Abstract
Purpose
This study was undertaken to determine the efficacy of reinflation of the tourniquet after its early release in TKA compared to early release alone, in terms of surgical field visualization and operative time. We also questioned whether tourniquet reinflation after its early release is safe, with respect to post-operative blood loss, post-operative pain and other tourniquet-related complications.
Methods
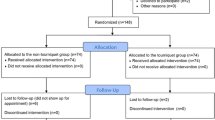
Two hundred and six patients undergoing TKA were randomly allocated to either the early release (deflation) group (n = 105) or reinflation after early release (reinflation) group (n = 101). Efficacy was measured in terms of surgical field visualization, specifically the number of wound clearances, and operative time. Safety outcomes were drained volume, decline in haemoglobin on post-operative days 2 and 5, the frequency of transfusion, knee and thigh pain visual analog scale, local wound complications, tourniquet site complications and other complications, including infection, deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
Results
Surgical field visualization was better in the reinflation group; however, the operative time did not differ between the two groups. There were no differences between the two groups in post-operative blood loss, decline in haemoglobin on days 2 and 5, transfusion rate, pain level, local complications and other complications.
Conclusion
Reinflation of tourniquet is a safe alternative to its early release after deflation in that it improves surgical field visualization during TKA.
Level of evidence
Therapeutic study, Level I.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barwell J, Anderson G, Hassan A, Rawlings I (1997) The effects of early tourniquet release during total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized double-blind study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:265–268
Cho HJ, Chang CB, Kim KW, Park JH, Yoo JH, Koh IJ, Kim TK (2011) Gender and prevalence of knee osteoarthritis types in elderly Koreans. J Arthroplasty 26:994–999
Christodoulou AG, Ploumis AL, Terzidis IP, Chantzidis P, Metsovitis SR, Nikiforos DG (2004) The role of timing of tourniquet release and cementing on perioperative blood loss in total knee replacement. Knee 11:313–317
Fitzgibbons PG, Digiovanni C, Hares S, Akelman E (2012) Safe tourniquet use: a review of the evidence. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 20:310–319
Fukuda A, Hasegawa M, Kato K, Shi D, Sudo A, Uchida A (2007) Effect of tourniquet application on deep vein thrombosis after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127:671–675
Hernandez-Castanos DM, Ponce VV, Gil F (2008) Release of ischaemia prior to wound closure in total knee arthroplasty: a better method? Int Orthop 32:635–638
Huang ZY, Pei FX, Ma J, Yang J, Zhou ZK, Kang PD, Shen B (2014) Comparison of three different tourniquet application strategies for minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty: a prospective non-randomized clinical trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134:561–570
Husted H, Toftgaard Jensen T (2005) Influence of the pneumatic tourniquet on patella tracking in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study in 100 patients. J Arthroplasty 20:694–697
Ishii Y, Noguchi H, Matsuda Y, Takeda M, Higashihara T (2008) A new tourniquet system that determines pressures in synchrony with systolic blood pressure in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 23:1050–1056
Jones RED (2011) Total Knee arthroplasty without the use of a tourniquet. Semin Arthroplasty 22:176–178
Kam PC, Kavanagh R, Yoong FF (2001) The arterial tourniquet: pathophysiological consequences and anaesthetic implications. Anaesthesia 56:534–545
Kim I, Kim HA, Seo YI, Song YW, Jeong JY, Kim DH (2010) The prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in elderly community residents in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 25:293–298
Kim TK, Chang CB, Kang YG, Seo ES, Lee JH, Yun JH, Lee SH (2014) Clinical value of tranexamic acid in unilateral and simultaneous bilateral TKAs under a contemporary blood-saving protocol: a randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:1870–1878
Koh IJ, Chang CB, Lee JH, Jeon YT, Kim TK (2013) Preemptive low-dose dexamethasone reduces postoperative emesis and pain after TKA: a randomized controlled study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:3010–3020
Koh IJ, Kang YG, Chang CB, Do SH, Seong SC, Kim TK (2012) Does periarticular injection have additional pain relieving effects during contemporary multimodal pain control protocols for TKA?: a randomised, controlled study. Knee 19:253–259
