Abstract
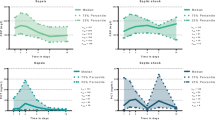
Objective: To compare the respiratory burst of neutrophils in sepsis and control patients using lipopolysaccharide (LPS), autologous plasma, and a combination of the two. Design: Prospective, consecutive case study. Setting: A 16-bed intensive care unit (ICU) in a university teaching hospital. Interventions: None. Patients: Plasma was obtained from 23 healthy patients scheduled for minor surgery immediately prior to induction of anesthesia (controls) and from 23 ICU patients within 24 h of diagnosis of sepsis or septic shock. Measurements and main results: Respiratory burst was determined by lucigenin chemiluminescence expressed as mean ± SEM of peak values of relative light units per neutrophil. There were no significant differences between neutrophils of septic patients and controls for the stimuli saline, phorbol myristate acetate, formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalenine, and LPS alone. Septic patients showed a lower respiratory burst than controls (p < 0.05) under the following stimuli: plasma alone (5911 ± 803 vs 15 397 ± 3038) and LPS and plasma combined (13 857 ± 1537 vs 23 026 ± 2640). However, when stimulated with plasma after priming with LPS, septic patients elicited a higher value than control subjects (11 373 ± 1758 vs 5987 ± 1234, p < 0.05). Conclusions: (1) Some components of the plasma of septic patients may have a profound effect on neutrophil response; (2) plasma as a respiratory burst stimulus differentiates between sepsis and non-sepsis samples better than other common stimuli; (3) precautions must be taken when using plasma together with LPS because of the different response depending on whether LPS-priming precedes the plasma stimulus or both are introduced simultaneously and whether septic or nonseptic plasma is used.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 December 1997 Accepted: 26 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pascual, C., Bredle, D., Karzai, W. et al. Effect of plasma and LPS on respiratory burst of neutrophils in septic patients. Intensive Care Med 24, 1181–1186 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340050742
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340050742