Abstract
Purpose
The anteroposterior (AP) axis connecting the middle of the posterior cruciate ligament to the medial border of the patellar tendon at its attachment has been introduced as a reproducible and reliable reference perpendicular to the surgical epicondylar axis in healthy knees. A recent literature has reported that the AP axis of the tibia is, on average, almost perpendicular to the surgical epicondylar axis also in varus and valgus knees and can be used as a tibial rotational reference to minimize the risk for rotational mismatch between the femoral and tibial components in total knee arthroplasty (TKA). However, it is difficult to identify the AP axis after tibial resection. The purpose of the current study was to determine a modified AP axis that runs parallel to the AP axis and passes through the centre of the cut surface in osteoarthritic knees.
Methods
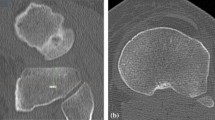
Preoperative computed tomography scans on 30 varus and 30 valgus knees undergoing TKA were studied using a three-dimensional software. The modified AP axis that runs parallel to the AP axis and passes through the centre of the cut surface was drawn. We investigated where the modified AP axis crossed the patellar tendon at its tibial attachment.
Results
The modified AP axis passed through the medial 1/6 of the patellar tendon (4 mm from medial edge) at its attachment in both varus and valgus knees.
Conclusions
The AP axis of the tibia is useful as a tibial rotational reference in cutting the proximal tibia, but it is difficult to identify the AP axis after tibial resection. The clinical relevance of this study is that medial 1/6 of the patellar tendon at its attachment would be a useful landmark in aligning the tibial component.
Level of evidence
IV.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi M, Matsusue Y, Mata T, Asada Y, Horiguchi M, Iida H, Nakamura T (1999) Effect of rotational alignment on patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 366:155–163
Akagi M, Mori S, Nishimura S, Nishimura A, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2005) Variability of extraarticular tibial rotation references for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:172–176
Akagi M, Oh M, Nonaka T, Tsujimoto H, Asano T, Hamanishi C (2004) An anteroposterior axis of the tibia for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 420:213–219
Anouchi YS, Whiteside LA, Kaiser AD, Milliano MT (1993) The effects of axial rotational alignment of the femoral component on knee stability and patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty demonstrated on autopsy specimens. Clin Orthop Relat Res 287:170–177
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE (1998) Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:144–153
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS (1993) Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 286:40–47
Dalury DF (2001) Observations of the proximal tibia in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 389:150–155
Eckhoff DG, Johnston RJ, Stamm ER, Kilcoyne RF, Wiedel JD (1994) Version of the osteoarthritic knee. J Arthroplasty 9:73–79
Hovinga KR, Lerner AL (2009) Anatomic variations between Japanese and Caucasian populations in the healthy young adult knee joint. J Orthop Res 27:1191–1196
Howell SM, Chen J, Hull ML (2012) Variability of the location of the tibial tubercle affects the rotational alignment of the tibial component in kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-012-1987-5
Insall JN, Easley ME (2001) Surgical techniques and instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. In: Insall JN, Scott WN (eds) Surgery of the knee, 3rd edn. Churchill livingstone, New York, pp 1553–1620
Insall JN (1993) Surgical techniques and instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. In: Insall JN, Windsor RE, Scott WN, Kelly M, Aglietti P (eds) Surgery of the knee, 2nd edn. Churchill livingstone, New York, pp 739–804
Kawahara S, Matsuda S, Okazaki K, Tashiro Y, Mitsuyasu H, Nakahara H, Iwamoto Y (2012) Relationship between the tibial anteroposterior axis and the surgical epicondylar axis in varus and valgus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:2073–2077
Lewis P, Rorabeck CH, Bourne RB, Devane P (1994) Posteromedial tibial polyethylene failure in total knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:11–17
Mantas JP, Bloebaum RD, Skedros JG, Hofmann AA (1992) Implications of reference axes used for rotational alignment of the femoral component in primary and revision knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 7:531–535
Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Hirata G, Iwamoto Y (2001) Effect of femoral and tibial component position on patellar tracking following total knee arthroplasty: 10-year follow-up of Miller-Galante I knees. Am J Knee Surg 14:152–156
Miller MC, Berger RA, Petrella AJ, Karmas A, Rubash HE (2001) Optimizing femoral component rotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:38–45
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ (1987) Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69:745–749
Moreland JR (1988) Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 226:49–64
Nagamine R, Whiteside LA, White SE, McCarthy DS (1994) Patellar tracking after total knee arthroplasty. The effect of tibial tray malrotation and articular surface configuration. Clin Orthop Relat Res 304:262–271
Sahin N, Atıcı T, Kurtoğlu U, Turgut A, Ozkaya G, Ozkan Y (2012) Centre of the posterior cruciate ligament and the sulcus between tubercle spines are reliable landmarks for tibial component placement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-012-2120-5
Schnurr C, Csécsei G, Nessler J, Eysel P, König DP (2011) How much tibial resection is required in total knee arthroplasty? Int Orthop 35:989–994
Su EP, Su SL, Della Valle AG (2010) Stiffness after TKR: how to avoid repeat surgery. Orthopedics 33:658
Tao K, Cai M, Li SH (2010) The anteroposterior axis of the tibia in total knee arthroplasty for Chinese knees. Orthopedics 33:799
Uehara K, Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Ohashi H, Yamano Y (2002) Bone anatomy and rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 402:196–201
Urabe K, Mahoney OM, Mabuchi K, Itoman M (2008) Morphologic differences of the distal femur between Caucasian and Japanese women. J Orthop Surg 16:312–315
Verlinden C, Uvin P, Labey L, Luyckx JP, Bellemans J, Vandenneucker H (2010) The influence of malrotation of the femoral component in total knee replacement on the mechanics of patellofemoral contact during gait: an in vitro biomechanical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92:737–742
Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty RM, Natarajan RN, Rosenberg AG (1994) Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:31–43
Yoshioka Y, Siu D, Cooke TD (1987) The anatomy and functional axes of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am 69:873–880
Yoshioka Y, Siu DW, Scudamore RA, Cooke TD (1989) Tibial anatomy and functional axes. J Orthop Res 7:132–137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawahara, S., Okazaki, K., Matsuda, S. et al. Medial sixth of the patellar tendon at the tibial attachment is useful for the anterior reference in rotational alignment of the tibial component. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22, 1070–1075 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2468-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2468-1