Koh IJ, Kim TK, Chang CB, Cho HJ, In Y (2013) Trends in use of total knee arthroplasty in Korea from 2001 to 2010. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471:1441–1450
Kvederas G, Porvaneckas N, Andrijauskas A, Svensen CH, Ivaskevicius J, Mazunaitis J, Marmaite U, Andrijauskas P (2013) A randomized double-blind clinical trial of tourniquet application strategies for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2790–2799
Lee GC, Hawes T, Cushner FD, Scott WN (2005) Current trends in blood conservation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:170–174
Lombardi AV Jr, Berend KR, Mallory TH, Dodds KL, Adams JB (2003) The relationship of lateral release and tourniquet deflation in total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg 16:209–214
Marson BM, Tokish JT (1999) The effect of a tourniquet on intraoperative patellofemoral tracking during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 14:197–199
Matziolis D, Perka C, Hube R, Matziolis G (2011) Influence of tourniquet ischemia on perioperative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. Orthopade 40:178–182
Mitsuyasu S, Hagihara A, Horiguchi H, Nobutomo K (2006) Relationship between total arthroplasty case volume and patient outcome in an acute care payment system in Japan. J Arthroplasty 21:656–663
Mont MA, Jacobs JJ, Boggio LN, Bozic KJ, Della Valle CJ, Goodman SB, Lewis CG, Yates AJ Jr, Watters WC 3rd, Turkelson CM, Wies JL, Donnelly P, Patel N, Sluka P, AAOS (2011) Preventing venous thromboembolic disease in patients undergoing elective hip and knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 19:768–776
Olivecrona C, Tidermark J, Hamberg P, Ponzer S, Cederfjall C (2006) Skin protection underneath the pneumatic tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial of 92 patients. Acta Orthop 77:519–523
Parvizi J, Zmistowski B, Berbari EF, Bauer TW, Springer BD, Della Valle CJ, Garvin KL, Mont MA, Wongworawat MD, Zalavras CG (2011) New definition for periprosthetic joint infection: from the Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:2992–2994
Pfitzner T, von Roth P, Voerkelius N, Mayr H, Perka C, Hube R (2014) Influence of the tourniquet on tibial cement mantle thickness in primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-014-3341-6
Pierson JL, Hannon TJ, Earles DR (2004) A blood-conservation algorithm to reduce blood transfusions after total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86:1512–1518
Rama KR, Apsingi S, Poovali S, Jetti A (2007) Timing of tourniquet release in knee arthroplasty. Meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:699–705
Seo ES, Yoon SW, Koh IJ, Chang CB, Kim TK (2010) Subcutaneous versus intraarticular indwelling closed suction drainage after TKA: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468:2168–2176
Smith TO, Hing CB (2010) Is a tourniquet beneficial in total knee replacement surgery? A meta-analysis and systematic review. Knee 17:141–147
Tarwala R, Dorr LD, Gilbert PK, Wan Z, Long WT (2014) Tourniquet use during cementation only during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:169–174
Tetro AM, Rudan JF (2001) The effects of a pneumatic tourniquet on blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Can J Surg 44:33–38
Thorey F, Stukenborg-Colsman C, Windhagen H, Wirth CJ (2008) The effect of tourniquet release timing on perioperative blood loss in simultaneous bilateral cemented total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized study. Technol Health Care 16:85–92
Wakai A, Winter DC, Street JT, Redmond PH (2001) Pneumatic tourniquets in extremity surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 9:345–351
Zan PF, Yang Y, Fu D, Yu X, Li GD (2015) Releasing of tourniquet before wound closure or not in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Arthroplasty 30:31–37
Zhang W, Li N, Chen S, Tan Y, Al-Aidaros M, Chen L (2014) The effects of a tourniquet used in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 9:13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this article.
Statement of human rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Na, Y.G., Bamne, A.B., Won, H.H. et al. After early release of tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty, should it be reinflated or kept deflated? A randomized trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25, 2769–2777 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3710-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3710-9