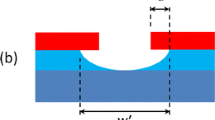
Abstract
Wire electrochemical machining (WECM) is a cutting process in which the workpiece acts as an anode and the wire as a cathode. WECM is typically used to cut plates and exhibits a great advantage over wire electro-discharge machining, namely, the absence of a heat-affected zone around the cutting area. The enhancement of WECM accuracy is a research topic of great interest. In WECM, the homogeneity of the machined slit has a decisive influence on the machining accuracy. This is the first study in which the integration of pulse electrochemical machining (ECM) and a reciprocated traveling wire electrode was used to improve the homogeneity of this slit. The experimental results show that the combination of pulse ECM and a reciprocated traveling wire electrode could enhance the accuracy of WECM and that generally a low applied voltage, pulse duty cycle, and electrolyte concentration; an appropriate traveling wire velocity; and a high pulse frequency and feeding rate enhance the accuracy and stability of WECM. Finally, a microstructure with a slit width of 177 μm, with a standard deviation of 1.5 μm, and with an aspect ratio of 113 was fabricated on a stainless steel substrate measuring 20 mm in thickness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajurkar KP, Zhu D, McGeough JA, Kozak J, De Silva A (1999) New developments in electrochemical machining. Ann CIRP 48(2):567–579
Zhu D, Zhu D, Xu ZY (2012) Optimal design of the sheet cathode using W-shaped electrolyte flow mode in ECM. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 62(1–4):147–156
Pattavanitch J, Hinduja S (2012) Machining of turbulated cooling channel holes in turbine blades. Ann CIRP 61(1):199–202
Pa PR (2008) Effective form design of electrode in electrochemical smoothing of end turning surface finishing. J Mater Process Technol 195(1–3):44–52
Klocke F, Zeis M, Klink A, Veselovac D (2012) Technological and economical comparison of roughing strategies via milling, EDM and ECM for titanium- and nickel-based blisks. Ann CIRP 61(2):98–101
Qu NS, Fang XL, Li W, Zeng YB, Zhu D (2013) Wire electrochemical machining with axial electrolyte flushing for titanium alloy. Chin J Aeronaut 26(1):224–229
Bejar MA, Eterovich F (1995) Wire-electrochemical cutting with a NaNO3 electrolyte. J Mater Process Technol 55:417–420
El-Taweel TA, Gouda SA (2011) Performance analysis of wire electrochemical turning process—RSM approach. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53:181–190
El-Taweel TA, Gouda SA (2011) Study on the wire electrochemical groove turning process. J Appl Electrochem 41(2):161–171
Osipenko VI, Stupak DO, Trigub OA, Bilan AV (2012) Calculation of the parameters of the technological-current density distribution during wire electrode electrochemical processing. Surf Eng Appl Electrochem 48(2):105–110
Mukherjee R, Chakraborty S (2013) Selection of the optimal electrochemical machining process parameters using biogeography-based optimization algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 64(5–8):781–791
Haridy S, Gouda SA, Wu Z (2011) An integrated framework of statistical process control and design of experiments for optimizing wire electrochemical turning process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53(1–4):191–207
Wu H, Xiao SH, Li QG, Zhang YJ (2011) Research of high efficiency combined wire electrochemical machining technology and its application. Adv Manuf Technol 1–3(314–316):1015–1019
Wang W, Liu ZX, Zhang W, Huang YH, Allen DM (2011) Abrasive electrochemical multi-wire slicing of solar silicon ingots into wafers. Ann CIRP 60(1):255–258
Zhu D, Wang K, Qu NS (2007) Micro wire electrochemical cutting by using in situ fabricated wire electrode. Ann CIRP 56(1):241–244
Wang SH, Zhu D, Zeng YB, Liu Y (2011) Micro wire electrode electrochemical cutting with low frequency and small amplitude tool vibration. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 53:535–544
Shin HS, Kim BH, Chu CN (2008) Analysis of the side gap resulting from micro electrochemical machining with a tungsten wire and ultrashort voltage pulses. J Micromech Microeng 18(7):1–6
Rosenkranz C, Lohrengel MM, Schultze JW (2005) The surface structure during pulsed ECM of iron in NaNO3. Electrochim Acta 50(10):2009–2016
Kozak J (2004) Thermal models of pulse electrochemical machining. Bull Pol Acad Sci Techn Sci 52(4):313–320
Rajurkar KP, Kozak J, Wei B, Mcgeough JA (1993) Study of pulse electrochemical machining characteristics. Ann CIRP 42(1):231–234
Bähre D, Weber O, Rebschläger A (2013) Investigation on pulse electrochemical machining characteristics of lamellar cast iron using a response surface methodology-based approach. Procedia CIRP 6:362–367
Ma N, Xu WJ, Wang XY, Wei ZF (2011) Mathematical modeling for finishing tooth surfaces of spiral bevel gears using pulse electrochemical dissolution. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 54(9–12):979–986
Spieser A, Ivanov A (2013) Recent developments and research challenges in electrochemical micromachining. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(1–4):563–581
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, N.S., Ji, H.J. & Zeng, Y.B. Wire electrochemical machining using reciprocated traveling wire. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 72, 677–683 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5704-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-014-5704-z