Dissertation, Anhui Agricultural University, Anhui Agricultural University (in Chinese)
Graat PCJ, Somers MAJ (1996) Simultaneous determination of composition and thickness of thin iron-oxide films from XPS Fe 2p spectra. Appl Surf Sci 100/101:36–40. doi:10.1016/0169-4332(96)00252-8
Rui Y, Yu J, Liang Y, Wei Y (2007) Inhibition behavior and mechanism of molybdate compound inhibitor for carbon steel in sea water. Environ Sci Technol 30(4):23–25 (in Chinese)
Wilson D, Langell MA (2014) XPS analysis of oleylamine/oleic acid capped Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a function of temperature. Appl Surf Sci 303:6–13. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.02.006
Joong Kim K, Moon DW, Lee SK, Jung K-H (2000) Formation of a highly oriented FeO thin film by phase transition of Fe3O4 and Fe nanocrystallines. Thin Solid Films 360:118–121. doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(99)00562-3
Gao X, Wu X, Zhang Z, Guan H, E-h H (2007) Characterization of oxide films grown on 316L stainless steel exposed to H2O2-containing supercritical water. J Supercrit Fluids 42(1):157–163. doi:10.1016/j.supflu.2006.12.020
Li Y, Gong M, Ramji K, Li Y (2009) Role of Cu-Benzotriazole nanoparticles in Passivation Film Formation. J Phys Chem C 113(42):18003–18013. doi:10.1021/jp904782t
Yao JL, Ren B, Huang ZF, Cao PG, Gu RA, Tian Z-Q (2003) Extending surface Raman spectroscopy to transition metals for practical applications IV. A study on corrosion inhibition of benzotriazole on bare Fe electrodes. Electrochim Acta 48(9):1263–1271. doi:10.1016/s0013-4686(02)00834-4
Dong J, Dong J, Han E, Liu C, Ke W (2009) Rusting evolvement of mild steel under wet/dry cyclic condition with pH 4.00 NaHSO3 solution. Corros Sci Protect Technol 21(1):1–4 (in Chinese)
Evans CJ, Paul E, Dornfeld D, Lucca DA, Byrne G, Tricard M, Klocke F, Dambon O, Mullany BA (2003) Material removal mechanisms in lapping and polishing. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 52(2):611–633. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60207-8
Fritz Klocke Eh, Kuchie A (2009) Lapping and polishing. In: Manufacturing processes 2. RWTHedition. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 338–369. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-92259-9_8
Dong J, Ke W (2009) The accelerated test of simulated atmospheric corrosion and the rust evolution of low carbon steel. Electrochemistry 15(2):170–178 (in Chinese)
Yang C, Zhang H, Guo W, Fu Y (2013) Effects of H2O2 addition on corrosion behavior of high-strength low-alloy steel in seawater. J Chin Soc Corros Protect 33(003):205–210 (in Chinese)
Ihnfeldt R, Talbot JB (2008) Effect of CMP slurry chemistry on copper nanohardness. J Electrochem Soc 155(6):H412–H420. doi:10.1149/1.2903293
Liao C, Guo D, Wen S, Luo J (2012) Effects of chemical additives of CMP slurry on surface mechanical characteristics and material removal of copper. Tribol Lett 45(2):309–317. doi:10.1007/s11249-011-9874-7
Li Y (2007) Microelectronic applications of chemical mechanical planarization. Wiley-Interscience, USA
Luo J, Dornfeld DA (2001) Material removal mechanism in chemical mechanical polishing: theory and modeling. IEEE Trans Semicond Manuf 14(2):112–133. doi:10.1109/66.920723
Yang X, Zheng W (2002) Analysis on the corrosion rust of weathering steel and carbon steel exposed to atmosphere for two years. Corros Protect 23(3):97–98 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Yao, W., He, Y. et al. An experimental investigation of double-side processing of cylindrical rollers using chemical mechanical polishing technique. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 82, 523–534 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7370-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7370-1