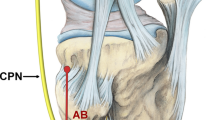
Abstract
To evaluate electrophysiological incidence and the type of peroneal nerve lesions seen after high tibial osteotomy we conducted an electrophysiological study (electromyography and nerve conduction velocity studies) in 11 patients who were suffering from medial gonarthrosis and treated by Maquet barrel-vault type high tibial valgization osteotomy. All the patients were tested both pre- and postoperatively. Every patient was examined postoperatively for a minimum of a 6 months after surgery to eliminate spontaneously reversible lesions. Results obtained from nonoperated legs served as controls. Three patients (27%) with peroneal nerve lesions were detected electrophysiologically; one had only motor involvement, one only sensory involvement, and one both motor and sensory involvement. Clinically only one of these patients was symptomatic, and the other two were detected by electrophysiological means. Peroneal nerve lesions which may be overlooked by mild weakness and hypesthesia in the early postoperative period can be detected by electrophysiological means at a higher rate than expected. These lesions persist a relatively long time and even can be permanent despite the absence of clinical symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aydoğdu, S., Çullu, E., Araç, N. et al. Prolonged peroneal nerve dysfunction after high tibial osteotomy: pre- and postoperative electrophysiological study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Art 8, 305–308 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001670000138
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001670000138