Abstract
Objective
To assess the relationship between optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) and intracranial pressure (ICP) in neurocritical care patients.
Design
Prospective, observational study.
Setting
Surgical critical care unit, level 1 trauma center.
Patients
A total number of 37 adult patients requiring sedation and ICP monitoring after severe traumatic brain injury, subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracranial hematoma, or stroke.
Measurements and main results
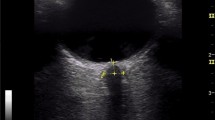
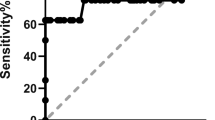
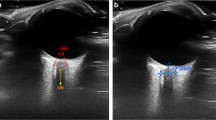
Optic nerve sheath diameter was measured with a 7.5 MHz linear ultrasound probe. ICP was measured invasively via a parenchymal device. Simultaneous measurements were performed atleast once a day during the first 2 days after ICP insertion and in cases of acute changes. There was a significant relationship between ONSD and ICP (78 simultaneous measures, r = 0.71, P < 0.0001). Changes in ICP were strongly correlated with changes in ONSD (39 measures, r = 0.73, P < 0.0001). Enlarged ONSD was a suitable predictor of elevated ICP (>20 mmHg) (area under ROC curve = 0.91). When ONSD was less than 5.86 mm, the negative likehood ratio for raised ICP was 0.06.
Conclusion
In sedated neurocritical care patients, non-invasive sonographic measurements of ONSD are correlated with invasive ICP, and the probability to have raised ICP if ONSD is less than 5.86 mm is very low. This method could be used as a screening test when raised ICP is suspected.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker DP, Miller JD, Ward JD, Greenberg RP, Young HF, Sakalas R (1977) The outcome from severe head injury with early diagnosis and intensive management. J Neurosurg 47:491–502
Marshall LF, Smith RW, Shapiro HM (1979) The outcome with aggressive treatment in severe head injuries. Part II: acute and chronic barbiturate administration in the management of head injury. J Neurosurg 50:26–30
Ghajar J (2000) Traumatic brain injury. Lancet 356:923–929
Barlow P, Mendelow AD, Lawrence AE, Barlow M, Rowan JO (1985) Clinical evaluation of two methods of subdural pressure monitoring. J Neurosurg 63:578–582
Liu D, Kahn M (1993) Measurement and relationship of subarachnoid pressure of the optic nerve to intracranial pressures in fresh cadavers. Am J Ophthalmol 116:548–556
Villain MA, Candon E, Arnaud B, Hamard H, Adenis JP (2003) Optic nerve sheath decompression in optic neuropathy complicating idiopathic intracranial hypertension: a new focus. J Fr Ophtalmol 26:191–197
Hayreh SS (1968) Pathogenesis of oedema of the optic disc. Doc Ophthalmol 24:289–411
Lichtenstein D (1992). In: Lichtenstein D (ed) L’echographie générale en réanimation. Springer, Berlin, p 115
Hansen HC, Helmke K (1996) The subarachnoid space surrounding the optic nerves. An ultrasound study of the optic nerve sheath. Surg Radiol Anat 18:323–328
Hansen HC, Helmke K (1997) Validation of the optic nerve sheath response to changing cerebrospinal fluid pressure: ultrasound findings during intrathecal infusion tests. J Neurosurg 87:34–40
Newman WD, Hollman AS, Dutton GN, Carachi R (2002) Measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter by ultrasound: a means of detecting acute raised intracranial pressure in hydrocephalus. Br J Ophthalmol 86:1109–1113
Blaivas M, Theodoro D, Sierzenski PR (2003) Elevated intracranial pressure detected by bedside emergency ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath. Acad Emerg Med 10:376–381
Helmke K, Burdelski M, Hansen HC (2000) Detection and monitoring of intracranial pressure dysregulation in liver failure by ultrasound. Transplantation 70:392–395
Tayal VS, Neulander M, Norton HJ, Foster T, Saunders T, Blaivas M (2006) Emergency department sonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter to detect findings of increased intracranial pressure in adult head injury patients. Ann Emerg Med 49:508–514
Geeraerts T, Launey Y, Martin L, Pottecher J, Vigue B, Duranteau J, Benhamou D (2007) Ultrasonography of the optic nerve sheath may be useful for detecting raised intracranial pressure after severe brain injury. Intensive Care Med 33:1704–1711
Stocchetti N (2007) Could intracranial pressure in traumatic brain injury be measured or predicted noninvasively? Almost. Intensive Care Med 33:1682–1683
Geeraerts T, Merceron S, Benhamou D, Vigué B, Duranteau J (2008) Noninvasive assessment of intracranial pressure using ocular sonography in neurocritical care patients. Crit Care 12(Suppl 2):S46
Le Gall JR, Lemeshow S, Saulnier F (1993) A new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. Jama 270:2957–2963
Civil ID, Schwab CW (1988) The Abbreviated Injury Scale, 1985 revision: a condensed chart for clinical use. J Trauma 28:87–90
Helmke K, Hansen HC (1996) Fundamentals of transorbital sonographic evaluation of optic nerve sheath expansion under intracranial hypertension. I. Experimental study. Pediatr Radiol 26:701–705
Helmke K, Hansen HC (1996) Fundamentals of transorbital sonographic evaluation of optic nerve sheath expansion under intracranial hypertension II. Patient study. Pediatr Radiol 26:706–710
Blaivas M, Theodoro D, Sierzenski PR (2002) A study of bedside ocular ultrasonography in the emergency department. Acad Emerg Med 9:791–799
Berges O, Koskas P, Lafitte F, Piekarski JD (2006) Sonography of the eye and orbit with a multipurpose ultrasound unit. J Radiol 87:345–353
Ballantyne SA, O’Neill G, Hamilton R, Hollman AS (2002) Observer variation in the sonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter in normal adults. Eur J Ultrasound 15:145–149
Patel HC, Bouamra O, Woodford M, King AT, Yates DW, Lecky FE (2005) Trends in head injury outcome from 1989 to 2003 and the effect of neurosurgical care: an observational study. Lancet 366:1538–1544
Ware AJ, D’Agostino AN, Combes B (1971) Cerebral edema: a major complication of massive hepatic necrosis. Gastroenterology 61:877–884
Han MK, Hyzy R (2006) Advances in critical care management of hepatic failure and insufficiency. Crit Care Med 34:S225–231
Ragauskas A, Daubaris G, Dziugys A, Azelis V, Gedrimas V (2005) Innovative non-invasive method for absolute intracranial pressure measurement without calibration. Acta Neurochir Suppl 95:357–361
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank Dr Olivier Berges (Foundation Opthalmologique Adolphe de Rothschild, Paris, France) for helpful discussion on ocular sonography.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors received no financial support for this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geeraerts, T., Merceron, S., Benhamou, D. et al. Non-invasive assessment of intracranial pressure using ocular sonography in neurocritical care patients. Intensive Care Med 34, 2062–2067 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1149-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-008-1149-x