Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effect of melatonin on the intestinal apoptosis along with oxidative damage in endotoxemic infant rats.
Design and setting
Prospective animal study in a university-based experimental research laboratory.
Subjects and interventions
Wistar albino 7-day-old rat pups (n = 21). The animals were randomized into three experimental groups: (1) controls; (2) endotoxemia; (3) endotoxemia treated with melatonin (10 mg/kg). Endotoxemia was induced in rats by intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (Escherichia coli serotype 0111:B4; 3 mg/kg).
Measurements and results
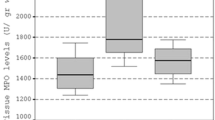
Four hours after LPS injection, the antioxidant enzyme activities, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) levels as an indicator of lipid peroxidation, were determined. Intestinal apoptosis was assessed by hematoxylin-eosin staining and terminal deoxynucleotide transferase-mediated fluorescein-dUTP nick end labeling. The administration of melatonin into endotoxemic rats prevented the increase in the TBARS levels, and increased the activities of antioxidant enzymes and attenuated apoptotic cell death in both intestinal epithelium and lamina propria.
Conclusions
Melatonin diminished the intestinal oxidative stress and apoptotic damage induced by endotoxemia in infant rats.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mehr SS, Sadowsky JL, Doyle LW, Carr J (2002) Sepsis in neonatal intensive care in the late 1990s. J Paediatr Child Health 38:246–251
Alexander C, Rietschel ET (2001) Bacterial lipopolysaccharides and innate immunity. J Endotoxin Res 7:167–202
Victor VM, Rocha M, Esplugues JV, de la Fuente M (2005) Role of free radicals in sepsis: antioxidant therapy. Curr Pharm Des 11:3141–3158
Victor VM, Rocha M, de la Fuente M (2004) Immune cells: free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol 4:327–347
Bhattacharyya J, Biswas S, Datta AG (2004) Mode of action of endotoxin: role of free radicals and antioxidants. Curr Med Chem 11:359–368
Goode HF, Webster NR (1993) Free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. Crit Care Med 21:1770–1776
Goode HF, Cowley HC, Walker BE, Howdle PD, Webster NR (1995) Decreased antioxidant status and increased lipid peroxidation in patients with septic shock and secondary organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 23:646–651
Robles R, Palomino N, Robles A (2001) Oxidative stress in the neonate. Early Hum Dev 65:S75–S81
Ozdemir D, Uysal N, Gonenc S, Acikgoz O, Sonmez A, Topcu A, Ozdemir N, Duman M, Semin I, Ozkan H (2005) Effect of melatonin on brain oxidative damage induced by traumatic brain injury in immature rats. Physiol Res 54:631–637
Cuzzocrea S, Reiter RJ (2001) Pharmacological action of melatonin in shock, inflammation and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Pharmacol 426:1–10
Rodriguez C, Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Antolin I, Herrera F, Martin V, Reiter RJ (2004) Regulation of antioxidant enzymes: a significant role for melatonin. J Pineal Res 36:1–9
Sewerynek E, Melchiorri D, Chen L, Reiter RJ (1995) Melatonin reduces both basal and bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced lipid peroxidation in vitro. Free Radic Biol Med 19:903–909
Sewerynek E, Abe M, Reiter RJ, Barlow-Walden LR, Chen L, McCabe TJ, Roman LJ, Diaz-Lopez B (1995) Melatonin administration prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative damage in phenobarbital-treated animals. J Cell Biochem 58:436–444
Crespo E, Macias M, Pozo D, Escames G, Martin M, Vives F, Guerrero JM, Acuna-Castroviejo D (1999) Melatonin inhibits expression of the inducible NO synthase II in liver and lung and prevents endotoxemia in lipopolysaccharide-induced multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in rats. FASEB J 13:1537–1546
Gitto E, Karbownik M, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Cuzzocrea S, Chiurazzi P, Cordaro S, Corona G, Trimarchi G, Barberi I (2001) Effects of melatonin treatment in septic newborns. Pediatr Res 50:756–760
Husain KD, Coopersmith CM (2003) Role of intestinal epithelial apoptosis in survival. Curr Opin Crit Care 9:159–163
Coopersmith CM, Stromberg PE, Dunne WM, Davis CG, Amiot DM II, Buchman TG, Karl IE, Hotchkiss RS (2002) Inhibition of intestinal epithelial apoptosis and survival in a murine model of pneumonia-induced sepsis. J Am Med Assoc 287:1716–1721
Coopersmith CM, Chang KC, Swanson PE, Tinsley KW, Stromberg PE, Buchman TG, Karl IE, Hotchkiss RS (2002) Overexpression of Bcl-2 in the intestinal epithelium improves survival in septic mice. Crit Care Med 30:195–201
Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD, Tinsley KW, Cobb JP, Matuschak GM, Buchman TG, Karl IE (1999) Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 27:1230–1251
Paskaloglu K, Sener G, Kapucu C, Ayanoglu-Dulger G (2004) Melatonin treatment protects against sepsis-induced functional and biochemical changes in rat ileum and urinary bladder. Life Sci 74:1093–1104
Carrillo MC, Kanai S, Nokubo M, Kitani K (1991) (-)Deprenyl induces activities of both superoxide dismutase and catalase but not of glutathione peroxidase in the striatum of young male rats. Life Sci 48:517–521
Rehncrona S, Smith DS, Akesson B, Westerberg E, Siesjo BK (1980) Peroxidative changes in brain cortical fatty acids and phospholipids, as characterized during Fe2+ and ascorbic acid-stimulated lipid peroxidation in vitro. J Neurochem 34:1630–1638
Cinel I, Buyukafsar K, Cinel L, Polat A, Atici S, Tamer L, Oral U (2002) The role of poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase inhibition in preventing endotoxemia-induced intestinal epithelial apoptosis. Pharmacol Res 46:119–127
Motoyama T, Okamoto K, Kukita I, Hamaguchi M, Kinoshita Y, Ogawa H (2003) Possible role of increased oxidant stress in multiple organ failure after systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Crit Care Med 31:1048–1052
Batra S, Kumar R, Seema Kapoor AK, Ray G (2000) Alterations in antioxidant status during neonatal sepsis. Ann Trop Paediatr 20:27–33
Buttke TM, Sandstrom PA (1994) Oxidative stress as a mediator of apoptosis. Immunol Today 15:7–10
Forrest VJ, Kang YH, McClain DE, Robinson DH, Ramakrishnan N (1994) Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis prevented by Trolox. Free Radic Biol Med 16:675–684
Curtin JF, Donovan M, Cotter TG (2002) Regulation and measurement of oxidative stress in apoptosis. J Immunol Methods 265:49–72
Leon J, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Escames G, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2005) Melatonin mitigates mitochondrial malfunction. J Pineal Res 38:1–9
Leon J, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Sainz RM, Mayo JC, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2004) Melatonin and mitochondrial function. Life Sci 75:765–790
Boveris A, Alvarez S, Navarro A (2002) The role of mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase in inflammation and septic shock. Free Radic Biol Med 33:1186–1193
Cuzzocrea S, Mazzon E, Serraino I, Lepore V, Terranova ML, Ciccolo A, Caputi AP (2001) Melatonin reduces dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. J Pineal Res 30:1–12
Wu KK (1995) Inducible cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase. Adv Pharmacol 33:179–207
Vane JR, Mitchell JA, Appleton I, Tomlinson A, Bishop-Bailey D, Croxtall J, Willoughby DA (1994) Inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric-oxide synthase in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2046–2050
Wadleigh DJ, Reddy ST, Kopp E, Ghosh S, Herschman HR (2000) Transcriptional activation of the cyclooxygenase-2 gene in endotoxin-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Biol Chem 275:6259–6266
Escames G, Leon J, Macias M, Khaldy H, Acuna-Castroviejo D (2003) Melatonin counteracts lipopolysaccharide-induced expression and activity of mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase in rats. FASEB J 17:932–934
Wu KK (2005) Control of cyclooxygenase-2 transcriptional activation by pro-inflammatory mediators. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 72:89–93
Mayo JC, Sainz RM, Tan DX, Hardeland R, Leon J, Rodriguez C, Reiter RJ (2005) Anti-inflammatory actions of melatonin and its metabolites, N1-acetyl-N2-formyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AFMK) and N1-acetyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AMK), in macrophages. J Neuroimmunol 165:139–149
Deng WG, Tang ST, Tseng HP, Wu KK (2006) Melatonin suppresses macrophage cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by inhibiting p52 acetylation and binding. Blood 15:518–524
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Dokuz Eylul University Research Foundation, grant no 02.KBSAG.059.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozdemir, D., Uysal, N., Tugyan, K. et al. The effect of melatonin on endotoxemia-induced intestinal apoptosis and oxidative stress in infant rats. Intensive Care Med 33, 511–516 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-006-0492-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-006-0492-z