Abstract
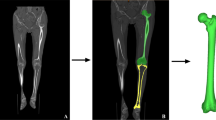
This study aims to investigate the results of distal femoral resection by determining the difference between mechanical and anatomical axes of femur using computerized tomography (CT) scout views in pre-operative planning of total knee arthroplasty. CT scout view of the lower extremities was taken before and after the operation in 16 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Distal femoral resection was performed according to the previously determined ideal resection angle (IRA) using intramedullary instrumentation. At post-operative scanogram, femoral component deviation (FCD) was measured. The results were statistically analyzed. The average IRA was 6.95 (5–9) degrees. At post-operative measurements, the average FCD was 0.63 (0–3) degrees. CT scout films improve the accuracy in distal femoral resection and femoral component alignment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P (2005) Total knee arthroplasty. Where do we stand today? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15 (epub ahead of print)
Cates HE, Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM (1993) Intramedullary versus extramedullary femoral alignment systems in total knee. Clin Orthop 286:32–39
Chidiac JJ, Shofer FS, Al-Kutoubi A, Laster LL, Ghafari J (2002) Comparison of CT scanograms and cephalometric radiographs in craniofacial imaging. Orthod Craniofac Res 5:104–113
Decking J, Theis C, Achenbach T, Roth E, Nafe B, Eckardt A (2004) Robotic total knee arthroplasty: the accuracy of CT-based component placement. Acta Orthop Scand 75(5):573–579
Dixon DR, Morgan R, Hollender LG (2002) Clinical application of spiral tomography in anterior implant placement: case report. J Periodontol 73(10):1202–1209
Engh GA, Petersen TL (1990) Comparative experience with intramedullary and extramedullary alignment in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 5(1):1–8
Farrar MJ, Newman RJ, Mawhinney RR, King R (1999) Computed tomography scan scout film for measurement of femoral axis in knee replacement. J Arthroplasty 14(8):1030–1031
Honl M, Dierk O, Gauk C, Carrero V, Lampe F, Dries S, Quante M, Schwieger K, Hille E, Morlock M (2003) Comparison of robot assisted and manual implantation of a primary total hip replacement. A prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85:1470–1478
Horton GA, Reckling FW (1995) Femoral pulse as a guide to the mechanical axis in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 10(6):780–784
Kinzel V, Scaddan M, Bradley B, Shakespeare D (2004) Varus/valgus alignment of the femur in total knee arthroplasty. Can accuracy be improved by preoperative CT scanning? Knee 11:197–201
Lam LO, Shakespeare D (2003) Varus/valgus alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Knee 10:237–241
Matsuda Y, Ishii Y, Ichimura K (2004) Identifying the center of the femoral head using ultrasonography to assess the higher accuracy of femoral extramedullary guides in TKA. J Orthop Sci 9(1):6–9
McGrory JE, Trousdale RT, Pagnano MW Nigbur M (2002) Preoperative hip to ankle radiographs in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 404:196–202
Nagamine R, Miura H, Bravo CV (2000) Anatomic variations should be considered in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci 5(3):232–237
Ogata K, Yoshii I, Kawamura H, Miura H, Arizona T, Sugioka Y (1991) Standing radiographs cannot determine the correction in high tibial osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg 73B(6):927–931
Romanowski CA, Underwood AC, Sprigg A (1994) Reduction of radiation doses in leg lengthening procedures by means of audit and computed tomography scanogram techniques. Br J Radiol 67:1103–1107
Teter KE, Bregman D, Colwell CW Jr (1995) The efficacy of intramedullary femoral alignment in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop 321:117–121
Uslu MM, Eksioğlu F, Ozsar B (2004) Arthroplasty in extraarticular deformity of tibia. J Arthroplasty Arthroscopic Surg 15(4):226–229
Uslu M, Ozsar B, Kendi T, Kara S, Tekdemir I, Atik S (2005) The use of computed tomography to determine femoral component size. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 63(1,2):49–53
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uslu, M.M., Ozsar, B., Cirpar, M. et al. Computerized tomography scout view for determining distal femoral resection angle in intramedullary instrumentation of total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthr 15, 78–82 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-006-0104-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-006-0104-z