Abstract
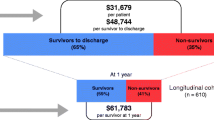
Objective: To evaluate patient outcome and the efficiency of stays in intensive care units (ICUs). Design: Prospective study. Setting: Seven ICUs of teaching hospitals in the Paris area. Patients: Two hundred eleven stays including one in three consecutive patients admitted from September to November 1996. Measurements and main results: For each patient, the following information was collected during the ICU stay: diagnosis, severity scores, organ failures, workload, cost and mortality. A cost-effectiveness ratio was computed for 176 stays with at least one organ failure, at hospital discharge and 6 months later. Quality of life was measured with EuroQol questionnaires 6 months after discharge in 64 patients representing 62% of the patients contacted. The mean total ICU cost per stay was US$ 14,130 (±6,550) (higher for non-survivors – US$ 19,060, median 10,590 – than for survivors – US$ 12,370, median 5,780). The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was US$ 1,150 per life-year saved and the incremental cost-utility ratio was US$ 4,100 per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) saved, without discounting. These results compare favourably with other health-care options. However substantial variations were observed according to age, severity, diagnosis, number of organ failures and discount rate. Intoxication had the lowest ratio (US$ 620/QALY) and acute renal insufficiency the highest (US$ 30,625/QALY). Conclusions: This work provides medical and economic information on ICU stays in teaching hospitals and enables comparisons with other health-care options.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Final revision received: 5 September 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sznajder, M., Aegerter, P., Launois, R. et al. A cost-effectiveness analysis of stays in intensive care units. Intensive Care Med 27, 146–153 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340000760
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340000760