Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to determine (1) variations in the shape of the proximal, middle, and distal femur in a series of Korean patients who had undergone total knee arthroplasty (TKA), (2) the preoperative relationship between these three parameters and the distal valgus cutting angle referenced off the femoral intramedullary guide, and (3) whether there was any relationship between femoral bowing and variations in the shape of the proximal or distal femur in the coronal plane.
Methods
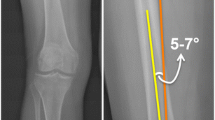
The preoperative long-standing anteroposterior radiographs of 316 consecutive osteoarthritis patients who underwent primary TKA from 2009 to 2011 were examined. The femoral neck shaft angle, the femoral shaft bowing angle, and the mechanical lateral distal femoral angle were measured to assess the shape of the proximal, middle, and distal femur, respectively. The valgus cutting angle of the femur was defined as the angle between the distal anatomical and mechanical axes of the femur.
Results
The study population showed large variations in femoral shape. The mean femoral intramedullary guide angle was 6.5° ± 1.3° (range: 4°–13°). The femoral shaft bowing angle was the factor that showed the strongest correlation with this angle (P < 0.001). The mechanical lateral distal femoral angle showed only a weak correlation (P = 0.001), and the femoral neck shaft angle showed no correlation (n.s.). The femoral shaft bowing angle showed a weak correlation with the mechanical lateral distal femoral angle (P = 0.001), but was not significantly correlated with the femoral neck shaft angle (n.s.). Apparent femoral bowing (>3° of lateral or medial bowing) was found in 42 (13.3 %) of cases (37 cases of lateral bowing and five of medial bowing). Cases with lateral apparent femoral bowing >3° had a distal cutting angle of 8.6° ± 2.2° relative to the femoral intramedullary guide.
Conclusion
The femoral intramedullary guide angle was mainly influenced by femoral shaft bowing among femoral deformities in the coronal plane. Therefore, to increase the accuracy of distal femoral cut during TKA, it is necessary to confirm femoral deformities and to measure the femoral intramedullary guide angle preoperatively from coronal radiographs covering the whole femur.
Level of evidence
IV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäthis H, Perlick L, Tïngart M, Lüring C, Zurakowski D, Grifka J (2004) Alignment in total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of computer-assisted surgery with the conventional technique. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86(5):682–687
Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MA (1983) Alignment in total knee arthroplasty: correlated biomechanical and clinical observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res 173:178–183
Cates HE, Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM (1993) Intramedullary versus extramedullary femoral alignment systems in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:32–39
Chang CB, Choi JY, Koh JI, Seo ES, Seong SC, Kim TK (2010) What should be considered in using standard knee radiographs to estimate mechanical alignment of the knee? Osteoarthritis Cartilage 18(4):530–538
Choi WC, Lee S, Seong SC, Jung JH, Lee MC (2010) Comparison between standard and high-flexion posterior-stabilized rotating-platform mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasties: a randomized controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(16):2634–2642
Engh GA, Petersen TL (1990) Comparative experience with intramedullary and extramedullary alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 5(1):1–8
Gebhard F, Krettek C, Hufner T, Grutzner PA, Stockle U, Imhoff AB, Lorenz S, Ljungqvist J, Keppler P (2011) Reliability of computer-assisted surgery as an intraoperative ruler in navigated high tibial osteotomy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131(3):297–302
Hinman RS, May RL, Crossely KM (2006) Is there an alternative to the full-leg radiograph for determining knee joint alignment in osteoarthritis? Arthritis Rheum 55(2):306–313
Howell SM, Kuznik K, Hull ML, Siston RA (2010) Longitudinal shapes of the tibia and femur unrelated and variable. Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(4):1142–1148
Iorio R, Pagnottelli M, Vadalà A, Giannetti S, Di Sette P, Papandrea P, Conteduca F, Ferretti A (2013) Open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: comparison between manual and computer-assisted techniques. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(1):113–119
Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA (1991) Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73(5):709–714
Jiang CC, Insall JN (1989) Effect of rotation on the axial alignment of the femur: pitfalls in the use of femoral intramedullary guides in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:50–56
Kharwadkar N, Kent RE, Sharara KH, Naique S (2006) 5° to 6° of distal femoral cut for uncomplicated primary total knee arthroplasty: is it safe? Knee 13(1):57–60
Kim D, Seong SC, Lee MC, Lee S (2012) Comparison of the tibiofemoral rotational alignment after mobile and fixed bearing total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(2):337–345
Kim YH, Choi Y, Kwon OR, Kim JS (2009) Functional outcome and range of motion of high-flexion posterior cruciate-retaining and high-flexion posterior cruciate-substituting total knee prostheses. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(4):753–760
Kraus VB, Vail TP, Worrell T, McDaniel G (2005) A comparative assessment of alignment angle of the knee by radiographic and physical examination methods. Arthritis Rheum 52(6):1730–1735
Lasam MP, Lee KJ, Chang CB, Kang YG, Kim TK (2013) Femoral lateral bowing and varus condylar orientation are prevalent and affect axial alignment of TKA in Koreans. Clin Orthop Relat Res 471(5):1472–1483
Lim HC, Bae JH, Yi JW, Park JH (2011) Bilateral stress fracture of the femoral shaft after total knee arthroplasty: a case report. Knee 18(5):354–357
McGrory JE, Trousdale RT, Pagnano MW (2002) Preoperative hip to ankle radiographs in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:196–202
Moreland JR (1988) Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:49–64
Na YG, Kang YG, Chang MJ, Chang CB, Kim TK (2013) Must bilaterality be considered in statistical analyses of total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res 471(6):1970–1981
Nagamine R, Miura H, Bravo CV, Urabe K, Matsuda S, Miyanishi K, Hirata G, Iwamoto Y (2000) Anatomic variations should be considered in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci 5(3):232–237
Nelitz M, Wehner T, Steiner M, Dürselen L, Lippacher S (2013) The effects of femoral external derotational osteotomy on frontal plane alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-013-2618-5
Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM (1993) Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment for femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 8(4):419–426
Pietsch M, Djahani O, Hochegger M, Plattner F, Hofmann S (2013) Patient-specific total knee arthroplasty: the importance of planning by the surgeon. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(10):2220–2226
Rand JA, Coventry MB (1988) Ten-year evaluation of geometric total knee arthroplasty. Clin Ortho Relat Res 232:168–173
Reed SC, Gollish J (1997) The accuracy of femoral intramedullary guides in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 12(6):677–682
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement: its effect on survival. Clin Ortho Relat Res 299:153–156
Seo JG, Kim BK, Moon YW, Kim JH, Yoon BH, Ahn TK, Lee DH (2009) Bony landmarks for determining the mechanical axis of the femur in the sagittal plane during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg 1(3):128–131
Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM, Ng TP (2007) Coronal bowing of the femur and tibia in Chinese: its incidence and effects on total knee arthroplasty planning. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 15(1):32–36
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012-0000479), and by a grant of the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A100054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JM., Hong, SH., Kim, JM. et al. Femoral shaft bowing in the coronal plane has more significant effect on the coronal alignment of TKA than proximal or distal variations of femoral shape. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23, 1936–1942 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3006-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3006-5