Abstract
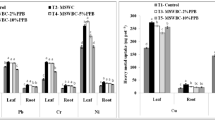
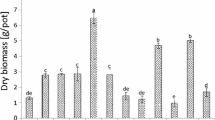
Immobilisation of heavy metals in a 30-year old active scrap metal yard soil using three waste materials, namely coconut tree sawdust (CTS), sugarcane bagasse (SB) and eggshell (ES) was investigated. The contaminated soil was amended with amendments at application rates of 0 %, 1 % and 3 % (w/w). The effects of amendments on metal accumulation in water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica) and soil metal bioavailability were studied in a pot experiment. All amendments increased biomass yield and reduced metal accumulation in the plant shoots. The bioconcentration factor and translocation factor values of the metals were in the order of Zn > Cu > Pb. The addition of ES, an alternative source of calcium carbonate (CaCO3), has significantly increased soil pH and resulted in marked reduction in soil metal bioavailability. Therefore, CTS, SB and ES are promising low-cost immobilising agents to restore metal contaminated land.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui Y, Wang Q, Dong Y, Li H, Christie P (2004) Enhanced uptake of soil Pb and Zn by Indian mustard and winter wheat following combined soil application of elemental sulphur and EDTA. Plant Soil 261:181–188
Ferber U, Grimski D (2002) Brownfields and redevelopment of urban areas. Report from the Contaminated Land Rehabilitation Network for Environmental Technologies
Gee G, Bauder JW (1986) Particle size analysis. In: Klute A (ed) Methods of soil analysis. Part I. Physical and mineralogical methods. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 383–411
Hu X, Yuan X, Dong L (2014) Coal fly ash and straw immobilize Cu, Cd and Zn from mining wasteland. Environ Chem Lett 12:289–295
Jensen JK, Holm PE, Nejrup J, Larsen MB, Borggaard OK (2009) The potential of willow for remediation of heavy metal polluted calcareous urban soils. Environ Pollut 157:931–937
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants, 4th edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kanwal U, Ali S, Shakoor MB, Farid M, Hussain S, Yasmeen T, Adrees M, Bharwana SA, Abbas F (2014) EDTA ameliorates phytoextraction of lead and plant growth by reducing morphological and biochemical injuries in Brassica napus L. under lead stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:9899–9910
Nakamoto K (2009) Infrared and Raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds. Part B: applications in coordination, organometallic, and bioinorganic chemistry. Wiley, New York
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1996) Nitrogen-total. In: Sparks DL (ed) Method of soil analysis: chemical methods. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1201–1229
Parry J (2009) Hundreds of Chinese children are left poisoned as metal smelting plants are ordered to close. BMJ 339:475
Sumner ME, Miller WP (1996) Cation exchange capacity and exchange coefficients. In: Sparks DL (ed) Method of soil analysis: chemical methods. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1031–1075
Yu XZ, Wang DQ, Zhang XH (2014) Chelator-induced phytoextraction of zinc and copper by rice seedlings. Ecotoxicol 23:749–756
Zhou H, Zhou X, Zeng M, Liao BH, Liu L, Yang WT, Wu YM, Qiu QY, Wang YJ (2014) Effects of combined amendments on heavy metal accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) planted on contaminated paddy soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 101:226–232
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris Malaysia under Research Grant GPU 2013-0120-102-01 and Ministry of Education Malaysia under Research Grant RACE 2012-0150-108-62.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Statement
The authors declare that they have performed experiments that comply with the current laws of Malaysia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamari, A., Putra, W.P., Yusoff, S.N.M. et al. Immobilisation of Cu, Pb and Zn in Scrap Metal Yard Soil Using Selected Waste Materials. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95, 790–795 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1650-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1650-1